ATM regulates NF-κB-dependent immediate-early genes via RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation coupled to CDK9 promoter recruitment
- PMID: 24957606
- PMCID: PMC4117761
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku529
ATM regulates NF-κB-dependent immediate-early genes via RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation coupled to CDK9 promoter recruitment
Abstract
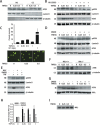
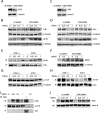
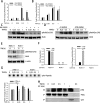
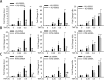
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM), a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-like kinase family, is a master regulator of the double strand DNA break-repair pathway after genotoxic stress. Here, we found ATM serves as an essential regulator of TNF-induced NF-kB pathway. We observed that TNF exposure of cells rapidly induced DNA double strand breaks and activates ATM. TNF-induced ROS promote nuclear IKKγ association with ubiquitin and its complex formation with ATM for nuclear export. Activated cytoplasmic ATM is involved in the selective recruitment of the E3-ubiquitin ligase β-TrCP to phospho-IκBα proteosomal degradation. Importantly, ATM binds and activates the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PKAc), ribosmal S6 kinase that controls RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation. In ATM knockdown cells, TNF-induced RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation is significantly decreased. We further observed decreased binding and recruitment of the transcriptional elongation complex containing cyclin dependent kinase-9 (CDK9; a kinase necessary for triggering transcriptional elongation) to promoters of NF-κB-dependent immediate-early cytokine genes, in ATM knockdown cells. We conclude that ATM is a nuclear damage-response signal modulator of TNF-induced NF-κB activation that plays a key scaffolding role in IκBα degradation and RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation. Our study provides a mechanistic explanation of decreased innate immune response associated with A-T mutation.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RelA Ser276 phosphorylation is required for activation of a subset of NF-kappaB-dependent genes by recruiting cyclin-dependent kinase 9/cyclin T1 complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(11):3623-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01152-07. Epub 2008 Mar 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18362169 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase mediates NF-κB serine 276 phosphorylation and interferon expression via the IRF7-RIG-I amplification loop in paramyxovirus infection.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2628-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02458-14. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25520509 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB/RelA Ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ROS-dependent PKAc pathway.Cell Signal. 2007 Jul;19(7):1419-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.01.020. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17317104
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
-
Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage.Cell Res. 2011 Jan;21(1):116-30. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.179. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21187855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Senescence as a Brake or Accelerator for Oncogenic Transformation and Role in Lymphatic Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2877. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032877. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RMP/URI inhibits both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis through different signaling pathways.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Oct 15;15(12):2692-2706. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.36829. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31754340 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular functions of the protein kinase ATM and their relevance to human disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Dec;22(12):796-814. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00394-2. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34429537 Review.
-
Getting up to speed with transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;16(3):167-77. doi: 10.1038/nrm3953. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25693130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of DNA repair enzyme OGG1 in innate immunity and its significance for lung cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Feb;194:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30240635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayden M.S., Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S., May M.J., Kopp E.B. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001;1:135–145. - PubMed
-
- Brasier A.R. The NF-kappaB regulatory network. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2006;6:111–130. - PubMed
-
- Jamaluddin M., Wang S., Boldogh I., Tian B., Brasier A.R. TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB/RelA Ser(276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by an ROS-dependent PKAc pathway. Cell. Signal. 2007;19:1419–1433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

