Cdc42 controls the dilation of the exocytotic fusion pore by regulating membrane tension
- PMID: 25143404
- PMCID: PMC4196869
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-07-1229
Cdc42 controls the dilation of the exocytotic fusion pore by regulating membrane tension
Abstract
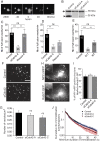
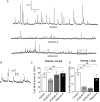
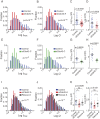
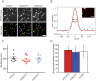
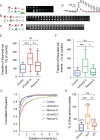
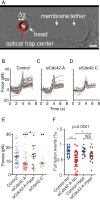
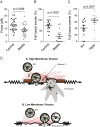
Membrane fusion underlies multiple processes, including exocytosis of hormones and neurotransmitters. Membrane fusion starts with the formation of a narrow fusion pore. Radial expansion of this pore completes the process and allows fast release of secretory compounds, but this step remains poorly understood. Here we show that inhibiting the expression of the small GTPase Cdc42 or preventing its activation with a dominant negative Cdc42 construct in human neuroendocrine cells impaired the release process by compromising fusion pore enlargement. Consequently the mode of vesicle exocytosis was shifted from full-collapse fusion to kiss-and-run. Remarkably, Cdc42-knockdown cells showed reduced membrane tension, and the artificial increase of membrane tension restored fusion pore enlargement. Moreover, inhibiting the motor protein myosin II by blebbistatin decreased membrane tension, as well as fusion pore dilation. We conclude that membrane tension is the driving force for fusion pore dilation and that Cdc42 is a key regulator of this force.
© 2014 Bretou, Jouannot, Fanget, et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures
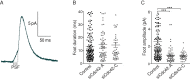
Similar articles
-
Phases of the exocytotic fusion pore.FEBS Lett. 2018 Nov;592(21):3532-3541. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13234. Epub 2018 Oct 1. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 30169901 Review.
-
Two distinct modes of exocytotic fusion pore expansion in large astrocytic vesicles.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16872-16881. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.468231. Epub 2013 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23620588 Free PMC article.
-
Exocytotic fusion pore stability and topological defects in the membrane with orientational degree of ordering.Cell Calcium. 2012 Sep-Oct;52(3-4):277-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.04.001. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22541648
-
Two modes of exocytosis in an artificial cell.Sci Rep. 2014 Jan 24;4:3847. doi: 10.1038/srep03847. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24457949 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic nature of exocytosis from large secretory vesicles. A view from electrochemistry and imaging.Cell Calcium. 2023 Mar;110:102699. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2023.102699. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Cell Calcium. 2023. PMID: 36708611 Review.
Cited by
-
SNARE-Mediated Exocytosis in Neuronal Development.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Aug 7;13:133. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00133. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32848598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fusion Pore Expansion and Contraction during Catecholamine Release from Endocrine Cells.Biophys J. 2020 Jul 7;119(1):219-231. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32562620 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42 Couples T Cell Receptor Endocytosis to GRAF1-Mediated Tubular Invaginations of the Plasma Membrane.Cells. 2019 Nov 4;8(11):1388. doi: 10.3390/cells8111388. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31690048 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane tension and membrane fusion.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015 Aug;33:61-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.07.010. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 26282924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Exocytotic Fusion Pores by SNARE Protein Transmembrane Domains.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Oct 10;10:315. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00315. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29066949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amatore C, Arbault S, Bonifas I, Bouret Y, Erard M, Guille M. Dynamics of full fusion during vesicular exocytotic events: release of adrenaline by chromaffin cells. Chemphyschem. 2003;4:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Amatore C, Arbault S, Bouret Y, Guille M, Lemaitre F, Verchier Y. Regulation of exocytosis in chromaffin cells by trans-insertion of lysophosphatidylcholine and arachidonic acid into the outer leaflet of the cell membrane. Chembiochem. 2006;7:1998–2003. - PubMed
-
- Amatore C, Bouret Y, Travis ER, Wightman RM. Adrenaline release by chromaffin cells: constrained swelling of the vesicle matrix leads to full fusion. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2000;39:1952–1955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

