Extracellular adenosine-mediated modulation of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 25071765
- PMCID: PMC4091046
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00304
Extracellular adenosine-mediated modulation of regulatory T cells
Abstract
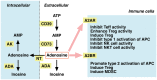
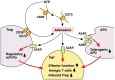
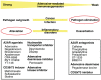
Extracellular adenosine-dependent suppression and redirection of pro-inflammatory activities are mediated by the signaling through adenosine receptors on the surface of most immune cells. The immunosuppression by endogenously-produced adenosine is pathophysiologically significant since inactivation of A2A/A2B adenosine receptor (A2AR/A2BR) and adenosine-producing ecto-enzymes CD39/CD73 results in the higher intensity of immune response and exaggeration of inflammatory damage. Regulatory T cells (Treg) can generate extracellular adenosine, which is implicated in the immunoregulatory activity of Tregs. Interestingly, adenosine has been shown to increase the numbers of Tregs and further promotes their immunoregulatory activity. A2AR-deficiency in Tregs reduces their immunosuppressive efficacy in vivo. Thus, adenosine is not only directly and instantly inhibiting to the immune response through interaction with A2AR/A2BR on the effector cells, but also adenosine signaling can recruit other immunoregulatory mechanisms, including Tregs. Such interaction between adenosine and Tregs suggests the presence of a positive feedback mechanism, which further promotes negative regulation of immune system through the establishment of immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Keywords: A2A-adenosine receptor; A2B-adenosine receptor; adenosine; immunosuppression; regulatory T cell; tumor microenvironment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The development and immunosuppressive functions of CD4(+) CD25(+) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells are under influence of the adenosine-A2A adenosine receptor pathway.Front Immunol. 2012 Jul 5;3:190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00190. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22783261 Free PMC article.
-
CD73 on T Cells Orchestrates Cardiac Wound Healing After Myocardial Infarction by Purinergic Metabolic Reprogramming.Circulation. 2017 Jul 18;136(3):297-313. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023365. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28432149
-
The abnormal function of CD39+ regulatory T cells could be corrected by high-dose dexamethasone in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia.Ann Hematol. 2019 Aug;98(8):1845-1854. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03716-9. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Ann Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31154474
-
CD39/CD73/A2AR pathway and cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Mar 2;22(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01733-x. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36859386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking antitumor immunity with adenosine receptor blockers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 25;6(4):748-767. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.63. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38263981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microgel-Assisted Delivery of Adenosine to Accelerate Fracture Healing.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022 Nov 14;8(11):4863-4872. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00977. Epub 2022 Oct 20. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 36266245 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious Tolerance as Seen With 2020 Vision: The Role of IL-35 and Extracellular Vesicles.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 26;11:1867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01867. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleoside transporters and immunosuppressive adenosine signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Potential therapeutic opportunities.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108300. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108300. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36283452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of CAR T Cell Metabolism for Therapeutic Efficacy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 4;14(21):5442. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215442. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T-Cell-Mediated Suppression of Conventional T-Cells and Dendritic Cells by Different cAMP Intracellular Pathways.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 2;7:216. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00216. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27313580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

