Neuropathic ulcers in leprosy treated with intralesional platelet-rich plasma
- PMID: 25196256
- PMCID: PMC7949963
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12359
Neuropathic ulcers in leprosy treated with intralesional platelet-rich plasma
Abstract
Neuropathic ulcers in leprosy represent a therapeutic challenge for clinicians. Chronic ulcers affect patient health, emotional state and quality of life, causing considerable morbidity and mortality in addition to contributing to significant health care costs. The pathogenesis is mainly related to the abnormally increased pressure in areas such as the sole of the foot, secondary to lack of sensation and deformities induced by peripheral sensory-motor neuropathy. Conventional treatment of these wounds can be slow due to their chronic inflammatory state and the senescence of local reparative cells. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may restore the healing process, leading to a reparative phase. We present two patients with four neuropathic leprosy ulcers that have responded satisfactory to PRP treatment. PRP therapy has been growing as a viable treatment alternative for chronic ulcers. However, stronger scientific evidence is required to support its potential benefit for use in chronic wounds.
Keywords: Leprosy; Neuropathic ulcer; Platelet-rich plasma.
© 2014 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2014 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
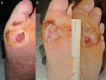
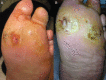
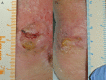
Similar articles
-
A case report on the use of sustained release platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of chronic pressure ulcers.J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34(1):122-7. doi: 10.1179/107902610X12923394765616. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011. PMID: 21528636 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of intralesional injection of platelet-rich plasma in accelerating the healing of chronic ulcers: an experimental and clinical study.Int Wound J. 2013 Aug;10(4):397-406. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.00996.x. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Int Wound J. 2013. PMID: 22672105 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of autologous platelet-rich plasma therapy with total contact casting versus total contact casting alone in treatment of trophic ulcer in leprosy: An observer-blind, randomized controlled trial.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020 May-Jun;86(3):262-271. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_571_18. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2020. PMID: 31997794 Clinical Trial.
-
Research development in the pathogenesis of neuropathic diabetic foot ulceration.Curr Diab Rep. 2004 Dec;4(6):419-23. doi: 10.1007/s11892-004-0050-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2004. PMID: 15539005 Review.
-
Autologous platelet-rich plasma for treating chronic wounds.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Oct 17;10:CD006899. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006899.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD006899. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006899.pub3. PMID: 23076929 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Applications in Medical and Aesthetic Dermatology.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021 Nov;14(11):44-57. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34980960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Management of Skin NTDs-Lessons Learned from Existing Practice and Field Research.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018 Nov 14;3(4):120. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed3040120. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30441754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effects of Human Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Healing in a Mouse Pressure Injury Model.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Oct 30;2019:3091619. doi: 10.1155/2019/3091619. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31781237 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on pressure ulcer healing in mouse].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 15;32(6):726-735. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201801031. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29905053 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Reinar LM, Forsetlund L, Bjørndal A, Lockwood D. Interventions for skin changes caused by nerve damage in leprosy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008;3:CD004833. - PubMed
-
- Arshdeep, Kumaran MS. Platelet‐rich plasma in dermatology: boon or a bane? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2014;80:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Conde‐Montero E, Horcajada‐Reales C, Suárez‐Fernández R. Utilidad del plasma rico en plaquetas en el tratamiento de las úlceras crónicas de la piel. Piel 2014;29:248–54.
-
- Villela DL, Santos VL. Evidence on the use of platelet‐rich plasma for diabetic ulcer: a systematic review. Growth Factors 2010;28:111–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

