Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases
- PMID: 25056707
- PMCID: PMC5712844
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3775
Non-small-cell lung cancers: a heterogeneous set of diseases
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Apr;15(4):247
Abstract
Non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs), the most common lung cancers, are known to have diverse pathological features. During the past decade, in-depth analyses of lung cancer genomes and signalling pathways have further defined NSCLCs as a group of distinct diseases with genetic and cellular heterogeneity. Consequently, an impressive list of potential therapeutic targets was unveiled, drastically altering the clinical evaluation and treatment of patients. Many targeted therapies have been developed with compelling clinical proofs of concept; however, treatment responses are typically short-lived. Further studies of the tumour microenvironment have uncovered new possible avenues to control this deadly disease, including immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
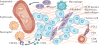
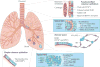
Similar articles
-
The Fire Within: NF-κB Involvement in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 1;80(19):4025-4036. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3578. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32616502 Review.
-
Abandoning the Notion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2019 Jul;25(7):585-594. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 May 30. Trends Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31155338 Review.
-
New Treatment Options in Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancer.Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019 Jan;39:e198-e206. doi: 10.1200/EDBK_237829. Epub 2019 May 17. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019. PMID: 31099625 Review.
-
Redefining Treatment Paradigms in First-line Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 15;25(16):4881-4887. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1894. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30910855 Review.
-
[Carcinogenesis of non small cell lung cancer and therapeutic implications].Tunis Med. 2014 Jun;92(6):368-72. Tunis Med. 2014. PMID: 25741836 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Hsa_circ_0109320 Serves as a Novel Circular RNA Biomarker in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Promoting Metastasis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 5. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01306-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39499388
-
Proline Dehydrogenase (PRODH) Is Expressed in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Modulates Cell Survival and 3D Growth by Inducing Cellular Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 5;25(2):714. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020714. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255788 Free PMC article.
-
NSCLC Driven by DDR2 Mutation Is Sensitive to Dasatinib and JQ1 Combination Therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Oct;14(10):2382-2389. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0077. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26206333 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, cellular effects, and biomarker value of circHIPK3.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 May 11;21(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01956-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33975598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of DNA Methylation with Infant Birth Weight in Women with Gestational Diabetes.Metabolites. 2024 Jun 27;14(7):361. doi: 10.3390/metabo14070361. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39057684 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2013. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013;11:645–653. - PubMed
-
- Langer CJ, Besse B, Gualberto A, Brambilla E, Soria JC. The evolving role of histology in the management of advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:5311–5320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

