Trigger-helix folding pathway and SI3 mediate catalysis and hairpin-stabilized pausing by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
- PMID: 25336618
- PMCID: PMC4227799
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku997
Trigger-helix folding pathway and SI3 mediate catalysis and hairpin-stabilized pausing by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
Abstract
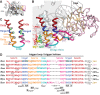
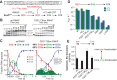
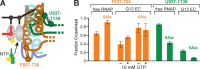
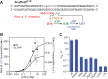
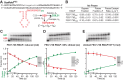
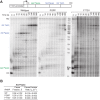
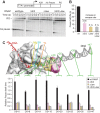
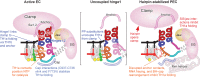
The conformational dynamics of the polymorphous trigger loop (TL) in RNA polymerase (RNAP) underlie multiple steps in the nucleotide addition cycle and diverse regulatory mechanisms. These mechanisms include nascent RNA hairpin-stabilized pausing, which inhibits TL folding into the trigger helices (TH) required for rapid nucleotide addition. The nascent RNA pause hairpin forms in the RNA exit channel and promotes opening of the RNAP clamp domain, which in turn stabilizes a partially folded, paused TL conformation that disfavors TH formation. We report that inhibiting TH unfolding with a disulfide crosslink slowed multiround nucleotide addition only modestly but eliminated hairpin-stabilized pausing. Conversely, a substitution that disrupts the TH folding pathway and uncouples establishment of key TH-NTP contacts from complete TH formation and clamp movement allowed rapid catalysis and eliminated hairpin-stabilized pausing. We also report that the active-site distal arm of the TH aids TL folding, but that a 188-aa insertion in the Escherichia coli TL (sequence insertion 3; SI3) disfavors TH formation and stimulates pausing. The effect of SI3 depends on the jaw domain, but not on downstream duplex DNA. Our results support the view that both SI3 and the pause hairpin modulate TL folding in a constrained pathway of intermediate states.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Transcriptional Pausing in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4007-4029. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31310765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obligate movements of an active site-linked surface domain control RNA polymerase elongation and pausing via a Phe pocket anchor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 7;118(36):e2101805118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101805118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34470825 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the RNA polymerase trigger loop in catalysis and pausing.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Jan;17(1):99-104. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1732. Epub 2009 Dec 6. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19966797 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase Accommodates a Pause RNA Hairpin by Global Conformational Rearrangements that Prolong Pausing.Mol Cell. 2018 Mar 1;69(5):802-815.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.018. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29499135 Free PMC article.
-
A Two-Way Street: Regulatory Interplay between RNA Polymerase and Nascent RNA Structure.Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Apr;41(4):293-310. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.009. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 26822487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Basic mechanisms and kinetics of pause-interspersed transcript elongation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 11;49(1):15-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1182. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33330935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Transcriptional Pausing in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4007-4029. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31310765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures of E. coli σS-transcription initiation complexes provide new insights into polymerase mechanism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 12;113(15):4051-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1520555113. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27035955 Free PMC article.
-
The elemental mechanism of transcriptional pausing.Elife. 2019 Jan 8;8:e40981. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40981. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30618376 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the trigger loop in translesion RNA synthesis by bacterial RNA polymerase.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 10;295(28):9583-9595. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011844. Epub 2020 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32439804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vassylyev D., Vassylyeva M., Zhang J., Palangat M., Artsimovitch I., Landick R. Structural basis for substrate loading in bacterial RNA polymerase. Nature. 2007;448:163–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

