Missense variant in CCDC22 causes X-linked recessive intellectual disability with features of Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome
- PMID: 24916641
- PMCID: PMC4402616
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.109
Missense variant in CCDC22 causes X-linked recessive intellectual disability with features of Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome
Erratum in
-
Missense variant in CCDC22 causes X-linked recessive intellectual disability with features of Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome.Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 May;23(5):720. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2014.278. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25880334 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
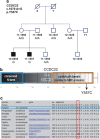
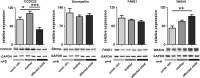
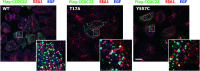
Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome (RSS)/3C (cranio-cerebro-cardiac) syndrome (OMIM#220210) is a rare and clinically heterogeneous developmental disorder characterized by intellectual disability, cerebellar brain malformations, congenital heart defects, and craniofacial abnormalities. A recent study of a Canadian cohort identified homozygous sequence variants in the KIAA0196 gene, which encodes the WASH complex subunit strumpellin, as a cause for a form of RSS/3C syndrome. We have searched for genetic causes of a phenotype similar to RSS/3C syndrome in an Austrian family with two affected sons. To search for disease-causing variants, whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed on samples from two affected male children and their parents. Before WES, CGH array comparative genomic hybridization was applied. Validation of WES and segregation studies was done using routine Sanger sequencing. Exome sequencing detected a missense variant (c.1670A>G; p.(Tyr557Cys)) in exon 15 of the CCDC22 gene, which maps to chromosome Xp11.23. Western blots of immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from the affected individual showed decreased expression of CCDC22 and an increased expression of WASH1 but a normal expression of strumpellin and FAM21 in the patients cells. We identified a variant in CCDC22 gene as the cause of an X-linked phenotype similar to RSS/3C syndrome in the family described here. A hypomorphic variant in CCDC22 was previously reported in association with a familial case of syndromic X-linked intellectual disability, which shows phenotypic overlap with RSS/3C syndrome. Thus, different inactivating variants affecting CCDC22 are associated with a phenotype similar to RSS/3C syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expansion of the CCDC22 associated Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome and review of the literature: Should the minimal diagnostic criteria be revised?Eur J Med Genet. 2021 Jul;64(7):104246. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2021.104246. Epub 2021 May 18. Eur J Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 34020006 Review.
-
Delineating the CCDC22-related Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome phenotype in the original family.Am J Med Genet A. 2022 Nov;188(11):3324-3330. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62963. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Am J Med Genet A. 2022. PMID: 36073196
-
A novel mutation in KIAA0196: identification of a gene involved in Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome in a First Nations cohort.J Med Genet. 2013 Dec;50(12):819-22. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101715. Epub 2013 Sep 24. J Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 24065355
-
Biallelic VPS35L pathogenic variants cause 3C/Ritscher-Schinzel-like syndrome through dysfunction of retriever complex.J Med Genet. 2020 Apr;57(4):245-253. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106213. Epub 2019 Nov 11. J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 31712251
-
Subtelomeric deletions of chromosome 6p: molecular and cytogenetic characterization of three new cases with phenotypic overlap with Ritscher-Schinzel (3C) syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2005 Apr 1;134A(1):3-11. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30573. Am J Med Genet A. 2005. PMID: 15704124 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Organization of the Retriever-CCC Endosomal Recycling Complex.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 16:rs.3.rs-3026818. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3026818/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jun;31(6):910-924. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01184-4 PMID: 37397996 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes.Nature. 2015 Sep 17;525(7569):339-44. doi: 10.1038/nature14877. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26344197 Free PMC article.
-
X-chromosome association studies of congenital heart defects.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Jan;182(1):250-254. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61411. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 31729158 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Missense variants in DPYSL5 cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with corpus callosum agenesis and cerebellar abnormalities.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 May 6;108(5):951-961. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.004. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33894126 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal Microarray Analysis as First-Tier Genetic Test for Schizophrenia.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 1;12:620496. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.620496. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34659328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonardi ML, Pai GS, Wilkes B, Lebel RR. Ritscher-Schinzel cranio-cerebello-cardiac (3C) syndrome: report of four new cases and review. Am J Med Genet. 2001;102:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Elliott AM, Simard LR, Coghlan G, et al. A novel variant in KIAA0196: identification of a gene involved in Ritscher-Schinzel/3C syndrome in a First Nations cohort. J Med Genet. 2013;50:819–822. - PubMed
-
- Craft E, Wildig CE, Crow YJ. 3C syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:1026–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

