Role of Nrf2/ARE pathway in protective effect of electroacupuncture against endotoxic shock-induced acute lung injury in rabbits
- PMID: 25115759
- PMCID: PMC4130631
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104924
Role of Nrf2/ARE pathway in protective effect of electroacupuncture against endotoxic shock-induced acute lung injury in rabbits
Abstract
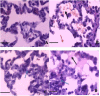
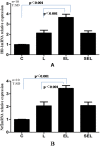
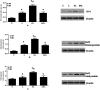
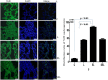
NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a major transcription factor and acts as a key regulator of antioxidant genes to exogenous stimulations. The aim of current study was to determine whether Nrf2/ARE pathway is involved in the protective effect of electroacupuncture on the injured lung in a rabbit model of endotoxic shock. A dose of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) 5 mg/kg was administered intravenously to replicate the model of acute lung injury induced by endotoxic shock. Electroacupuncture pretreatment was handled bilaterally at Zusanli and Feishu acupoints for five consecutive days while sham electroacupuncture punctured at non-acupoints. Fourty anesthetized New England male rabbits were randomized into normal control group (group C), LPS group (group L), electroacupuncture + LPS group (group EL) and sham electroacupuncture + LPS (group SEL). At 6 h after LPS administration, the animals were sacrificed and the blood samples were collected for biochemical measurements. The lungs were removed for calculation of wet-to-dry weight ratios (W/D), histopathologic examination, determination of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 protein and mRNA, Nrf2 total and nucleoprotein, as well as Nrf2 mRNA expression, and evaluation of the intracellular distribution of Nrf2 nucleoprotein. LPS caused extensive morphologic lung damage, which was lessened by electroacupuncture treatment. Besides, lung W/D ratios were significantly decreased, the level of malondialdehyde was inhibited, plasma levels of TNF-α and interleukin-6 were decreased, while the activities of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase were enhanced in the electroacupucnture treated animals. In addition, electroacupuncture stimulation distinctly increased the expressions of HO-1 and Nrf2 protein including Nrf2 total protein and nucleoprotein as well as mRNA in lung tissue, while these effects were blunted in the sham electroacupuncture group. We concluded that electroacupuncture treatment at ST36 and BL13 effectively attenuates lung injury in a rabbit model of endotoxic shock through activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway and following up-regulation of HO-1 expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Acute Renal Injury in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Rabbits via Induction of HO-1 through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 2;10(11):e0141622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141622. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26524181 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ERK1/2 signaling pathway in electro-acupuncture mediated up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 in lungs of rabbits with endotoxic shock.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Aug 16;20:1452-60. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890736. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25139460 Free PMC article.
-
Role of HO-1 in protective effect of electro-acupuncture against endotoxin shock-induced acute lung injury in rabbits.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 Jun;238(6):705-12. doi: 10.1177/1535370213489487. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 23918882
-
Electroacupuncture Attenuates Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Lung Injury Via p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor-2/Heme Oxygenase Pathway.J Surg Res. 2020 Feb;246:170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.08.021. Epub 2019 Oct 4. J Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 31590030
-
Acute renal injury induced by endotoxic shock in rats is alleviated via PI3K/Nrf2 pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Aug;22(16):5394-5401. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201808_15742. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30178867
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Regularizes Gastric Contraction and Reduces Apoptosis of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Diabetic Rats.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;12:560738. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.560738. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33867995 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Mechanisms of Acupuncture for Functional Dyspepsia Based on Pathophysiology.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 25;15:781215. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.781215. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35145373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strawberry Leaf Extract Treatment Alleviates Cognitive Impairment by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Rats With Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Jul 23;12:201. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00201. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32792939 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in pulmonary diseases.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jul 26;13(7):649. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05070-7. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35882850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Roles of Ferroptosis in Pathophysiology and Treatment of Acute Lung Injury.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Sep 14;16:4073-4085. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S420676. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37727372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ghosh S, Latimer RD, Gray BM, Harwood RJ, Oduro A (1993) Endotoxin-induced organ injury. Crit Care Med 21: S19–24. - PubMed
-
- Mikawa K, Maekawa N, Nishina K, Takao Y, Yaku H, et al. (1994) Effect of lidocaine pretreatment on endotoxin-induced lung injury in rabbits. Anesthesiology 81: 689–699. - PubMed
-
- Yu JB, Zhou F, Yao SL, Tang ZH, Wang M, et al. (2009) Effect of heme oxygenase-1 on the kidney during septic shock in rats. Transel Res 153: 283–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

