Pathological features and diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas
- PMID: 25232456
- PMCID: PMC4163729
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v6.i9.311
Pathological features and diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas
Abstract
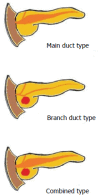
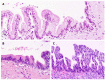
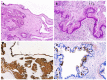
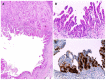
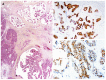
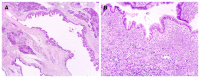
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas is a noninvasive epithelial neoplasm of mucin-producing cells arising in the main duct (MD) and/or branch ducts (BD) of the pancreas. Involved ducts are dilated and filled with neoplastic papillae and mucus in variable intensity. IPMN lacks ovarian-type stroma, unlike mucinous cystic neoplasm, and is defined as a grossly visible entity (≥ 5 mm), unlike pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasm. With the use of high-resolution imaging techniques, very small IPMNs are increasingly being identified. Most IPMNs are solitary and located in the pancreatic head, although 20%-40% are multifocal. Macroscopic classification in MD type, BD type and mixed or combined type reflects biological differences with important prognostic and preoperative clinical management implications. Based on cytoarchitectural atypia, IPMN is classified into low-grade, intermediate-grade and high-grade dysplasia. Based on histological features and mucin (MUC) immunophenotype, IPMNs are classified into gastric, intestinal, pancreatobiliary and oncocytic types. These different phenotypes can be observed together, with the IPMN classified according to the predominant type. Two pathways have been suggested: gastric phenotype corresponds to less aggressive uncommitted cells (MUC1 -, MUC2 -, MUC5AC +, MUC6 +) with the capacity to evolve to intestinal phenotype (intestinal pathway) (MUC1 -, MUC2 +, MUC5AC +, MUC6 - or weak +) or pancreatobiliary /oncocytic phenotypes (pyloropancreatic pathway) (MUC1 +, MUC 2-, MUC5AC +, MUC 6 +) becoming more aggressive. Prognosis of IPMN is excellent but critically worsens when invasive carcinoma arises (about 40% of IPMNs), except in some cases of minimal invasion. The clinical challenge is to establish which IPMNs should be removed because of their higher risk of developing invasive cancer. Once resected, they must be extensively sampled or, much better, submitted in its entirety for microscopic study to completely rule out associated invasive carcinoma.
Keywords: Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Mucinous pancreatic cysts; Mucins.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MUC2 expression and prevalence of high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma in mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.Pancreatology. 2013 Nov-Dec;13(6):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Pancreatology. 2013. PMID: 24280573
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas with distinct pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas are frequently of gastric subtype.Ann Surg. 2013 Jul;258(1):141-51. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828cd008. Ann Surg. 2013. PMID: 23532108
-
Frequency of subtypes of biliary intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and their MUC1, MUC2, and DPC4 expression patterns differ from pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.J Am Coll Surg. 2012 Jan;214(1):27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2011.09.025. Epub 2011 Nov 23. J Am Coll Surg. 2012. PMID: 22112419
-
Thirty years of experience with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: from discovery to international consensus.Digestion. 2014;90(4):265-72. doi: 10.1159/000370111. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Digestion. 2014. PMID: 25591885 Review.
-
Pancreatic tumors with cystic dilatation of the ducts: intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000 Feb;17(1):16-30. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10721804 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA profiling of primary pulmonary enteric adenocarcinoma in members from the same family reveals some similarities to pancreatic adenocarcinoma-a step towards personalized therapy.Clin Epigenetics. 2015 Dec 16;7:129. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0162-5. eCollection 2015. Clin Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26677401 Free PMC article.
-
Confocal Endomicroscopy Characteristics of Different Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Subtypes.JOP. 2017 May;18(Suppl 2):198-202. JOP. 2017. PMID: 28824351 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Detection of Circulating Epithelial Cells in Patients with Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms.Oncologist. 2018 Jan;23(1):121-127. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0234. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Oncologist. 2018. PMID: 28860411 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of the 2006 Sendai and 2012 Fukuoka guidelines for the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: A single-center experience with 138 surgically treated patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(38):e4922. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004922. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27661043 Free PMC article.
-
Common features between neoplastic and preneoplastic lesions of the biliary tract and the pancreas.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 21;25(31):4343-4359. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4343. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31496617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND (eds) WHO Classification of Tumors of the Digestive System. Lyon: IARC Press; 1997. pp. 279–337.
-
- Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA (eds) WHO Classification of Tumors. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Digestive System. Lyon: IARC Press; 2000. pp. 219–251.
-
- Furukawa T, Klöppel G, Volkan Adsay N, Albores-Saavedra J, Fukushima N, Horii A, Hruban RH, Kato Y, Klimstra DS, Longnecker DS, et al. Classification of types of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: a consensus study. Virchows Arch. 2005;447:794–799. - PubMed
-
- Hruban RH, Takaori K, Klimstra DS, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Biankin AV, Biankin SA, Compton C, Fukushima N, Furukawa T, et al. An illustrated consensus on the classification of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:977–987. - PubMed
-
- Maguchi H, Tanno S, Mizuno N, Hanada K, Kobayashi G, Hatori T, Sadakari Y, Yamaguchi T, Tobita K, Doi R, et al. Natural history of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a multicenter study in Japan. Pancreas. 2011;40:364–370. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

