B-cell depletion attenuates serological biomarkers of fibrosis and myofibroblast activation in IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 25143523
- PMCID: PMC4806785
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205799
B-cell depletion attenuates serological biomarkers of fibrosis and myofibroblast activation in IgG4-related disease
Abstract
Objectives: Fibrosis is a predominant feature of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). B-cell depletion induces a prompt clinical and immunological response in patients with IgG4-RD, but the effects of this intervention on fibrosis in IgG4-RD are unknown. We used the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) score to address the impact of rituximab on fibroblast activation. The ELF score is an algorithm based on serum concentrations of procollagen-III aminoterminal propeptide, tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and hyaluronic acid.
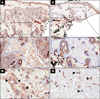
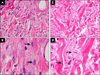
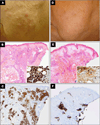
Methods: Ten patients with active, untreated IgG4-RD were enrolled. ELF scores were measured and correlated with the IgG4-RD Responder Index, serum IgG4, circulating plasmablasts and imaging studies. Through immunohistochemical stains for CD3, CD20, IgG4 and α-smooth muscle actin, we assessed the extent of the lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and the degree of fibroblast activation in one patient with tissue biopsies before and after rituximab.
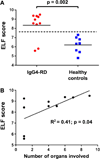
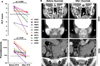
Results: The ELF score was increased in patients with IgG4-RD compared with healthy controls (8.3±1.4 vs 6.2±0.9; p=0.002) and correlated with the number of organs involved (R(2)=0.41; p=0.04). Rituximab induced significant reductions in the ELF score, the number of circulating plasmablasts and the IgG4-RD Responder Index (p<0.05 for all three parameters). Rituximab reduced both the lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and myofibroblast activation. IgG4-RD relapse coincided with recurrent increases in the ELF score, indicating reactivation of collagen deposition.
Conclusions: The ELF score may be a clinically useful indicator of active fibrosis and the extent of disease in IgG4-RD. B-cell depletion has the potential to halt continued collagen deposition by attenuating the secretory phenotype of myofibroblasts in IgG4-RD lesions.
Keywords: B cells; Fibroblasts; Inflammation.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative measurement of 18F-FDG PET/CT uptake reflects the expansion of circulating plasmablasts in IgG4-related disease.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017 Dec 1;56(12):2084-2092. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex234. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 28977663
-
Association of serum levels of fibrosis-related biomarkers with disease activity in patients with IgG4-related disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Dec 14;20(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1777-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30547825 Free PMC article.
-
De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Sep;134(3):679-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.034. Epub 2014 May 6. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24815737 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related disease.Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:315-47. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104708. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24111912 Review.
-
[Histopathology of IgG4-related disease].Z Rheumatol. 2016 Sep;75(7):666-74. doi: 10.1007/s00393-016-0130-2. Z Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27405315 Review. German.
Cited by
-
IgG4-related hepatobiliary disease: an overview.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Oct;13(10):601-12. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.132. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27625195 Review.
-
IL-1RA autoantibodies: insights into mechanisms and associated diseases.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Feb 15;16(2):374-386. doi: 10.62347/NTVU5728. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38463591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the immunosuppressive landscape of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: implications for innovative immunotherapy strategies.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 25;14:1349308. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1349308. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38590651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological mechanism of IgG4-related disease.J Transl Autoimmun. 2020 Mar 19;3:100047. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2020.100047. eCollection 2020. J Transl Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32743528 Free PMC article.
-
A CD8α- Subset of CD4+SLAMF7+ Cytotoxic T Cells Is Expanded in Patients With IgG4-Related Disease and Decreases Following Glucocorticoid Treatment.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Jul;70(7):1133-1143. doi: 10.1002/art.40469. Epub 2018 May 20. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29499100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–551. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1181–1192. - PubMed
-
- Geyer JT, Ferry JA, Harris NL, et al. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner tumor) is an IgG4-associated disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:202–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
