Impact of a telenursing service on satisfaction and health outcomes of children with inflammatory rheumatic diseases and their families: a crossover randomized trial study protocol
- PMID: 24939642
- PMCID: PMC4067521
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-151
Impact of a telenursing service on satisfaction and health outcomes of children with inflammatory rheumatic diseases and their families: a crossover randomized trial study protocol
Abstract
Background: Pediatric rheumatic diseases have a significant impact on children's quality of life and family functioning. Disease control and management of the symptoms are important to minimize disability and pain. Specialist clinical nurses play a key role in supporting medical teams, recognizing poor disease control and the need for treatment changes, providing a resource to patients on treatment options and access to additional support and advice, and identifying best practices to achieve optimal outcomes for patients and their families. This highlights the importance of investigating follow-up telenursing (TN) consultations with experienced, specialist clinical nurses in rheumatology to provide this support to children and their families.
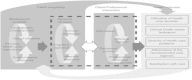
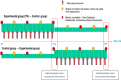
Methods/design: This randomized crossover, experimental longitudinal study will compare the effects of standard care against a novel telenursing consultation on children's and family outcomes. It will examine children below 16 years old, recently diagnosed with inflammatory rheumatic diseases, who attend the pediatric rheumatology outpatient clinic of a tertiary referral hospital in western Switzerland, and one of their parents. The telenursing consultation, at least once a month, by a qualified, experienced, specialist nurse in pediatric rheumatology will consist of providing affective support, health information, and aid to decision-making. Cox's Interaction Model of Client Health Behavior serves as the theoretical framework for this study. The primary outcome measure is satisfaction and this will be assessed using mixed methods (quantitative and qualitative data). Secondary outcome measures include disease activity, quality of life, adherence to treatment, use of the telenursing service, and cost. We plan to enroll 56 children.
Discussion: The telenursing consultation is designed to support parents and children/adolescents during the course of the disease with regular follow-up. This project is novel because it is based on a theoretical standardized intervention, yet it allows for individualized care. We expect this trial to confirm the importance of support by a clinical specialist nurse in improving outcomes for children and adolescents with inflammatory rheumatisms.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrial.gov identifier: NCT01511341 (December 1st, 2012).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of a nurse led telephone intervention on satisfaction and health outcomes of children with inflammatory rheumatic diseases and their families: a crossover randomized clinical trial.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0926-5. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28716081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Structured, intensive education maximising engagement, motivation and long-term change for children and young people with diabetes: a cluster randomised controlled trial with integral process and economic evaluation - the CASCADE study.Health Technol Assess. 2014 Mar;18(20):1-202. doi: 10.3310/hta18200. Health Technol Assess. 2014. PMID: 24690402 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
Virtual outreach: a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of joint teleconferenced medical consultations.Health Technol Assess. 2004 Dec;8(50):1-106, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta8500. Health Technol Assess. 2004. PMID: 15546515 Review.
-
Improving the referral process for familial breast cancer genetic counselling: findings of three randomised controlled trials of two interventions.Health Technol Assess. 2005 Feb;9(3):iii-iv, 1-126. doi: 10.3310/hta9030. Health Technol Assess. 2005. PMID: 15694064 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the impact of nursing clinics in the rheumatology services.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Sep;36(9):1309-17. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3518-z. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27435921
-
Effect of online solution-focused counseling on the sexual quality of life of women with a history of breast cancer: a clinical trial.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Jun 21;23(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02468-z. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37344830 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of a nurse led telephone intervention on satisfaction and health outcomes of children with inflammatory rheumatic diseases and their families: a crossover randomized clinical trial.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Jul 17;17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0926-5. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28716081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Jeanneret C, Saurenmann R, Cannizzaro E, Sauvain M, Bolt I, Bolz D, Kaiser D, Berthet G, Huemer C, Schlam S, Rüdt R, Hofer M. Pediatric Rheumatology in Switzerland: data from the Swiss Pediatric Rheumatology registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(suppl3):306.
-
- Quartier P, Prieur A-M. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. (I). Clinical aspects. Rev Prat. 2007;57(11):1171–1178. - PubMed
-
- Barr T, Carmichael NM, Sandor GKB. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a chronic pediatric musculoskeletal condition with significant orofacial manifestations. J Can Dent Assoc. 2008;74(9):813–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources