A reversible Renilla luciferase protein complementation assay for rapid identification of protein-protein interactions reveals the existence of an interaction network involved in xyloglucan biosynthesis in the plant Golgi apparatus
- PMID: 25326916
- PMCID: PMC4265154
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eru401
A reversible Renilla luciferase protein complementation assay for rapid identification of protein-protein interactions reveals the existence of an interaction network involved in xyloglucan biosynthesis in the plant Golgi apparatus
Abstract
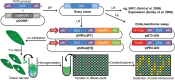
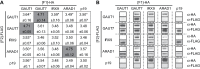
A growing body of evidence suggests that protein-protein interactions (PPIs) occur amongst glycosyltransferases (GTs) required for plant glycan biosynthesis (e.g. cell wall polysaccharides and N-glycans) in the Golgi apparatus, and may control the functions of these enzymes. However, identification of PPIs in the endomembrane system in a relatively fast and simple fashion is technically challenging, hampering the progress in understanding the functional coordination of the enzymes in Golgi glycan biosynthesis. To solve the challenges, we adapted and streamlined a reversible Renilla luciferase protein complementation assay (Rluc-PCA), originally reported for use in human cells, for transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana. We tested Rluc-PCA and successfully identified luminescence complementation amongst Golgi-localizing GTs known to form a heterodimer (GAUT1 and GAUT7) and those which homooligomerize (ARAD1). In contrast, no interaction was shown between negative controls (e.g. GAUT7, ARAD1, IRX9). Rluc-PCA was used to investigate PPIs amongst Golgi-localizing GTs involved in biosynthesis of hemicelluloses. Although no PPI was identified among six GTs involved in xylan biosynthesis, Rluc-PCA confirmed three previously proposed interactions and identified seven novel PPIs amongst GTs involved in xyloglucan biosynthesis. Notably, three of the novel PPIs were confirmed by a yeast-based split-ubiquitin assay. Finally, Gateway-enabled expression vectors were generated, allowing rapid construction of fusion proteins to the Rluc reporters and epitope tags. Our results show that Rluc-PCA coupled with transient expression in N. benthamiana is a fast and versatile method suitable for analysis of PPIs between Golgi resident proteins in an easy and mid-throughput fashion in planta.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Golgi apparatus; Nicotiana benthamiana; Renilla luciferase; glycosyltransferase; plant cell wall; polysaccharides; protein–protein interaction; type II membrane protein; xyloglucan..
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GO-PROMTO illuminates protein membrane topologies of glycan biosynthetic enzymes in the Golgi apparatus of living tissues.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031324. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363620 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interactions among xyloglucan-synthesizing enzymes and formation of Golgi-localized multiprotein complexes.Plant Cell Physiol. 2015 Feb;56(2):255-67. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu161. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25392066
-
Subcompartment localization of the side chain xyloglucan-synthesizing enzymes within Golgi stacks of tobacco suspension-cultured cells.Plant J. 2010 Dec;64(6):977-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04388.x. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 21143678
-
Critical Review of Plant Cell Wall Matrix Polysaccharide Glycosyltransferase Activities Verified by Heterologous Protein Expression.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jul 16;10:915. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00915. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31379900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Golgi-localized enzyme complexes for plant cell wall biosynthesis.Trends Plant Sci. 2013 Jan;18(1):49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Aug 25. Trends Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 22925628 Review.
Cited by
-
Pectin Synthesis and Pollen Tube Growth in Arabidopsis Involves Three GAUT1 Golgi-Anchoring Proteins: GAUT5, GAUT6, and GAUT7.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 11;11:585774. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.585774. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33072156 Free PMC article.
-
Xylan in the Middle: Understanding Xylan Biosynthesis and Its Metabolic Dependencies Toward Improving Wood Fiber for Industrial Processing.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Feb 25;10:176. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00176. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30858858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Techniques for the Analysis of Protein-Protein Interactions in Vivo.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):727-58. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00470. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the molecular logic of a metabotropic glutamate receptor heterodimer.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 3;15(1):8552. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52822-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39362861 Free PMC article.
-
Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase increases tightly-bound xyloglucan and chain number but decreases chain length contributing to the defense response that Glycine max has to Heterodera glycines.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 14;16(1):e0244305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244305. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33444331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atmodjo MA, Sakuragi Y, Zhu X, Burrell AJ, Mohanty SS, Atwood JA, Orlando R, Scheller HV, Mohnen D. 2011. Galacturonosyltransferase (GAUT)1 and GAUT7 are the core of a plant cell wall pectin biosynthetic homogalacturonan:galacturonosyltransferase complex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 108, 20225–20230. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blancaflor EB. 2002. The cytoskeleton and gravitropism in higher plants. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 21, 120–136. - PubMed
-
- Boevink P, Oparka K, Cruz SS, Martin B, Betteridge A, Hawes C. 1998. Stacks on tracks: the plant Golgi apparatus traffics on an actin/ER network. The Plant Journal 15, 441–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

