Mathematical model of renal interstitial fibrosis
- PMID: 25225370
- PMCID: PMC4191765
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1413970111
Mathematical model of renal interstitial fibrosis
Abstract
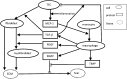
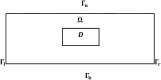
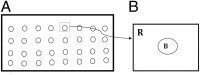
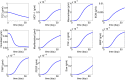
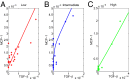
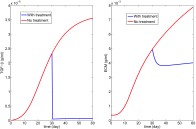
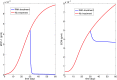
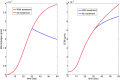
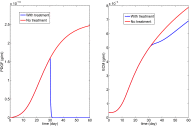
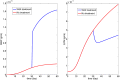
Lupus nephritis (LN) is an autoimmune disease that occurs when autoantibodies complex with self-antigen and form immune complexes that accumulate in the glomeruli. These immune complexes initiate an inflammatory response resulting in glomerular injury. LN often concomitantly affects the tubulointerstitial compartment of the kidney, leading first to interstitial inflammation and subsequently to interstitial fibrosis and atrophy of the renal tubules if not appropriately treated. Presently the only way to assess interstitial inflammation and fibrosis is through kidney biopsy, which is invasive and cannot be repeated frequently. Hence, monitoring of disease progression and response to therapy is suboptimal. In this paper we describe a mathematical model of the progress from tubulointerstitial inflammation to fibrosis. We demonstrate how the model can be used to monitor treatments for interstitial fibrosis in LN with drugs currently being developed or used for nonrenal fibrosis.
Keywords: math modeling; renal fibrosis; tubulointerstitial inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunolocalization of fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1), its receptor (FGFR-1), and fibroblast-specific protein-1 (FSP-1) in inflammatory renal disease.Kidney Int. 2005 Dec;68(6):2621-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00734.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16316338
-
Brief Report: Tubulointerstitial Damage in Lupus Nephritis: A Comparison of the Factors Associated With Tubulointerstitial Inflammation and Renal Scarring.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;70(11):1801-1806. doi: 10.1002/art.40575. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29851285 Free PMC article.
-
Correlative insights into immunoexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, transforming growth factor beta-1 and CD68+ cells in lupus nephritis.Pol J Pathol. 2005;56(3):115-20. Pol J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16334978
-
Experimental insights into the tubulointerstitial disease accompanying primary glomerular lesions.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994 Dec;5(6):1273-87. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V561273. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994. PMID: 7893992 Review.
-
Proteinuria and growth factors in the development of tubulointerstitial injury and scarring in kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005 Jan;14(1):43-52. doi: 10.1097/00041552-200501000-00008. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005. PMID: 15586015 Review.
Cited by
-
Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis of Living Donor Kidneys Associates with Urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1.Am J Nephrol. 2016;43(6):454-9. doi: 10.1159/000446851. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Am J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27288357 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblasts: Diverse Cells Critical to Biomaterials Integration.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Apr 9;4(4):1223-1232. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00244. Epub 2017 Jun 13. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 31440581 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal control strategies for preventing hepatitis B infection and reducing chronic liver cirrhosis incidence.Infect Dis Model. 2019 Dec 27;5:91-110. doi: 10.1016/j.idm.2019.12.006. eCollection 2020. Infect Dis Model. 2019. PMID: 31930183 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy for melanoma with BRAF/MEK inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor: a mathematical model.BMC Syst Biol. 2017 Jul 19;11(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12918-017-0446-9. BMC Syst Biol. 2017. PMID: 28724377 Free PMC article.
-
Serum uPAR as Biomarker in Breast Cancer Recurrence: A Mathematical Model.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0153508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153508. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27078836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rovin BH, Birmingham DJ, Nadasdy T. Renal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Schrier R, Neilson E, Molitoris B, Coffman T, Falk R, editors. Schrier’s Diseases of the Kidney. 9th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012. pp. 1522–1556.
-
- Dhingra S, Qureshi R, Abdellatif A, Gaber LW, Truong LD. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Innocent bystander or ominous presage. Histol Histopathol. 2014;29(5):553–565. - PubMed
-
- Müller GA, Markovic-Lipkovski J, Frank J, Rodemann HP. The role of interstitial cells in the progression of renal diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992;2(10, Suppl):S198–S205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

