Protease-activated receptor (PAR)1, PAR2 and PAR4 expressions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25297082
- PMCID: PMC4790359
- DOI: 10.13918/j.issn.2095-8137.2014.5.420
Protease-activated receptor (PAR)1, PAR2 and PAR4 expressions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
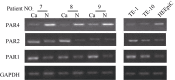
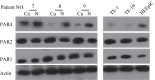
Here, we used reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) and western blot to detect protease-activated receptor (PAR) 1, PAR 2 and PAR 4 expression in cancer tissues and cell lines of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and investigated the co-relationship between PAR expression and clinic-pathological data for esophageal cancer. The methylation of PAR4 gene promoter involved in esophageal carcinoma was also analyzed. By comparing the mRNA expressions of normal esophageal tissue and human esophageal epithelial cells (HEEpiC), we found that among the 28 cases of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, PAR1 (60%) and PAR2 (71%) were elevated in 17 and 20 cases, respectively, and PAR4 (68%) expression was lowered in 19 cases. Whereas, in human esophageal squamous cells (TE-1 and TE-10), PAR1 and PAR2 expression was increased but PAR4 was decreased. Combined with clinical data, the expression of PAR1 in poorly differentiated (P=0.016) and middle and lower parts of the esophagus (P=0.016) was higher; expression of PAR4 in poorly differentiated carcinoma was lower (P=0.049). Regarding TE-1 and TE-10 protein expression, we found that in randomized esophageal carcinoma, PAR1 (P=0.027) and PAR2 (P=0.039) expressions were increased, but lowered for PAR4 (P=0.0001). In HEEpiC, TE-1, TE-10, esophageal and normal esophagus tissue samples (case No. 7), the frequency of methylation at the 19 CpG loci of PAR4 was 35.4%, 95.2%, 83.8%, 62.6% and 48.2%, respectively. Our results indicate that the expression of PAR1 and PAR2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is increased but PAR4 is decreased. Hypermethylation of the promoter of the PAR4 gene may contribute to reduced expression of PAR4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Methylation; PAR1; PAR2; PAR4; PCR; Western Blot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory mediators modulate thrombin and cathepsin-G signaling in human bronchial fibroblasts by inducing expression of proteinase-activated receptor-4.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Mar;292(3):L788-98. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00226.2006. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17142351
-
The decreased expression of protease-activated receptor 4 in esophageal squamous carcinoma.Neoplasma. 2014;61(5):546-52. doi: 10.4149/neo_2014_067. Neoplasma. 2014. PMID: 25030438
-
Activity of protease-activated receptors in the human submucous plexus.Gastroenterology. 2011 Dec;141(6):2088-2097.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.034. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21875497
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating Proteinase-Activated Receptors (PARs).FEBS J. 2021 Apr;288(8):2697-2726. doi: 10.1111/febs.15829. Epub 2021 Apr 6. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33742547 Review.
-
Protease-activated receptor 4: a critical participator in inflammatory response.Inflammation. 2015 Apr;38(2):886-95. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9999-6. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25120239 Review.
Cited by
-
PAR4 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration.Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5745-5752. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9407. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30333860 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of chimeric antigen receptor T cells against protease-activated receptor 1 for treating pancreatic cancer.BMC Med. 2023 Sep 4;21(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03053-9. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37667257 Free PMC article.
-
Teleocidin A2 inhibits human proteinase-activated receptor 2 signaling in tumor cells.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016 Jun 10;4(4):e00230. doi: 10.1002/prp2.230. eCollection 2016 Aug. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016. PMID: 28116092 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Landscape of PARs in Epithelial Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 2;19(11):3451. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113451. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30400241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression of protease-activated receptors in esophageal carcinoma cells: the relationship between changes in gene expression and cell proliferation, apoptosis in vitro and growing ability in vivo.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Jun 7;18:81. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0577-0. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 29977156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caruso R, Pallone F, Fina D, Gioia V, Peluso I, Caprioli F, Stolfi C, Perfetti A, Spagnoli LG, Palmieri G, Macdonald TT, Monteleone G. 2006. Protease-activated receptor-2 activation in gastric cancer cells promotes epidermal growth factor receptor trans-activation and proliferation. The American Journal of Pathology, 169(1): 268-78. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cunningham MR, McIntosh KA, Pediani JD, Robben J, Cooke AE, Nilsson M, Gould GW, Mundell S, Milligan G, Plevin R. 2012. Novel role for proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) in membrane trafficking of proteinase-activated receptor 4 (PAR4). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287(20): 16656-69. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Darmoul D, Gratio V, Devaud H, Laburthe M. 2004. Protease-activated receptor 2 in colon cancer: trypsin-induced MAPK phosphorylation and cell proliferation are mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(20): 20927-34. - PubMed
-
- Déry O, Corvera CU, Steinhoff M, Bunnett NW. 1998. Proteinase-activated receptors: novel mechanisms of signaling by serine proteases. The American Journal of Physiology, 274(6): C1429-52. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto D, Hirono Y, Goi T, Katayama K, Hirose K, Yamaguchi A. 2006. Expression of protease activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) in gastric cancer. Journal of Surgical Oncology, 93(2): 139-44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical