Indian hedgehog signaling regulates transcription and expression of collagen type X via Runx2/Smads interactions
- PMID: 25028519
- PMCID: PMC4155658
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570507
Indian hedgehog signaling regulates transcription and expression of collagen type X via Runx2/Smads interactions
Abstract
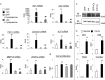
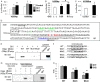
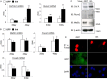
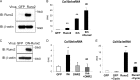
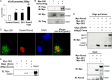
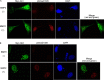
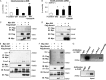
Indian hedgehog (Ihh) is essential for chondrocyte differentiation and endochondral ossification and acts with parathyroid hormone-related peptide in a negative feedback loop to regulate early chondrocyte differentiation and entry to hypertrophic differentiation. Independent of this function, we and others recently reported independent Ihh functions to promote chondrocyte hypertrophy and matrix mineralization in vivo and in vitro. However, the molecular mechanisms for these actions and their functional significance are still unknown. We recently discovered that Ihh overexpression in chondrocytes stimulated the expression of late chondrocyte differentiation markers and induced matrix mineralization. Focusing on collagen type X (Col10α1) expression and transcription, we observed that hedgehog downstream transcription factors GLI-Krüppel family members (Gli) 1/2 increased COL10A1 promoter activity and identified a novel Gli1/2 response element in the 250-bp basic promoter. In addition, we found that Ihh induced Runx2 expression in chondrocytes without up-regulating other modulators of chondrocyte maturation such as Mef2c, Foxa2, and Foxa3. Runx2 promoted Col10α1 expression in cooperation with Ihh. Further analyses using promoter assays, immunofluorescence, and binding assays showed the interaction of Gli1/2 in a complex with Runx2/Smads induces chondrocyte differentiation. Finally, we could demonstrate that Ihh promotes in vitro matrix mineralization using similar molecular mechanisms. Our data provide an in vitro mechanism for Ihh signaling to positively regulate Col10α1 transcription. Thus, Ihh signaling could be an important player for not only early chondrocyte differentiation but maturation and calcification of chondrocytes.
Keywords: Calcification; Chondrocyte; Col10a1; Differentiation; Gli1/Gli2-responsive Element; Hedgehog Signaling Pathway; Maturation; Runx2; Smads; Transcription.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β regulates expression of Indian hedgehog during chondrocytes differentiation.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 8;9(8):e104547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104547. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25105964 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 governs differentiation stage-specific gene expression in growth plate chondrocytes via direct concomitant transactivation and repression.PLoS Genet. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002356. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22072985 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Foxc1 is necessary for Ihh-Gli2-regulated endochondral ossification.Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 26;6:6653. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7653. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25808752
-
Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;149(4):313-323. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1640-6. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29356961 Review.
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
Cited by
-
The PROTAC selectively degrading Bcl-xL represents a novel Hedgehog pathway inhibitor with capacity of combating resistance to Smoothened inhibitors while sparing bone growth.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 24;12(17):7476-7490. doi: 10.7150/thno.75421. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438482 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological mechanism of chondrocytes and the surrounding environment during osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):4902-4911. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16514. Epub 2021 May 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33949768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of terminal hypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation in Prmt5 mutant mice modeling infantile idiopathic scoliosis.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Dec 17;12(12):dmm041251. doi: 10.1242/dmm.041251. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 31848143 Free PMC article.
-
miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 7;12(4):1313. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041313. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835852 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting bivalency de-represses Indian Hedgehog and inhibits self-renewal of colorectal cancer-initiating cells.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 29;10(1):1436. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09309-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30926792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Crombrugghe B., Lefebvre V., Nakashima K. (2001) Regulatory mechanisms in the pathways of cartilage and bone formation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 721–727 - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg H. M. (2003) Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 423, 332–336 - PubMed
-
- Gao B., Guo J., She C., Shu A., Yang M., Tan Z., Yang X., Guo S., Feng G., He L. (2001) Mutations in IHH, encoding Indian hedgehog, cause brachydactyly type A-1. Nat. Genet. 28, 386–388 - PubMed
-
- Lanske B., Karaplis A. C., Lee K., Luz A., Vortkamp A., Pirro A., Karperien M., Defize L. H., Ho C., Mulligan R. C., Abou-Samra A. B., Jüppner H., Segre G. V., Kronenberg H. M. (1996) PTH/PTHrP receptor in early development and Indian hedgehog-regulated bone growth. Science 273, 663–666 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

