In vivo crystallography at X-ray free-electron lasers: the next generation of structural biology?
- PMID: 24914164
- PMCID: PMC4052873
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0497
In vivo crystallography at X-ray free-electron lasers: the next generation of structural biology?
Abstract
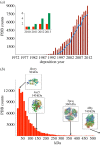
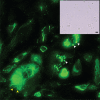
The serendipitous discovery of the spontaneous growth of protein crystals inside cells has opened the field of crystallography to chemically unmodified samples directly available from their natural environment. On the one hand, through in vivo crystallography, protocols for protein crystal preparation can be highly simplified, although the technique suffers from difficulties in sampling, particularly in the extraction of the crystals from the cells partly due to their small sizes. On the other hand, the extremely intense X-ray pulses emerging from X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) sources, along with the appearance of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) is a milestone for radiation damage-free protein structural studies but requires micrometre-size crystals. The combination of SFX with in vivo crystallography has the potential to boost the applicability of these techniques, eventually bringing the field to the point where in vitro sample manipulations will no longer be required, and direct imaging of the crystals from within the cells will be achievable. To fully appreciate the diverse aspects of sample characterization, handling and analysis, SFX experiments at the Japanese SPring-8 angstrom compact free-electron laser were scheduled on various types of in vivo grown crystals. The first experiments have demonstrated the feasibility of the approach and suggest that future in vivo crystallography applications at XFELs will be another alternative to nano-crystallography.
Keywords: X-ray free-electron laser; in vivo crystallography; serial femtosecond crystallography.
© 2014 The Author(s) Published by the Royal Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic Structural Biology Experiments at XFEL or Synchrotron Sources.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2305:203-228. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1406-8_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33950392 Review.
-
[What Kind of Measurements Can Be Made with an X-ray Free Electron Laser at SACLA?].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(5):479-485. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00203-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35491153 Review. Japanese.
-
Liquid sample delivery techniques for serial femtosecond crystallography.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;369(1647):20130337. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0337. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24914163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microcrystallization techniques for serial femtosecond crystallography using photosystem II from Thermosynechococcus elongatus as a model system.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;369(1647):20130316. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0316. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24914149 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Biological Samples Using Ultra-Short and Ultra-Bright XFEL Pulses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;3234:141-162. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-52193-5_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38507205
Cited by
-
Serial femtosecond crystallography: A revolution in structural biology.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Jul 15;602:32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.036. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27143509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for sample delivery for femtosecond crystallography.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019 Feb 1;75(Pt 2):160-177. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318017953. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 30821705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can (We Make) Bacillus thuringiensis Crystallize More Than Its Toxins?Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 26;13(7):441. doi: 10.3390/toxins13070441. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time investigation of dynamic protein crystallization in living cells.Struct Dyn. 2015 May 22;2(4):041712. doi: 10.1063/1.4921591. eCollection 2015 Jul. Struct Dyn. 2015. PMID: 26798811 Free PMC article.
-
Microcrystallography of Protein Crystals and In Cellulo Diffraction.J Vis Exp. 2017 Jul 21;(125):55793. doi: 10.3791/55793. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28784967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

