Integrins and epithelial cell polarity
- PMID: 24994933
- PMCID: PMC4117227
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.146142
Integrins and epithelial cell polarity
Abstract
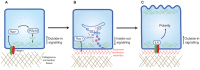
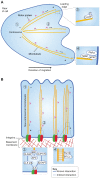
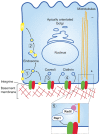
Cell polarity is characterised by differences in structure, composition and function between at least two poles of a cell. In epithelial cells, these spatial differences allow for the formation of defined apical and basal membranes. It has been increasingly recognised that cell-matrix interactions and integrins play an essential role in creating epithelial cell polarity, although key gaps in our knowledge remain. This Commentary will discuss the mounting evidence for the role of integrins in polarising epithelial cells. We build a model in which both inside-out signals to polarise basement membrane assembly at the basal surface, and outside-in signals to control microtubule apical-basal orientation and vesicular trafficking are required for establishing and maintaining the orientation of epithelial cell polarity. Finally, we discuss the relevance of the basal integrin polarity axis to cancer. This article is part of a Minifocus on Establishing polarity.
Keywords: +TIPS; Basement membrane; Breast; Endocytosis; Epithelium; ILK; Integrin; Laminin; Mammary; Microtubule; Polarity.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Comment in
-
ERM proteins at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2014 Aug 1;127(Pt 15):3199-204. doi: 10.1242/jcs.098343. Epub 2014 Jun 20. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24951115 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
An integrin-ILK-microtubule network orients cell polarity and lumen formation in glandular epithelium.Nat Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;15(1):17-27. doi: 10.1038/ncb2646. Nat Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23263281 Free PMC article.
-
ERM proteins at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2014 Aug 1;127(Pt 15):3199-204. doi: 10.1242/jcs.098343. Epub 2014 Jun 20. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24951115 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins contribute to the establishment and maintenance of cell polarity in the follicular epithelium of the Drosophila ovary.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(7):925-32. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072418af. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956322
-
Integrin and microtubule crosstalk in the regulation of cellular processes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Nov;75(22):4177-4185. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2913-x. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30206641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial polarity--generating and integrating signals from the ECM with integrins.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Jun 10;334(2):337-49. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25597426 Review.
Cited by
-
Chapter 22: Structural and signaling functions of integrins.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 May 1;1862(5):183206. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183206. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 31991120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Campylobacter jejuni Triggers Signaling through Host Cell Focal Adhesions To Inhibit Cell Motility.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0149421. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01494-21. Epub 2021 Aug 24. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34425711 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule Motors in Establishment of Epithelial Cell Polarity.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Feb 1;10(2):a027896. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027896. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 28264820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Gastric Cancer: Genetics and Molecular Classification.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:277-304. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_12. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28124158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An integrated in silico-in vitro approach for bioprinting core-shell bioarchitectures.Int J Bioprint. 2023 Jun 12;9(5):771. doi: 10.18063/ijb.771. eCollection 2023. Int J Bioprint. 2023. PMID: 37457929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bañón-Rodríguez I., Gálvez-Santisteban M., Vergarajauregui S., Bosch M., Borreguero-Pascual A., Martín-Belmonte F. (2014). EGFR controls IQGAP1 basolateral membrane localization and mitotic spindle orientation during epithelial morphogenesis. EMBO J. 33, 129–145 10.1002/embj.201385946 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

