HDAC-inhibition counteracts everolimus resistance in renal cell carcinoma in vitro by diminishing cdk2 and cyclin A
- PMID: 24935000
- PMCID: PMC4073177
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-152
HDAC-inhibition counteracts everolimus resistance in renal cell carcinoma in vitro by diminishing cdk2 and cyclin A
Abstract
Background: Targeted therapies have improved therapeutic options of treating renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, drug response is temporary due to resistance development.
Methods: Functional and molecular changes in RCC Caki-1 cells, after acquired resistance to the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-inhibitor everolimus (Cakires), were investigated with and without additional application of the histone deacetylase (HDAC)-inhibitor valproic acid (VPA). Cell growth was evaluated by MTT assay, cell cycle progression and apoptosis by flow cytometry. Target molecules of everolimus and VPA, apoptotic and cell cycle regulating proteins were investigated by western blotting. siRNA blockade was performed to evaluate the functional relevance of the proteins.
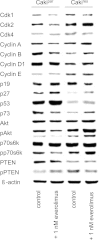
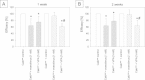
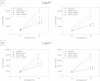
Results: Everolimus resistance was accompanied by significant increases in the percentage of G2/M-phase cells and in the IC50. Akt and p70S6K, targets of everolimus, were activated in Cakires compared to drug sensitive cells. The most prominent change in Cakires cells was an increase in the cell cycle activating proteins cdk2 and cyclin A. Knock-down of cdk2 and cyclin A caused significant growth inhibition in the Cakires cells. The HDAC-inhibitor, VPA, counteracted everolimus resistance in Cakires, evidenced by a significant decrease in tumor growth and cdk2/cyclin A.
Conclusion: It is concluded that non-response to everolimus is characterized by increased cdk2/cyclin A, driving RCC cells into the G2/M-phase. VPA hinders everolimus non-response by diminishing cdk2/cyclin A. Therefore, treatment with HDAC-inhibitors might be an option for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma and acquired everolimus resistance.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resistance after chronic application of the HDAC-inhibitor valproic acid is associated with elevated Akt activation in renal cell carcinoma in vivo.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053100. Epub 2013 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372654 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane as an adjunctive to everolimus counteracts everolimus resistance in renal cancer cell lines.Phytomedicine. 2017 Apr 15;27:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.01.016. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28314474
-
Combining the receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor AEE788 and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor RAD001 strongly inhibits adhesion and growth of renal cell carcinoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2009 May 27;9:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-161. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19473483 Free PMC article.
-
Sunitinib, sorafenib and mTOR inhibitors in renal cancer.J BUON. 2007 Sep;12 Suppl 1:S151-62. J BUON. 2007. PMID: 17935273 Review.
-
Everolimus for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 May;12(7):1143-55. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.571382. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 21470068 Review.
Cited by
-
Valproic acid, an inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases, reverses acquired Erlotinib-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells: a Connectivity Mapping analysis and an experimental study.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 15;5(7):2202-11. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26328250 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane inhibits proliferation and invasive activity of everolimus-resistant kidney cancer cells in vitro.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85208-85219. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13421. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27863441 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder Cancer Metastasis Induced by Chronic Everolimus Application Can Be Counteracted by Sulforaphane In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 4;21(15):5582. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155582. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32759798 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Treatment with Valproic Acid and 5-Aza-2'-Deoxycytidine Synergistically Inhibits Human Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Growth and Migration.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Feb 19;24:1034-1043. doi: 10.12659/msm.906020. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29457966 Free PMC article.
-
RAPTOR up-regulation contributes to resistance of renal cancer cells to PI3K-mTOR inhibition.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 1;13(2):e0191890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191890. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29389967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Urbanowitz G, Berg WJ, Kay A, Lebwohl D, Ravaud A. RECORD-1 Study Group: Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9637):449–456. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61039-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Kay A, Ravaud A. RECORD‒1 Study Group: Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010;116(18):4256–4265. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O'Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ. Global ARCC Trial: Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(22):2271–2281. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa066838. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

