Mechanisms of regulation of PFKFB expression in pancreatic and gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 25320508
- PMCID: PMC4194554
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13705
Mechanisms of regulation of PFKFB expression in pancreatic and gastric cancer cells
Abstract
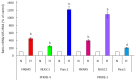
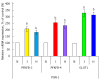
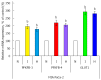
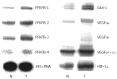
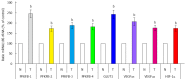
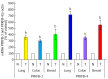
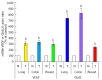
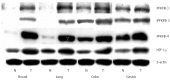
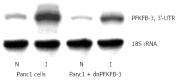
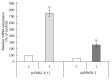
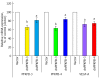
Enzymes 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 and -4 (PFKFB-3 and PFKFB-4) play a significant role in the regulation of glycolysis in cancer cells as well as its proliferation and survival. The expression of these mRNAs is increased in malignant tumors and strongly induced in different cancer cell lines by hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) through active HIF binding sites in promoter region of PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 genes. Moreover, the expression and hypoxia responsibility of PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 was also shown for pancreatic (Panc1, PSN-1, and MIA PaCa-2) as well as gastric (MKN45 and NUGC3) cancer cells. At the same time, their basal expression level and hypoxia responsiveness vary in the different cells studied: the highest level of PFKFB-4 protein expression was found in NUGC3 gastric cancer cell line and lowest in Panc1 cells, with a stronger response to hypoxia in the pancreatic cancer cell line. Overexpression of different PFKFB in pancreatic and gastric cancer cells under hypoxic condition is correlated with enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Glut1 mRNA as well as with increased level of HIF-1α protein. Increased expression of different PFKFB genes was also demonstrated in gastric, lung, breast, and colon cancers as compared to corresponding non-malignant tissue counterparts from the same patients, being more robust in the breast and lung tumors. Moreover, induction of PFKFB-4 mRNA expression in the breast and lung cancers is stronger than PFKFB-3 mRNA. The levels of both PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 proteins in non-malignant gastric and colon tissues were more pronounced than in the non-malignant breast and lung tissues. It is interesting to note that Panc1 and PSN-1 cells transfected with dominant/negative PFKFB-3 (dnPFKFB-3) showed a lower level of endogenous PFKFB-3, PFKFB-4, and VEGF mRNA expressions as well as a decreased proliferation rate of these cells. Moreover, a similar effect had dnPFKFB-4. In conclusion, there is strong evidence that PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 isoenzymes are induced under hypoxia in pancreatic and other cancer cell lines, are overexpressed in gastric, colon, lung, and breast malignant tumors and undergo changes in their metabolism that contribute to the proliferation and survival of cancer cells. Thus, targeting these PFKFB may therefore present new therapeutic opportunities.
Keywords: 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3; 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-4; Gastric cancer; Hypoxia; Hypoxia inducible factor; Lung cancer; MKN45; NUGC3; PST-1; Panc1.
Figures


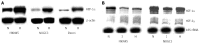
Similar articles
-
Hypoxic regulation of PFKFB-3 and PFKFB-4 gene expression in gastric and pancreatic cancer cell lines and expression of PFKFB genes in gastric cancers.Acta Biochim Pol. 2006;53(4):789-99. Epub 2006 Dec 4. Acta Biochim Pol. 2006. PMID: 17143338
-
Overexpression of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-4 in the human breast and colon malignant tumors.Biochimie. 2005 Nov;87(11):1005-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.04.007. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15925437
-
Splice isoform of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-4: expression and hypoxic regulation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 Dec;280(1-2):227-34. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-8009-6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16311927
-
Regulation of glucose metabolism by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatases in cancer.Exp Mol Pathol. 2009 Jun;86(3):174-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2009.01.003. Epub 2009 Jan 14. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19454274 Review.
-
6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 and 4: A pair of valves for fine-tuning of glucose metabolism in human cancer.Mol Metab. 2019 Feb;20:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30553771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes and the role of PDK4 in CD14+ monocytes of coronary artery disease.Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR20204124. doi: 10.1042/BSR20204124. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33739370 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of NSCLC metabolic remodeling on immunotherapy effectiveness.Biomark Res. 2022 Aug 29;10(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00412-1. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 36038935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mir-488 alleviates chemoresistance and glycolysis of colorectal cancer by targeting PFKFB3.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jan;35(1):e23578. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23578. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 32990355 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 in Cancer: Genetic Basis, Impact on Disease Development/Progression, and Potential as Therapeutic Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;13(4):909. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040909. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptotanshinone inhibits PFK-mediated aerobic glycolysis by activating AMPK pathway leading to blockade of cutaneous melanoma.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 7;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00913-1. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38454519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaccaro V, Gelibter A, Bria E, Iapicca P, Cappello P, Di Modugno F, Pino MS, Nuzzo C, Cognetti F, Novelli F, et al. Molecular and genetic bases of pancreatic cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 2012;13:731–743. - PubMed
-
- Höckel M, Vaupel P. Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:266–276. - PubMed
-
- Chiche J, Rouleau M, Gounon P, Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouysségur J, Mazure NM. Hypoxic enlarged mitochondria protect cancer cells from apoptotic stimuli. J Cell Physiol. 2010;222:648–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

