Channel-forming bacterial toxins in biosensing and macromolecule delivery
- PMID: 25153255
- PMCID: PMC4147595
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins6082483
Channel-forming bacterial toxins in biosensing and macromolecule delivery
Abstract
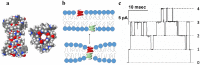
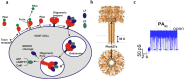
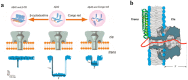
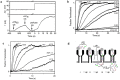
To intoxicate cells, pore-forming bacterial toxins are evolved to allow for the transmembrane traffic of different substrates, ranging from small inorganic ions to cell-specific polypeptides. Recent developments in single-channel electrical recordings, X-ray crystallography, protein engineering, and computational methods have generated a large body of knowledge about the basic principles of channel-mediated molecular transport. These discoveries provide a robust framework for expansion of the described principles and methods toward use of biological nanopores in the growing field of nanobiotechnology. This article, written for a special volume on "Intracellular Traffic and Transport of Bacterial Protein Toxins", reviews the current state of applications of pore-forming bacterial toxins in small- and macromolecule-sensing, targeted cancer therapy, and drug delivery. We discuss the electrophysiological studies that explore molecular details of channel-facilitated protein and polymer transport across cellular membranes using both natural and foreign substrates. The review focuses on the structurally and functionally different bacterial toxins: gramicidin A of Bacillus brevis, α-hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus, and binary toxin of Bacillus anthracis, which have found their "second life" in a variety of developing medical and technological applications.
Figures
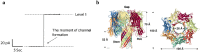



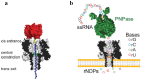
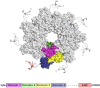
Similar articles
-
Pore-forming activity of clostridial binary toxins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1858(3):512-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26278641 Review.
-
Channel formation by RTX-toxins of pathogenic bacteria: Basis of their biological activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1858(3):526-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.025. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26523409 Review.
-
Clostridial pore-forming toxins: powerful virulence factors.Anaerobe. 2014 Dec;30:220-38. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Anaerobe. 2014. PMID: 24952276 Review.
-
[Therapeutic applications of pore-forming lytic toxins: potential use of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin].Medicina (B Aires). 2002;62(1):66-72. Medicina (B Aires). 2002. PMID: 11965855 Spanish.
-
The pesticidal Cry6Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis is structurally similar to HlyE-family alpha pore-forming toxins.BMC Biol. 2016 Aug 30;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0295-9. BMC Biol. 2016. PMID: 27576487 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Alphatoxin Nanopore Detection of Aflatoxin, Ochratoxin and Fumonisin in Aqueous Solution.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;15(3):183. doi: 10.3390/toxins15030183. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36977074 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin, Naringenin and Catechin: Flavonoids Inhibit Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Hemolysis and Modify Membranes of Bacteria and Erythrocytes.Molecules. 2023 Jan 27;28(3):1252. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031252. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770917 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Inside of Cells with Biologicals: Toxin Routes in a Therapeutic Context.BioDrugs. 2023 Mar;37(2):181-203. doi: 10.1007/s40259-023-00580-y. Epub 2023 Feb 2. BioDrugs. 2023. PMID: 36729328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-hemolysin nanopore allows discrimination of the microcystins variants.RSC Adv. 2019 May 10;9(26):14683-14691. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10384d. eCollection 2019 May 9. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35516306 Free PMC article.
-
A Note of Caution: Gramicidin Affects Signaling Pathways Independently of Its Effects on Plasma Membrane Conductance.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Oct 21;2021:2641068. doi: 10.1155/2021/2641068. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34722759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parker M.W., Feil S.C. Pore-forming protein toxins: From structure to function. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005;88:91–142. - PubMed
-
- Van der Goot G., editor. Pore-Forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag; New York, NY, USA: 2001. p. 168.
-
- Alouf J.E. Pore-forming bacterial protein toxins: An overview. In: Gisou van der Goot F., editor. Pore-Forming Toxins. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; Berlin, Germany: 2001. pp. 1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

