Remarkable acceleration of a DNA/RNA inter-strand functionality transfer reaction to modify a cytosine residue: the proximity effect via complexation with a metal cation
- PMID: 24957600
- PMCID: PMC4117767
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku538
Remarkable acceleration of a DNA/RNA inter-strand functionality transfer reaction to modify a cytosine residue: the proximity effect via complexation with a metal cation
Abstract
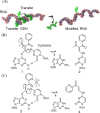
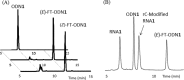
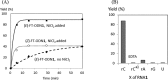
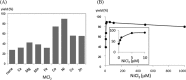
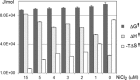
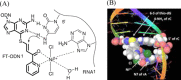
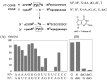
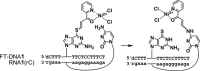
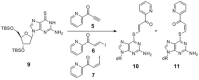
Modified nucleosides in natural RNA molecules are essential for their functions. Non-natural nucleoside analogues have been introduced into RNA to manipulate its structure and function. We have recently developed a new strategy for the in situ modification of RNA based on the functionality transfer reaction between an oligodeoxynucleotide probe and an RNA substrate. 2'-Deoxy-6-thioguanosine (6-thio-dG) was used as the platform to anchor the transfer group. In this study, a pyridinyl vinyl ketone moiety was newly designed as the transfer group with the expectation that a metal cation would form a chelate complex with the pyridinyl-2-keto group. It was demonstrated that the (E)-pyridinyl vinyl keto group was efficiently and specifically transferred to the 4-amino group of the opposing cytosine in RNA in the presence of NiCl2 with more than 200-fold accelerated rate compared with the previous system with the use of the diketo transfer group. Detailed mechanistic studies suggested that NiCl2 forms a bridging complex between the pyridinyl keto moiety and the N7 of the purine residue neighboring the cytosine residue of the RNA substrate to bring the groups in close proximity.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
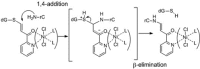
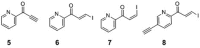

Similar articles
-
Site-specific modification of the 6-amino group of adenosine in RNA by an interstrand functionality-transfer reaction with an s-functionalized 4-thiothymidine.Chembiochem. 2015 May 26;16(8):1199-204. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500084. Epub 2015 May 4. Chembiochem. 2015. PMID: 25940822
-
Oligodeoxynucleotide containing s-functionalized 2'-deoxy-6-thioguanosine: facile tools for base-selective and site-specific internal modification of RNA.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2012 Mar;Chapter 4:Unit 4.49.1-16. doi: 10.1002/0471142700.nc0449s48. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2012. PMID: 22395968
-
A new usage of functionalized oligodeoxynucleotide probe for site-specific modification of a guanine base within RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Mar;38(5):1760-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp930. Epub 2010 Jan 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20123727 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Novel Functional Molecules Targeting DNA and RNA.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019;67(6):505-518. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c19-00169. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 31155555 Review.
-
Oligonucleotide n3'-->p5' phosphoramidates and thio-phoshoramidates as potential therapeutic agents.Chem Biodivers. 2010 Mar;7(3):477-93. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200900187. Chem Biodivers. 2010. PMID: 20232321 Review.
Cited by
-
Directing Quinone Methide-Dependent Alkylation and Cross-Linking of Nucleic Acids with Quaternary Amines.Bioconjug Chem. 2020 May 20;31(5):1486-1496. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00166. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Bioconjug Chem. 2020. PMID: 32298588 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting duplex DNA with the reversible reactivity of quinone methides.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:16009-. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2016.9. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016. PMID: 28458944 Free PMC article.
-
Programmable site-selective labeling of oligonucleotides based on carbene catalysis.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 16;12(1):1681. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21839-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33727561 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

