Evidence that small molecule enhancement of β-hexosaminidase activity corrects the behavioral phenotype in Dutch APP(E693Q) mice through reduction of ganglioside-bound Aβ
- PMID: 25349165
- PMCID: PMC5189927
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2014.135
Evidence that small molecule enhancement of β-hexosaminidase activity corrects the behavioral phenotype in Dutch APP(E693Q) mice through reduction of ganglioside-bound Aβ
Abstract
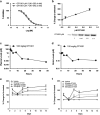
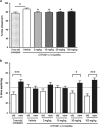
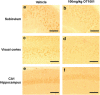
Certain mutant Alzheimer's amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides (that is, Dutch mutant APP(E693Q)) form complexes with gangliosides (GAβ). These mutant Aβ peptides may also undergo accelerated aggregation and accumulation upon exposure to GM2 and GM3. We hypothesized that increasing β-hexosaminidase (β-hex) activity would lead to a reduction in GM2 levels, which in turn, would cause a reduction in Aβ aggregation and accumulation. The small molecule OT1001 is a β-hex-targeted pharmacological chaperone with good bioavailability, blood-brain barrier penetration, high selectivity for β-hex and low cytotoxicity. Dutch APP(E693Q) transgenic mice accumulate oligomeric Aβ as they age, as well as Aβ oligomer-dose-dependent anxiety and impaired novel object recognition (NOR). Treatment of Dutch APP(E693Q) mice with OT1001 caused a dose-dependent increase in brain β-hex levels up to threefold over those observed at baseline. OT1001 treatment was associated with reduced anxiety, improved learning behavior in the NOR task and dramatically reduced GAβ accumulation in the subiculum and perirhinal cortex, both of which are brain regions required for normal NOR. Pharmacological chaperones that increase β-hex activity may be useful in reducing accumulation of certain mutant species of Aβ and in preventing the associated behavioral pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Within the past 5 years, SG has held research grants from Baxter Pharmaceuticals and Amicus Therapeutics. SG is also a member of the Data and Safety Monitoring Board for the Pfizer-Janssen Alzheimer's Immunotherapy Alliance. BAW, ACS, DJL, JWS and ERS are employees or shareholders of OrPhi Therapeutics. HNW and REB are employees and shareholders of Amicus Therapeutics.
Figures
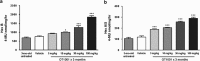
Similar articles
-
Reversible pathologic and cognitive phenotypes in an inducible model of Alzheimer-amyloidosis.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 27;33(9):3765-79. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4251-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23447589 Free PMC article.
-
Days to criterion as an indicator of toxicity associated with human Alzheimer amyloid-beta oligomers.Ann Neurol. 2010 Aug;68(2):220-30. doi: 10.1002/ana.22052. Ann Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20641005 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking the apolipoprotein E/amyloid-β interaction reduces fibrillar vascular amyloid deposition and cerebral microhemorrhages in TgSwDI mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;24(2):269-85. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101401. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21239853 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of the relationship between amyloid-β levels and measures of transgenic mouse cognitive deficit in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;44(3):787-95. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142208. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25362040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganglioside-Mediated Assembly of Amyloid β-Protein: Roles in Alzheimer's Disease.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;156:413-434. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.10.005. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747822 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations of beta-amyloid precursor protein alter the consequence of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Apr;14(4):658-665. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.247469. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30632506 Free PMC article.
-
GM1 ganglioside and Alzheimer's disease.Glycoconj J. 2015 May;32(3-4):87-91. doi: 10.1007/s10719-015-9579-5. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Glycoconj J. 2015. PMID: 25903682 Review.
-
Cyclodextrin has conflicting actions on autophagy flux in vivo in brains of normal and Alzheimer model mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Mar 1;26(5):843-859. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx001. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28062666 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected partial correction of metabolic and behavioral phenotypes of Alzheimer's APP/PSEN1 mice by gene targeting of diabetes/Alzheimer's-related Sorcs1.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016 Feb 25;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0282-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016. PMID: 26916443 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance: a connecting link between Alzheimer's disease and metabolic disorder.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Jan;36(1):67-83. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00622-2. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 32986168 Review.
References
-
- Daniele A, Albanese A. Early visual memory deficits: a neuropsychological marker of GBA mutations in PD? Neurology 2012; 78: 1372–1373. - PubMed
-
- Zervas M, Somers KL, Thrall MA, Walkley SU. Critical role for glycosphingolipids in Niemann-Pick disease type C. Curr Biol 2001; 11: 1283–1287. - PubMed
-
- Malnar M, Hecimovic S, Mattsson N, Zetterberg H. Bidirectional links between Alzheimer's disease and Niemann-Pick type C disease. Neurobiol Dis advance online publication, 4 June 2014; doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2014.05.033(e-pub ahead of print). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

