Successful surgical approach for a patient with encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis after hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 25160862
- PMCID: PMC4149037
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2482-14-57
Successful surgical approach for a patient with encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis after hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS) is a rare surgical complication that can occur after intraperitoneal treatment. It is also a serious and potentially fatal complication of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. The present report describes a case of surgically treated EPS that probably occurred as a complication of hyperthermic intraperitonal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
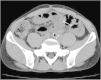
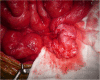
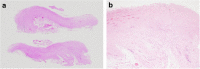
Case presentation: A 39-year-old man required sigmoidectomy for serosal invasive advanced sigmoid colon cancer. HIPEC with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C were given as adjuvant therapy. Subsequently, intestinal obstruction developed at 15 months postoperatively, and the patient was hospitalized. Abdominal computed tomography showed a dilated small intestine enveloped by a thickened membrane. We found no evidence of peritoneal recurrence, but exploratory surgery revealed EPS, probably caused by HIPEC. We peeled the capsule off of the intestine. The patient's postoperative course was uneventful, and sufficient nutritional intake after surgery was noted. Seven months after surgery, he is well with no recurrence.
Conclusion: The surgical treatment via peritonectomy and enterolysis for postoperative EPS appears safe and effective. A diagnosis of EPS should be considered when intestinal obstruction does not show improvement with conservative treatment in patients who have undergone HIPEC, provided the possibility of peritoneal cancer recurrence is excluded.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 28;24(28):3101-3111. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3101. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30065556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effective Remedy for Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis with Ureteroileal Fistula.Perit Dial Int. 2017 Nov-Dec;37(6):648-649. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2017.00074. Perit Dial Int. 2017. PMID: 29123001
-
A Successful Treatment of Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis in an Adolescent Boy on Long-term Peritoneal Dialysis: A Case Report.Prague Med Rep. 2020;121(4):254-261. doi: 10.14712/23362936.2020.22. Prague Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33270013
-
Liver cirrhosis with encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis after 4 years of peritoneal dialysis: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Dec 23;100(51):e28350. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028350. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34941145 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulating Peritoneal Sclerosis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Oct 4;21:e925341. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.925341. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33011732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Severe peritoneal sclerosis after repeated pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy with oxaliplatin (PIPAC OX): report of two cases and literature survey.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018 Mar;35(3):103-108. doi: 10.1007/s10585-018-9895-9. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018. PMID: 29705882 Review.
-
Sclerosing encapsulating peritonitis as a rare cause of intestinal obstruction after the treatment of peritoneal mesothelioma: a case report and review of the literature.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;10(6):3074-3080. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-3259. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116616 Free PMC article.
-
Sclerosing encapsulating peritonitis causing fatal bowel obstruction.BMJ Case Rep. 2023 Nov 3;16(11):e255625. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-255625. BMJ Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37923337
-
Side-effects of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with gastrointestinal cancers.PeerJ. 2023 Apr 28;11:e15277. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15277. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37138820 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 28;24(28):3101-3111. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3101. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30065556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shimizu T, Murata S, Sonoda H, Mekata E, Ohta H, Takebayashi K, Miyake T, Tani T. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy with mitomycin C and 5-fluorouracil in patients at high risk of peritoneal metastasis from colorectal cancer: A preliminary clinical study. Mol Clin Oncol. 2014;2:399–404. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T, Sonoda H, Murata S, Takebayashi K, Ohta H, Miyake T, Mekata E, Shiomi H, Naka S, Tani T. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy using a combination of mitomycin C, 5-fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin in patients at high risk of colorectal peritoneal metastasis: A Phase I clinical study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:521–528. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.12.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takebayashi K, Murata S, Yamamoto H, Ishida M, Yamaguchi T, Kojima M, Shimizu T, Shiomi H, Sonoda H, Naka S, Mekata E, Okabe H, Tani T. Surgery-induced peritoneal cancer cells in patients who have undergone curative gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:1991–1997. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3525-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

