Transition-state analysis of 2-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose hydrolysis by human macrodomain 1
- PMID: 25051211
- PMCID: PMC4201351
- DOI: 10.1021/cb500485w
Transition-state analysis of 2-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose hydrolysis by human macrodomain 1
Abstract
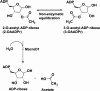
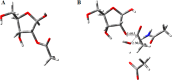
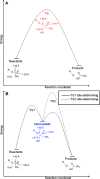
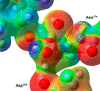
Macrodomains, including the human macrodomain 1 (MacroD1), are erasers of the post-translational modification of monoadenosinediphospho-ribosylation and hydrolytically deacetylate the sirtuin product O-acetyl-ADP-ribose (OAADPr). OAADPr has been reported to play a role in cell signaling based on oocyte microinjection studies, and macrodomains affect an array of cell processes including transcription and response to DNA damage. Here, we investigate human MacroD1 by transition-state (TS) analysis based on kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) from isotopically labeled OAADPr substrates. Competitive radiolabeled-isotope effects and mass spectrometry were used to obtain KIE data to yield intrinsic KIE values. Intrinsic KIEs were matched to a quantum chemical structure of the TS that includes the active site residues Asp184 and Asn174 and a structural water molecule. Transition-state analysis supports a concerted mechanism with an early TS involving simultaneous nucleophilic water attack and leaving group bond cleavage where the breaking C-O ester bond=1.60 Å and the C-O bond to the attacking water nucleophile=2.30 Å. The MacroD1 TS provides mechanistic understanding of the OAADPr esterase chemistry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrolysis of O-acetyl-ADP-ribose isomers by ADP-ribosylhydrolase 3.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21110-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.237636. Epub 2011 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21498885 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the mechanism of Escherichia coli YmdB: A 2'-O-acetyl-ADP-ribose deacetylase.J Struct Biol. 2015 Dec;192(3):478-486. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 19. J Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 26481419
-
Analysis of O-acetyl-ADP-ribose as a target for Nudix ADP-ribose hydrolases.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 6;277(49):47114-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208997200. Epub 2002 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12370179
-
Function and metabolism of sirtuin metabolite O-acetyl-ADP-ribose.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1804(8):1617-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20176146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIR2: the biochemical mechanism of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylation and ADP-ribosyl enzyme intermediates.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Apr;11(7):807-26. doi: 10.2174/0929867043455675. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15078167 Review.
Cited by
-
PARP14 is a writer, reader, and eraser of mono-ADP-ribosylation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105096. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105096. Epub 2023 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37507011 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular toolbox for ADP-ribosyl binding proteins.Cell Rep Methods. 2021 Dec 20;1(8):100121. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100121. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Cell Rep Methods. 2021. PMID: 34786571 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the MacroD1-mediated hydrolysis of ADP-ribosylation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Oct;94:102899. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102899. Epub 2020 Jun 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32683309 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-ribosylation systems in bacteria and viruses.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Apr 17;19:2366-2383. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.023. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of dePARylation in DNA damage repair and cancer suppression.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Apr;76:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 30807923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ladurner A. G. (2003) Inactivating chromosomes: A macro domain that minimizes transcription. Mol. Cell 12, 1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

