LRIG and cancer prognosis
- PMID: 25180912
- PMCID: PMC4438349
- DOI: 10.3109/0284186X.2014.953258
LRIG and cancer prognosis
Abstract
Background: Optimal treatment decisions for cancer patients require reliable prognostic and predictive information. However, this information is inadequate in many cases. Several recent studies suggest that the leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains (LRIG) genes, transcripts, and proteins have prognostic implications in various cancer types.
Material and methods: Relevant literature was identified on PubMed using the key words lrig1, lrig2, and lrig3. LRIG mRNA expression in cancer versus normal tissues was investigated using the Oncomine database.
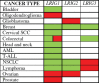
Results: The three human LRIG genes, LRIG1, LRIG2, and LRIG3, encode single-pass transmembrane proteins. LRIG1 is a negative regulator of growth factor signaling that has been shown to function as a tumor suppressor in vitro and in vivo in mice. The functions of LRIG2 and LRIG3 are less well defined. LRIG gene and protein expression are commonly dysregulated in human cancer. In early stage breast cancer, LRIG1 copy number was recently shown to predict early and late relapse in addition to overall survival; in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, loss of LRIG1 is also associated with poor survival. LRIG gene and protein expression have prognostic value in breast cancer, uterine cervical cancer, head-and-neck cancer, glioma, non-small cell lung cancer, prostate cancer, and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. In general, expression of LRIG1 and LRIG3 is associated with good survival, whereas expression of LRIG2 is associated with poor survival. Additionally, LRIG1 regulates cellular sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs, which indicates a possible role as a predictive marker.
Conclusions: LRIG gene statuses and mRNA and protein expression are clinically relevant prognostic indicators in several types of human cancer. We propose that LRIG analyses could become important when making informed and individualized clinical decisions regarding the management of cancer patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LMO7 and LIMCH1 interact with LRIG proteins in lung cancer, with prognostic implications for early-stage disease.Lung Cancer. 2018 Nov;125:174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.09.017. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30429017
-
Expression of LRIG1 and LRIG3 correlates with human papillomavirus status and patient survival in cervical adenocarcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2013 Jan;42(1):247-52. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1702. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23165628
-
LRIG2 in contrast to LRIG1 predicts poor survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix.Acta Oncol. 2010 Aug;49(6):812-5. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2010.492789. Acta Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20553099
-
LRIGs: A Prognostically Significant Family with Emerging Therapeutic Competence against Cancers.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017;17(1):3-16. doi: 10.2174/156800961701161202200445. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 27628597 Review.
-
The LRIG family: enigmatic regulators of growth factor receptor signaling.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(6):R431-43. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0179. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25183430 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The soluble form of pan-RTK inhibitor and tumor suppressor LRIG1 mediates downregulation of AXL through direct protein-protein interaction in glioblastoma.Neurooncol Adv. 2019 Sep 6;1(1):vdz024. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdz024. eCollection 2019 May-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2019. PMID: 32642659 Free PMC article.
-
The Chorion Proteome of Diaphorina citri, the Vector of Huanglongbing Disease in Citrus.Insects. 2021 Oct 21;12(11):959. doi: 10.3390/insects12110959. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34821760 Free PMC article.
-
Lrig2 and Hpse2, mutated in urofacial syndrome, pattern nerves in the urinary bladder.Kidney Int. 2019 May;95(5):1138-1152. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.040. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30885509 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of LRIG proteins as possible prognostic factors in primary vaginal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 25;12(8):e0183816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183816. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28841699 Free PMC article.
-
LRIG3 Suppresses Angiogenesis by Regulating the PI3K/AKT/VEGFA Signaling Pathway in Glioma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:621154. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.621154. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindstrom AK, Ekman K, Stendahl U, Tot T, Henriksson R, Hedman H, et al. LRIG1 and squamous epithelial uterine cervical cancer: Correlation to prognosis, other tumor markers, sex steroid hormones, and smoking. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2008;18:312–7. - PubMed
-
- Hedman H, Lindstrom AK, Tot T, Stendahl U, Henriksson R, Hellberg D. LRIG2 in contrast to LRIG1 predicts poor survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Acta Oncol. 2010;49:812–5. - PubMed
-
- Muller S, Lindquist D, Kanter L, Flores-Staino C, Henriksson R, Hedman H, et al. Expression of LRIG1 and LRIG3 correlates with human papillomavirus status and patient survival in cervical adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:247–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
