Regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) by redox-dependent proteolysis
- PMID: 25237187
- PMCID: PMC4223318
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.579771
Regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) by redox-dependent proteolysis
Abstract
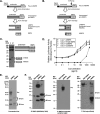
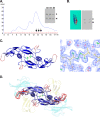
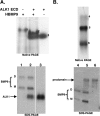
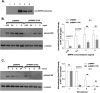
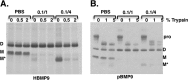
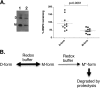
BMP9, a member of the TGFβ superfamily, is a homodimer that forms a signaling complex with two type I and two type II receptors. Signaling through high-affinity activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells, circulating BMP9 acts as a vascular quiescence factor, maintaining endothelial homeostasis. BMP9 is also the most potent BMP for inducing osteogenic signaling in mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and promoting bone formation in vivo. This activity requires ALK1, the lower affinity type I receptor ALK2, and higher concentrations of BMP9. In adults, BMP9 is constitutively expressed in hepatocytes and secreted into the circulation. Optimum concentrations of BMP9 are essential to maintain the highly specific endothelial-protective function. Factors regulating BMP9 stability and activity remain unknown. Here, we showed by chromatography and a 1.9 Å crystal structure that stable BMP9 dimers could form either with (D-form) or without (M-form) an intermolecular disulfide bond. Although both forms of BMP9 were capable of binding to the prodomain and ALK1, the M-form demonstrated less sustained induction of Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation. The two forms could be converted into each other by changing the redox potential, and this redox switch caused a major alteration in BMP9 stability. The M-form displayed greater susceptibility to redox-dependent cleavage by proteases present in serum. This study provides a mechanism for the regulation of circulating BMP9 concentrations and may provide new rationales for approaches to modify BMP9 levels for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP); Cell Signaling; Crystal Structure; Disulfide; Endothelial Cell; Redox Regulation.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A heterodimer formed by bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) and BMP10 provides most BMP biological activity in plasma.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 13;293(28):10963-10974. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002968. Epub 2018 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29789425 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) and BMP10 enhance tumor necrosis factor-α-induced monocyte recruitment to the vascular endothelium mainly via activin receptor-like kinase 2.J Biol Chem. 2017 Aug 18;292(33):13714-13726. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778506. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28646109 Free PMC article.
-
Serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 as a novel transcriptional target of bone morphogenetic protein-ALK1 receptor signaling in vascular endothelial cells.Angiogenesis. 2018 May;21(2):415-423. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9605-x. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Angiogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29478089
-
Regulation of the ALK1 ligands, BMP9 and BMP10.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Aug 15;44(4):1135-41. doi: 10.1042/BST20160083. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27528761 Review.
-
Advances in the molecular regulation of endothelial BMP9 signalling complexes and implications for cardiovascular disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Jun 28;47(3):779-791. doi: 10.1042/BST20180137. Epub 2019 May 24. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31127068 Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structures of BMPRII extracellular domain in binary and ternary receptor complexes with BMP10.Nat Commun. 2022 May 3;13(1):2395. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30111-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35504921 Free PMC article.
-
Role of soluble endoglin in BMP9 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 3;116(36):17800-17808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816661116. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31431534 Free PMC article.
-
The wonders of BMP9: From mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, angiogenesis, neurogenesis, tumorigenesis, and metabolism to regenerative medicine.Genes Dis. 2019 Jul 24;6(3):201-223. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.07.003. eCollection 2019 Sep. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 32042861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural perspective of BMP ligands and signaling.Bone. 2020 Nov;140:115549. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115549. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32730927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone mesenchymal stem cells co-expressing VEGF and BMP-6 genes to combat avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):954-962. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5455. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29399103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- David L., Mallet C., Mazerbourg S., Feige J. J., Bailly S. (2007) Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood 109, 1953–1961 - PubMed
-
- Johnson D. W., Berg J. N., Baldwin M. A., Gallione C. J., Marondel I., Yoon S. J., Stenzel T. T., Speer M., Pericak-Vance M. A., Diamond A., Guttmacher A. E., Jackson C. E., Attisano L., Kucherlapati R., Porteous M. E., Marchuk D. A. (1996) Mutations in the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat. Genet. 13, 189–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

