Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010
- PMID: 25333036
- PMCID: PMC4202458
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.04.05
Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010
Abstract
Purpose: To estimate the cancer incidences and mortalities in China in 2010.
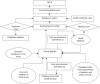
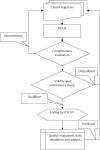
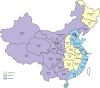
Methods: On basis of the evaluation procedures and data quality criteria described in the National Central Cancer Registry (NCCR), data from 219 cancer registries were evaluated. Data from 145 registries were identified as qualified and then accepted for the 2010 cancer registry report. The incidences and mortalities of major cancers and the overall incidence and mortality were stratified by residency (urban or rural), areas (eastern, middle, and western), gender, and age. The cancer cases and deaths were estimated based on age-specific rate and national population in 2010. The China 2010 Population Census data and Segi's world population data were used for calculating the age-standardized cancer incidence/mortality rates.
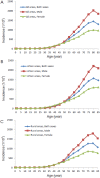
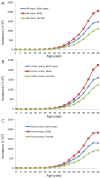
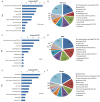
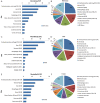
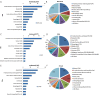
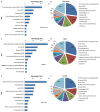
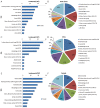
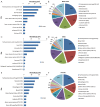
Results: Data were obtained from a total of 145 cancer registries (63 in urban areas and 82 in rural areas) covering 158,403,248 people (92,433,739 in urban areas and 65,969,509 in rural areas). The percentage of morphologically verified cases (MV%) were 67.11%; 2.99% of incident cases were identified through proportion of death certification only (DCO%), with the mortality to incidence ratio of (M/I) 0.61. The estimates of new cancer cases and cancer deaths were 3,093,039 and 1,956,622 in 2010, respectively. The crude incidence was 235.23/10(5) (268.65/10(5) in males and 200.21/10(5) in females), the age-standardized rates by Chinese standard population (ASR China) and by world standard population (ASR world) were 184.58/10(5) and 181.49/10(5), and the cumulative incidence rate (0-74 age years old) was 21.11%. The cancer incidence and ASR China were 256.41/10(5) and 187.53/10(5) in urban areas and 213.71/10(5) and 181.10/10(5) in rural areas. The crude cancer mortality in China was 148.81/10(5) (186.37/10(5) in males and 109.42/10(5) in females), the age-standardized mortalities by Chinese standard population and by world standard population were 113.92/10(5) and 112.86/10(5), and the cumulative mortality rate (0-74 age years old) was 12.78%. The cancer mortality and ASR China were 156.14/10(5) and 109.21/10(5) in urban areas 141.35/10(5) and 119.00/10(5) in rural areas, respectively. Lung cancer, female breast cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer, colorectal cancer, and cervical cancer were the most common cancers. Lung cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and pancreatic cancer were the leading causes of cancer deaths.
Conclusions: The coverage of cancer registration has rapidly increased in China in recent years and may reflect more accurate cancer burdens among populations living in different areas. As the basis of cancer control program, cancer registration plays an irreplaceable role in cancer surveillance, intervention evaluation, and policy-making. Given the increasing cancer burden in the past decades, China should strengthen its cancer prevention and control.
Keywords: Cancer registry; China; incidence; malignant tumor; mortality.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2010.Chin J Cancer. 2014 Aug;33(8):402-5. doi: 10.5732/cjc.014.10084. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Chin J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25011459 Free PMC article.
-
Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer registries, 2009.Chin J Cancer Res. 2013 Feb;25(1):10-21. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2012.12.04. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23372337 Free PMC article.
-
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.Chin J Cancer Res. 2014 Feb;26(1):48-58. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.01.08. Chin J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24653626 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer incidence and mortality in the Greater Poland Region-Analysis of the year 2010 and future trends.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2014 Jul 9;19(5):296-300. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2014.04.001. eCollection 2014 Sep. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2014. PMID: 25184053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer registration in China and its role in cancer prevention and control.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jul;21(7):e342-e349. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30073-5. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32615118 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between WT1 polymorphisms and susceptibility to breast cancer: results from a case-control study in a southwestern Chinese population.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;5(3):1234-50. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26046002 Free PMC article.
-
KPNA2 promotes metabolic reprogramming in glioblastomas by regulation of c-myc.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 16;37(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0861-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30115078 Free PMC article.
-
Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00707 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by sponging miR-206.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 31;12:4331-4340. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S198140. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31213848 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of Cancer Patients in Northeast China: Analysis of Sampled Cancers from Population-Based Cancer Registries.Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Oct;49(4):1106-1113. doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.613. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28161932 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of analytic performances of Cellsearch and iFISH approach in detecting circulating tumor cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8801-8806. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6688. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28187533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J, Chen WQ. Chinese Cancer Registry Annual Report. Beijing: Military Medical Science Press, 2012.
-
- Felay J, Burkhard C, Whelan S, et al. Check and Conversion Programs for Cancer Registries. IARC Technical Report No.42. Lyon: IARC 2005.
-
- Felay J. The IARCcrgTools program [EB/OL]. http: //www.iacr.com.fr/iarccrgtools.htm Lyon: IARC 2006.
-
- Bray F, Parkin DM. Evaluation of data quality in the cancer registry: principles and methods. Part I: comparability, validity and timeliness. Eur J Cancer 2009;45:747-55. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Chen VW, Ferlay J, et al. Comparability and Quality Control in Cancer Registration. IARC Technical Report No.19. Lyon: IARC 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
