Development and characterization of solid dispersion of piroxicam for improvement of dissolution rate using hydrophilic carriers
- PMID: 25337467
- PMCID: PMC4204039
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2014.007
Development and characterization of solid dispersion of piroxicam for improvement of dissolution rate using hydrophilic carriers
Abstract
Introduction: The main objective of this study was preparation and characterization of solid dispersion of piroxicam to enhance its dissolution rate.
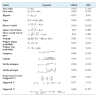
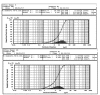
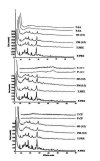
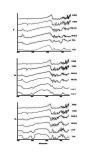
Methods: Solid dispersion formulations with different carriers including crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, Elaeagnus angustifolia fruit powder, with different drug to carrier ratios were prepared employing cogrinding method. Dissolution study of the piroxicam powders, physical mixtures and solid dispersions was performed in simulated gastric fluid and simulated intestinal fluid using USP Apparatus type II. The physical characterization of formulations were analyzed using powder X ray diffraction (PXRD), particle size analyzer and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Interactions between the drug and carriers were evaluated by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic method.
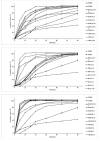
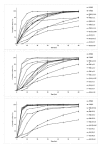
Results: It was revealed that all of three carriers increase the dissolution rate of piroxicam from physical mixtures and especially in solid dispersions compared to piroxicam pure and treated powders. PXRD and DSC results confirmed the reduction of crystalline form of piroxicam. FT-IR analysis did not show any physicochemical interaction between drug and carriers in the solid dispersion formulations.
Conclusion: Dissolution rate was dependent on the type and ratio of drug to carrier as well as pH of dissolution medium. Dissolution data of formulations were fitted well into the linear Weibull as well as non-linear logistic and suggested models.
Keywords: Cogrinding; Dissolution rate; Piroxicam; Solid dispersion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and characterization of solid dispersion for dissolution improvement of furosemide by cogrinding method.Adv Pharm Bull. 2014 Dec;4(4):391-9. doi: 10.5681/apb.2014.058. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Adv Pharm Bull. 2014. PMID: 25436197 Free PMC article.
-
The dissolution enhancement of piroxicam in its physical mixtures and solid dispersion formulations using gluconolactone and glucosamine hydrochloride as potential carriers.Pharm Dev Technol. 2015 Jan;20(1):74-83. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2013.871029. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Pharm Dev Technol. 2015. PMID: 24392858
-
Dissolution, bioavailability and ulcerogenic studies on piroxicam-nicotinamide solid dispersion formulations.Boll Chim Farm. 2003 Apr;142(3):119-24. Boll Chim Farm. 2003. PMID: 12806831 Clinical Trial.
-
Reciprocal powered time model for release kinetic analysis of ibuprofen solid dispersions in oleaster powder, microcrystalline cellulose and crospovidone.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010;13(2):152-61. doi: 10.18433/j3jg61. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 20816002
-
To enhance dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs: glucosamine hydrochloride as a potential carrier in solid dispersion formulations.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010 Mar 1;76(1):170-8. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.10.030. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010. PMID: 19945828
Cited by
-
An Integrative QbD Approach for the Development and Optimization of Controlled Release Compressed Coated Formulation of Water-Soluble Drugs.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Apr 22;23(5):120. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02225-9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35460024
-
Recent advances in improving oral drug bioavailability by cocrystals.Bioimpacts. 2018;8(4):305-320. doi: 10.15171/bi.2018.33. Epub 2018 May 31. Bioimpacts. 2018. PMID: 30397585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do lipid-based drug delivery systems affect the pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution of amiodarone? A comparative study of liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, and nanoemulsions.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(7):857-867. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75152.16292. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38800017 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Bioavailability of Wogonin by Different Administration Routes in Beagles.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Oct 16;22:3737-3745. doi: 10.12659/msm.897621. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27744456 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Solid Dispersion and Carriers Used Therein for Solubility Enhancement of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs.Adv Pharm Bull. 2020 Jul;10(3):359-369. doi: 10.34172/apb.2020.044. Epub 2020 May 11. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 32665894 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adibkia K, Barzegar-Jalali M, Maheri-Esfanjani H, Ghanbarzadeh S, Shokri J, Sabzevari A. et al. Physicochemical characterization of naproxen solid dispersions prepared via spray drying technology. Powder Technology. 2013;246:448–55. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2013.05.044. - DOI
-
- Adibkia K, Barzegar-Jalali M, Mohammadi G, Ebrahimnejhad H, Alaei-Beirami M. Effect of sodium alginate chain length and Ca2+and Al 3+on the release of diltiazem from matrices. Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2011;16:221–8.
-
- De Zordi N, Moneghini M, Kikic I, Grassi M, Del Rio Castillo AE, Solinas D. et al. Applications of supercritical fluids to enhance the dissolution behaviors of Furosemide by generation of microparticles and solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;81:131–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reverchon E, Adami R, Caputo G, De Marco I. Spherical microparticles production by supercritical antisolvent precipitation: Interpretation of results. J Supercrit Fluids. 2008;47:70–84. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2008.06.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources