FixingTIM: interactive exploration of sequence and structural data to identify functional mutations in protein families
- PMID: 25237390
- PMCID: PMC4155608
- DOI: 10.1186/1753-6561-8-S2-S3
FixingTIM: interactive exploration of sequence and structural data to identify functional mutations in protein families
Abstract
Background: Knowledge of the 3D structure and functionality of proteins can lead to insight into the associated cellular processes, speed up the creation of pharmaceutical products, and develop drugs that are more effective in combating disease.
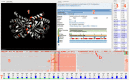
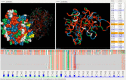
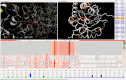
Methods: We present the design and implementation of a visual mining and analysis tool to help identify protein mutations across a family of structural models and to help discover the effect of these mutations on protein function. We integrate 3D structure and sequence information in a common visual interface; multiple linked views and a computational backbone allow comparison at the molecular and atomic levels, while a novel trend-image visual abstraction allows for the sorting and mining of large collections of sequences and of their residues.
Results: We evaluate our approach on the triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) family structural models and sequence data and show that our tool provides an effective, scalable way to navigate a family of proteins, as well as a means to inspect the structure and sequence of individual proteins.
Conclusions: The TIM application shows that our tool can assist in the navigation of families of proteins, as well as in the exploration of individual protein structures. In conjunction with domain expert knowledge, this interactive tool can help provide biophysical insight into why specific mutations affect function and potentially suggest additional modifications to the protein that could be used to rescue functionality.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Discovery of Functional Motifs from the Interface Region of Oligomeric Proteins Using Frequent Subgraph Mining.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019 Sep-Oct;16(5):1537-1549. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2756879. Epub 2017 Sep 26. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 28961123
-
Methods for visual mining of genomic and proteomic data atlases.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Apr 23;13:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-58. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22524279 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012).Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):040301. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912807
-
A guide to the effects of a large portion of the residues of triosephosphate isomerase on catalysis, stability, druggability, and human disease.Proteins. 2017 Jul;85(7):1190-1211. doi: 10.1002/prot.25299. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Proteins. 2017. PMID: 28378917 Review.
-
Novel function discovery through sequence and structural data mining.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016 Jun;38:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2016.05.017. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27289211 Review.
Cited by
-
Activity-Centered Domain Characterization for Problem-Driven Scientific Visualization.IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2018 Jan;24(1):913-922. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2017.2744459. Epub 2017 Aug 29. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph. 2018. PMID: 28866550 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the sequence requirements of protein families: insights from the BioVis 2013 contests.BMC Proc. 2014 Aug 28;8(Suppl 2 Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Symposium on Biologica):S1. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-8-S2-S1. eCollection 2014. BMC Proc. 2014. PMID: 25237388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhong W, Altum G, Harrison R, Tai PC, Pan Y. Mining protein sequence motifs representing common 3d structures. 2005. pp. 215–216. - PubMed
-
- Chen N, Harris TW, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Bradnam K, Canaran P, Chan J, Chen C, Chen WJ, Cunningham F, Davis P, Kenny E, Kishore R, Lawson D, Lee R, Muller H, Nakamura C, Pai S, Ozersky P, Petcherski A, Rogers A, Sabo A, Schwarz EM, Van Auken K, Wang Q, Durbin R, Spieth J, Sternberg PW, Stein LD. Wormbase: A comprehensive data resource for caenorhabditis biology and genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(1):383–389. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

