Insilico analysis of hypothetical proteins unveils putative metabolic pathways and essential genes in Leishmania donovani
- PMID: 25206363
- PMCID: PMC4144268
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00291
Insilico analysis of hypothetical proteins unveils putative metabolic pathways and essential genes in Leishmania donovani
Abstract
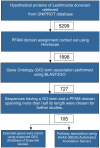
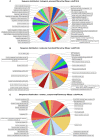
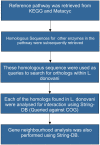
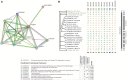
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Leishmania, which is active in two broad forms namely, Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL or Kala Azar) and Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (CL). The disease is most prevalent in the tropical regions and poses a threat to over 70 countries across the globe. About 200 million people are estimated to be at risk of developing VL in the Indian subcontinent, and this refers to around 67% of the global VL disease burden. The Indian state of Bihar alone accounts for 50% of the total VL cases. While no vaccination exists, several pentavalent antimonials and drugs like Paromomycin, Amphotericin, Miltefosine etc. are used in the treatment of Leishmaniasis. However, due to their low efficacies and the resistance developed by the bug to these medications, there is an urgent need to look into newer species specific targets. The proteome information available suggests that among the 7960 proteins in Leishmania donavani, a staggering 65% remains classified as a hypothetical uncharacterized set. In this background, we have attempted to assign probable functions to these hypothetical sequences present in this parasite, to explore their plausible roles as druggable receptors. Thus, putative functions have been defined to 105 hypothetical proteins, which exhibited a GO term correlation and PFAM domain coverage of more than 50% over the query sequence length. Of these, 27 sequences were found to be associated with a reference pathway in KEGG as well. Further, using homology approaches, four pathways viz., Ubiquinone biosynthesis, Fatty acid elongation in Mitochondria, Fatty Acid Elongation in ER and Seleno-cysteine Metabolism have been reconstructed. In addition, 7 new putative essential genes have been mined with the help of Eukaryotic Database of Essential Genes (DEG). All these information related to pathways and essential genes indeed show promise for exploiting the select molecules as potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Leishmania donovani; drug targets; fatty acid elongation; hypothetical proteins; seleno-cysteine metabolism; ubiquinone biosynthesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Relapse after treatment with miltefosine for visceral leishmaniasis is associated with increased infectivity of the infecting Leishmania donovani strain.mBio. 2013 Oct 8;4(5):e00611-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00611-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24105765 Free PMC article.
-
Drug susceptibility in Leishmania isolates following miltefosine treatment in cases of visceral leishmaniasis and post kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(5):e1657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001657. Epub 2012 May 22. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22629478 Free PMC article.
-
Antiparasitic chemotherapy: tinkering with the purine salvage pathway.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;625:116-32. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77570-8_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18365663 Review.
-
Data enabled prediction analysis assigns folate/biopterin transporter (BT1) family to 36 hypothetical membrane proteins in Leishmania donovani.Bioinformation. 2019 Oct 18;15(10):697-708. doi: 10.6026/97320630015697. eCollection 2019. Bioinformation. 2019. PMID: 31831951 Free PMC article.
-
Leishmaniasis: an update of current pharmacotherapy.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013 Jan;14(1):53-63. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2013.755515. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23256501 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying miltefosine-resistant key genes in protein-protein interactions network and experimental verification in Iranian Leishmania major.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Oct;46(5):5371-5388. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04992-4. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31385238
-
Questing functions and structures of hypothetical proteins from Campylobacter jejuni: a computer-aided approach.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;40(6):BSR20193939. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193939. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32458979 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the functional role of hypothetical proteins from Chloroflexus aurantiacs J-10-f1 using bioinformatics approach.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2020 Sep;9(3):129-139. doi: 10.22099/mbrc.2020.36894.1495. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 33313333 Free PMC article.
-
In silico functional prediction of hypothetical proteins from the core genome of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biovar ovis.PeerJ. 2020 Aug 26;8:e9643. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9643. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32913672 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Casein Kinase 1.1 in Leishmania donovani Using the CRISPR Cas9 Toolkit.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4635605. doi: 10.1155/2017/4635605. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29333442 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

