An emerging role for the miR-26 family in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 25066487
- PMCID: PMC4150842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2014.06.003
An emerging role for the miR-26 family in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
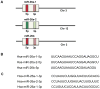
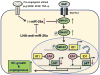
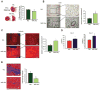
In response to acute myocardial infarction (MI), a complex series of cellular and molecular signaling events orchestrate the myocardial remodeling that ensues weeks to months after injury. Clinical, epidemiological, and pathological studies demonstrate that inadequate or impaired angiogenesis after myocardial injury is often associated with decreased left ventricular (LV) function and clinical outcomes. The microRNA family, miR-26, plays diverse roles in regulating key aspects of cellular growth, development, and activation. Recent evidence supports a central role for the miR-26 family in cardiovascular disease by controlling critical signaling pathways, such as BMP/SMAD1 signaling, and targets relevant to endothelial cell growth, angiogenesis, and LV function post-MI. Emerging studies of the miR-26 family in other cell types including vascular smooth muscle cells, cardiac fibroblasts, and cardiomyocytes suggest that miR-26 may bear important implications for a range of cardiovascular repair mechanisms. This review examines the current knowledge of the miR-26 family's role in key cell types that critically control cardiovascular disease under pathological and physiological stimuli.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of miR-181 family in regulating vascular inflammation and immunity.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014 Apr;24(3):105-12. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014. PMID: 24183793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling.Circ Res. 2013 Nov 8;113(11):1231-41. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301780. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 24047927 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-132 inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and myocardial remodeling in myocardial infarction by targeting IL-1β.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar;235(3):2710-2721. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29175. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31621911
-
Overexpression of microRNA-99a attenuates heart remodelling and improves cardiac performance after myocardial infarction.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 May;18(5):919-28. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12242. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24628978 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-26a inhibits the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells via regulating CDC6 expression.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Feb 15;8(2):1037-46. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27158389 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Based and Selected Cell-Free Therapies for Myocardial Infarction: How Do They Compare to the Current Treatment Options?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10314. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810314. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miR-26a-1, miR-146a and miR-199a-1 are potential candidate biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction.Mol Med. 2019 May 15;25(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s10020-019-0086-1. Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31092195 Free PMC article.
-
miR-26a Limits Muscle Wasting and Cardiac Fibrosis through Exosome-Mediated microRNA Transfer in Chronic Kidney Disease.Theranostics. 2019 Mar 7;9(7):1864-1877. doi: 10.7150/thno.29579. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31037144 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA: A new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2016 Jul;26(5):407-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2016. PMID: 27013138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam O, Lohfelm B, Thum T, et al. Role of miR-21 in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrosis. Basic Res Cardiol. 2012;107:278. - PubMed
-
- Atienza F, Almendral J, Moreno J, et al. Activation of inward rectifier potassium channels accelerates atrial fibrillation in humans: evidence for a reentrant mechanism. Circulation. 2006;114:2434–2442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

