Targeting strategies for delivery of anti-HIV drugs
- PMID: 25119469
- PMCID: PMC7114626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.08.003
Targeting strategies for delivery of anti-HIV drugs
Abstract
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection remains a significant cause of mortality globally. Though antiretroviral therapy has significantly reduced AIDS-related morbidity and mortality, there are several drawbacks in the current therapy, including toxicity, drug-drug interactions, development of drug resistance, necessity for long-term drug therapy, poor bio-availability and lack of access to tissues and reservoirs. To circumvent these problems, recent anti-HIV therapeutic research has focused on improving drug delivery systems through drug delivery targeted specifically to host cells infected with HIV or could potentially get infected with HIV. In this regard, several surface molecules of both viral and host cell origin have been described in recent years, that would enable targeted drug delivery in HIV infection. In the present review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the need for novel drug delivery systems, and the successes and challenges in the identification of novel viral and host-cell molecules for the targeted drug delivery of anti-HIV drugs. Such targeted anti-retroviral drug delivery approaches could pave the way for effective treatment and eradication of HIV from the body.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; Host targets; Targeted drug delivery; Viral targets.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
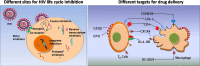
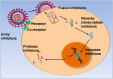
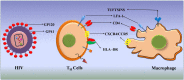


Similar articles
-
Target Molecules and Delivery Vehicles for Anti-HIV Drugs In vitro and In vivo.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(29):3393-3401. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180608124549. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 29886823 Review.
-
Drug delivery systems in HIV pharmacotherapy: what has been done and the challenges standing ahead.J Control Release. 2009 Aug 19;138(1):2-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 May 13. J Control Release. 2009. PMID: 19445981 Review.
-
Targeting anti-HIV drugs to the CNS.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009 Aug;6(8):771-84. doi: 10.1517/17425240903081705. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009. PMID: 19566446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage targeted nanocarrier delivery systems in HIV therapeutics.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Jul;17(7):903-918. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1762565. Epub 2020 May 26. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32347124 Review.
-
Recent developments of nanotherapeutics for targeted and long-acting, combination HIV chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019 May;138:75-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.04.014. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019. PMID: 29678735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmaceutical Approaches to HIV Treatment and Prevention.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2018 Oct;1(6):1800054. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201800054. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2018. PMID: 32775613 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and comparison of CD4-targeting lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles using different binding ligands.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018 May;106(5):1177-1188. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36315. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018. PMID: 29271128 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Brain Reservoirs: Toward an HIV Cure.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 30;7:397. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00397. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27746784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic cell membrane-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for biomedical applications.Bioeng Transl Med. 2022 Nov 2;8(2):e10441. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10441. eCollection 2023 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36925703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-Cell-Mimicking Nanoparticles Can Neutralize HIV Infectivity.Adv Mater. 2018 Nov;30(45):e1802233. doi: 10.1002/adma.201802233. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30252965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piot P., Bartos M., Ghys P.D., Walker N., Schwartländer B. The global impact of HIV/AIDS. Nature. 2001;410:968–973. - PubMed
-
- Carr A., Samaras K., Chisholm D.J., Cooper D.A. Pathogenesis of HIV-1-protease inhibitor-associated peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia, and insulin resistance. Lancet. 1998;351:1881–1883. - PubMed
-
- Gerber J.G. Using pharmacokinetics to optimize antiretroviral drug–drug interactions in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000;30:S123–S129. - PubMed
-
- Eagling V., Wiltshire H., Whitcombe I., Back D. CYP3A4-mediated hepatic metabolism of the HIV-1 protease inhibitor saquinavir in vitro. Xenobiotica. 2002;32:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

