A scalable method for biochemical purification of Salmonella flagellin
- PMID: 25050462
- PMCID: PMC4175188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.07.005
A scalable method for biochemical purification of Salmonella flagellin
Abstract
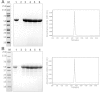
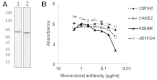
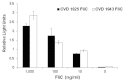
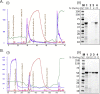
Flagellins are the main structural proteins of bacterial flagella and potent stimulators of innate and adaptive immunity in mammals. The flagellins of Salmonella are virulence factors and protective antigens, and form the basis of promising vaccines. Despite broad interest in flagellins as antigens and adjuvants in vaccine formulations, there have been few advances towards the development of scalable and economical purification methods for these proteins. We report here a simple and robust strategy to purify flagellin monomers from the supernatants of liquid growth culture. Phase 1 flagellins from Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium (i epitope) and Enteritidis (g,m epitopes) were purified directly from conditioned fermentation growth media using sequential cation- and anion-exchange chromatography coupled with a final tangential flow-filtration step. Conventional porous chromatography resin was markedly less efficient than membrane chromatography for flagellin purification. Recovery after each process step was robust, with endotoxin, nucleic acid and residual host-cell protein effectively removed. The final yield was 200-300 mg/L fermentation culture supernatant, with ∼45-50% overall recovery. A final pH 2 treatment step was instituted to ensure uniformity of flagellin in the monomeric form. Flagellins purified by this method were recognized by monoclonal anti-flagellin antibodies and maintained capacity to activate Toll-like Receptor 5. The process described is simple, readily scalable, uses standard bioprocess methods, and requires only a few steps to obtain highly purified material.
Keywords: Flagellin; Purification; Salmonella; Scalable; TLR5; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salmonella flagellin, a microbial target of the innate and adaptive immune system.Immunol Lett. 2005 Nov 15;101(2):117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.05.004. Epub 2005 Jun 6. Immunol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15975666 Review.
-
Injection of flagellin into the host cell cytosol by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 23;282(47):33897-901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700181200. Epub 2007 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17911114
-
Antibodies against Marinobacter algicola and Salmonella typhimurium flagellins do not cross-neutralize TLR5 activation.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048466. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23155384 Free PMC article.
-
Introducing a cost-effective method for purification of bioactive flagellin from several flagellated gram-negative bacteria.Protein Expr Purif. 2019 Mar;155:48-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Protein Expr Purif. 2019. PMID: 30465849
-
Immune responses to epitopes inserted in Salmonella flagellin.Int Rev Immunol. 1994;11(2):167-78. doi: 10.3109/08830189409061724. Int Rev Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7519231 Review.
Cited by
-
Salmonella Typhi Bactericidal Antibodies Reduce Disease Severity but Do Not Protect against Typhoid Fever in a Controlled Human Infection Model.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 17;8:1916. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01916. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29387052 Free PMC article.
-
Two homologous Salmonella serogroup C1-specific genes are required for flagellar motility and cell invasion.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jul 5;22(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07759-z. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34225670 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraminidase 1-mediated desialylation of the mucin 1 ectodomain releases a decoy receptor that protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 11;294(2):662-678. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006022. Epub 2018 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30429216 Free PMC article.
-
Deletions in guaBA and htrA but not clpX or rfaL constitute a live-attenuated vaccine strain of Salmonella Newport to protect against serogroup C2-C3Salmonella in mice.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1427-1435. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1491499. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 29927725 Free PMC article.
-
Simple method for purification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae.Protein Expr Purif. 2016 Mar;119:130-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Protein Expr Purif. 2016. PMID: 26581778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beatson S.A., Minamino T., Pallen M.J. Variation in bacterial flagellins: from sequence to structure. Trends Microbiol. 2006;14:151–155. - PubMed
-
- Yonekura K., Maki-Yonekura S., Namba K. Complete atomic model of the bacterial flagellar filament by electron cryomicroscopy. Nature. 2003;424:643–650. - PubMed
-
- McSorley S.J., Cookson B.T., Jenkins M.K. Characterization of CD4+ T cell responses during natural infection with Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Immunol. 2000;164:986–993. - PubMed
-
- Simon R., Tennant S.M., Wang J.Y., Schmidlein P.J., Lees A., Ernst R.K., Pasetti M.F., Galen J.E., Levine M.M. Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis core O polysaccharide conjugated to H:g, m flagellin as a candidate vaccine for protection against invasive infection with S. Enteritidis. Infect. Immun. 2011;79:4240–4249. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

