EGFR blockade enriches for lung cancer stem-like cells through Notch3-dependent signaling
- PMID: 25125655
- PMCID: PMC4263272
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3724
EGFR blockade enriches for lung cancer stem-like cells through Notch3-dependent signaling
Abstract
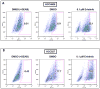
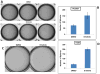
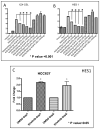
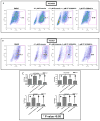
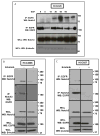
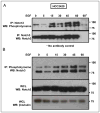
Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are the most common actionable genetic abnormalities yet discovered in lung cancer. However, targeting these mutations with kinase inhibitors is not curative in advanced disease and has yet to demonstrate an impact on potentially curable, early-stage disease, with some data suggesting adverse outcomes. Here, we report that treatment of EGFR-mutated lung cancer cell lines with erlotinib, while showing robust cell death, enriches the ALDH(+) stem-like cells through EGFR-dependent activation of Notch3. In addition, we demonstrate that erlotinib treatment increases the clonogenicity of lung cancer cells in a sphere-forming assay, suggesting increased stem-like cell potential. We demonstrate that inhibition of EGFR kinase activity leads to activation of Notch transcriptional targets in a γ secretase inhibitor-sensitive manner and causes Notch activation, leading to an increase in ALDH high(+) cells. We also find a kinase-dependent physical association between the Notch3 and EGFR receptors and tyrosine phosphorylation of Notch3. This could explain the worsened survival observed in some studies of erlotinib treatment at early-stage disease, and suggests that specific dual targeting might overcome this adverse effect.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stem cell-like ALDH(bright) cellular states in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a novel mechanism of acquired resistance to erlotinib targetable with the natural polyphenol silibinin.Cell Cycle. 2013 Nov 1;12(21):3390-404. doi: 10.4161/cc.26417. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 24047698 Free PMC article.
-
Notch3 cooperates with the EGFR pathway to modulate apoptosis through the induction of bim.Oncogene. 2010 Jan 28;29(4):589-96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.366. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 19881544 Free PMC article.
-
Tyr1068-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) predicts cancer stem cell targeting by erlotinib in preclinical models of wild-type EGFR lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Aug 6;6(8):e1850. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.217. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26247735 Free PMC article.
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity selects for lung adenocarcinoma stem cells dependent on notch signaling.Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 1;70(23):9937-48. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0881. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21118965 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular histology of lung cancer: from targets to treatments.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Apr;41(4):361-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 25825324 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug tolerant persister cell plasticity in cancer: A revolutionary strategy for more effective anticancer therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Aug 14;9(1):209. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01891-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39138145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SOS1 and KSR1 modulate MEK inhibitor responsiveness to target resistant cell populations based on PI3K and KRAS mutation status.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 21;120(47):e2313137120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313137120. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37972068 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of EGFR-TKIs with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy or EGFR-TKIs alone in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation.Biologics. 2018 Nov 30;12:183-190. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S169305. eCollection 2018. Biologics. 2018. PMID: 30555222 Free PMC article.
-
Notch3 Targeting: A Novel Weapon against Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Jan 6;2019:6264931. doi: 10.1155/2019/6264931. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 30723507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Oct 31;17(1):1724-1741. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0585. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 36382054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adeno carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–57. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2380–8. - PubMed
-
- Kelly K, Chansky K, Gaspar LE, Albain KS, Jett J, Ung YC, et al. Phase III trial of maintenance gefitinib or placebo after concurrent chemoradiotherapy and docetaxel consolidation in inoperable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: SWOG S0023. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2450–6. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

