Preparation and characterization of amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions intended for enhancement of oral bioavailability
- PMID: 25126526
- PMCID: PMC4131384
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-973X.138344
Preparation and characterization of amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions intended for enhancement of oral bioavailability
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to prepare and investigate better and stable amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions for oral bioavailability enhancement.
Materials and methods: Nanosuspensions of ezetimibe were prepared by solvent-antisolvent precipitation technique using the surfactant, Tween 80 as stabilizer. The nanosuspension preparation was optimized for particle size by investigating two factors that is, solvent:antisolvent ratio and surfactant concentration, at three levels. The formulations were characterized for particle size, surface morphology, crystallinity, zeta potential, saturation solubility, in vitro drug release and in vivo drug absorption.
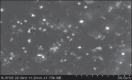
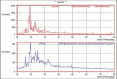
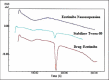
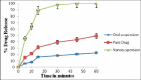
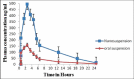
Results: The nanosuspensions of ezetimibe were successfully prepared using solvent-antisolvent precipitation. The two factors solvent:antisolvent ratio and surfactant concentration influenced the particle size of the nanosuspensions prepared. Nanosuspensions were smooth and spherical. The X-ray powdered diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry results indicated that the antisolvent-solvent method led to the amorphization of ezetimibe. Under storage, the amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions demonstrated significant physical stability. Ezetimibe nanosuspensions increased the saturation solubility to an extent of 4-times. Ezetimibe nanosuspensions completely dissolved in the dissolution medium within 1 h, while pure drug was dissolved up to 42% during same time. The Cmax with ezetimibe nanosuspension was approximately 3-fold higher when compared with that of ezetimibe conventional suspensions administered orally.
Conclusions: Stable amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions were successfully prepared and these nanosuspensions demonstrated dramatic improvement in oral bioavailability of the active.
Keywords: Dissolution rate; ezetimibe; nanosuspension; oral bioavailability; solvent-antisolvent precipitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro dissolution and bioavailability study of furosemide nanosuspension prepared using design of experiment (DoE).Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Jan;27(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 30662312 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Characterization of Stable Nanosuspension for Dissolution Rate Enhancement of Furosemide: A Quality by Design (QbD) Approach.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(5):672-685. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180123094320. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29359667
-
Fabrication of carvedilol nanosuspensions through the anti-solvent precipitation-ultrasonication method for the improvement of dissolution rate and oral bioavailability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012 Mar;13(1):295-304. doi: 10.1208/s12249-011-9750-7. Epub 2012 Jan 13. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012. PMID: 22246736 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterization, stability and in vitro-in vivo evaluation of pellet-layered Simvastatin nanosuspensions.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013 Jul;39(7):936-46. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2012.699067. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23046250 Review.
-
Nanosuspensions: Enhancing drug bioavailability through nanonization.Ann Pharm Fr. 2024 Jun 28:S0003-4509(24)00096-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pharma.2024.06.003. Online ahead of print. Ann Pharm Fr. 2024. PMID: 38945393 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Dec 3;11(12):647. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11120647. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31817021 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Strategy in Lipid-Lowering Therapy.Biomedicines. 2022 May 8;10(5):1090. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051090. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Evaluation of Tannic Acid-Coated Nanosuspension for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 13;13(9):1460. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091460. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575537 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Drug Delivery Properties of Risperidone via Preparation of Fast Dissolution Tablet Containing Nanostructured Microparticles.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Spring;20(2):183-196. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.112230.13621. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34567155 Free PMC article.
-
The Nanosuspension Formulations of Daidzein: Preparation and In Vitro Characterization.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022 Feb 28;19(1):84-92. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2021.81905. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35227054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawabata Y, Wada K, Nakatani M, Yamada S, Onoue S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int J Pharm. 2011;420:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Lakshmi PK, Srinivas Ch, Kalpana B. Preparation and comparative evaluation of liquisolid compacts and solid dispersions of valsartan. Stamford J Pharm Sci. 2012;4:47–57.
-
- Fahr A, Liu X. Drug delivery strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2007;4:403–16. - PubMed
-
- Stegemann S, Leveiller F, Franchi D, de Jong H, Lindén H. When poor solubility becomes an issue: From early stage to proof of concept. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;31:249–61. - PubMed
-
- Mauro VF, Tuckerman CE. Ezetimibe for management of hypercholesterolemia. Ann Pharmacother. 2003;37:839–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

