Serum level of substance P in patients with lung injuries due to sulfur mustard
- PMID: 25161984
- PMCID: PMC4139982
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.135154
Serum level of substance P in patients with lung injuries due to sulfur mustard
Abstract
Background: Chronic bronchiolitis is the most important problems of chemical victims of mustard gas. Diverse studies suggest that substance P (SP) as a member of tachykinin neuropeptides, has a significant role in the neurogenic inflammation processes of the airways and lungs. We aimed to determine the serum level of SP in chemical victims of mustard gas and compare it with normal subjects.
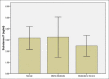
Materials and methods: The chemical victims were divided into the 2 groups of 30:A group with mild to moderate pulmonary symptoms and other group with moderate to severe symptoms and compared with 3(rd) group as healthy controls. After preparing our samples and using the SP kit, final analysis was performed with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader.
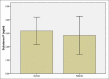
Results: The Concentration of circulatory SP levels in the chemical patients was 2.86 ± 1.47 ng/ml and had not a significant difference with the control group (3.15 ± 1.03 ng/ml) (P > 0.05). The circulatory SP levels were 2.48 ± 0.92 ng/ml and 3.28 ± 1.73 ng/ml in patients with moderate to severe symptoms and mild to moderates (P < 0.05) respectively.
Conclusion: The SP may have a role in pulmonary complications of mustard gas. The lower level of SP in the moderate to severe patients may be due to corticosteroid consumption in such severe cases. However, further studies are needed to clarify the roles and mechanism of SP in this setting.
Keywords: Lung injuries; substance P; sulfur mustard.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of serum level of interleukin-6 in severity of pulmonary complications of sulfur mustard injuries.Iran J Med Sci. 2014 Jul;39(4):382-6. Iran J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25031491 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Health Outcomes Among Survivors Exposed to Sulfur Mustard in Iran.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 1;3(12):e2028894. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.28894. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33301016 Free PMC article.
-
Late respiratory effects of sulfur mustard: how is the early symptoms severity involved?Chron Respir Dis. 2008;5(2):95-100. doi: 10.1177/1479972307087191. Chron Respir Dis. 2008. PMID: 18539723
-
The role of N-acetylcysteine in the management of acute and chronic pulmonary complications of sulfur mustard: a literature review.Inhal Toxicol. 2014 Aug;26(9):507-23. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2014.920439. Inhal Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25055840 Review.
-
Historical perspective on effects and treatment of sulfur mustard injuries.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Dec 5;206(3):512-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23816402 Review.
Cited by
-
Coughing in Small Animal Patients.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Jan 21;6:513. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00513. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32039252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Advenier C, Joos G, Molimard M, Lagente V, Pauwels R. Role of tachykinins as contractile agonists of human airways in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29:579–84. - PubMed
-
- Colten HR, Krause JE. Pulmonary inflammation: A balancing act. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1094–6. - PubMed
-
- Maggi CA. The effects of tachykinins on inflammatory and immune cells. Regul Pept. 1997;70:75–90. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki R, Furuno T, McKay DM, Wolvers D, Teshima R, Nakanishi M, et al. Direct neurite-mast cell communication in vitro occurs via the neuropeptide substance. P. J Immunol. 1999;163:2410–5. - PubMed
-
- Germonpre PR, Bullock GR, Lambrecht BN, Van De Velde V, Luyten WH, Joos GF, et al. Presence of substance P and neurokinin 1 receptors in human sputum macrophages and U-937 cells. Eur Respir J. 1999;14:776–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous