Multilevel examination of the association of urbanization with inflammation in Chinese adults
- PMID: 24908386
- PMCID: PMC4091901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2014.05.003
Multilevel examination of the association of urbanization with inflammation in Chinese adults
Abstract
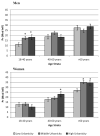
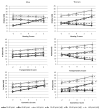
We examine the associations between overall urbanicity and specific physical and social components of community-level urbanization with C-reactive protein (CRP) in adults participating in the China Health and Nutrition Study. Higher overall urbanicity and environment-related urbanicity component scores, including education, housing quality, and access to markets, were associated with elevated CRP in multilevel models controlling for clustering by community. These associations differed by age and gender and persisted after controlling for individual-level anthropometric, diet, and pathogenic risk factors. These results highlight the importance of place in relation to inflammation across the spectrum of rural and urban environments.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; China; Inflammation; Neighborhood health; Urbanization.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of urbanization on metabolic syndrome via dietary intake and physical activity in Chinese adults: Multilevel mediation analysis with latent centering.Soc Sci Med. 2019 Aug;234:112372. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112372. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Soc Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 31254966
-
Differential associations of urbanicity and income with physical activity in adults in urbanizing China: findings from the population-based China Health and Nutrition Survey 1991-2009.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015 Dec 12;12:152. doi: 10.1186/s12966-015-0321-2. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015. PMID: 26653097 Free PMC article.
-
The association between urbanization and child height: a multilevel study in China.BMC Public Health. 2019 May 14;19(1):569. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6921-z. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31088440 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between urbanization and depression in China: the mediating role of neighborhood social capital.Int J Equity Health. 2018 Jul 24;17(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12939-018-0825-x. Int J Equity Health. 2018. PMID: 30041631 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal Variation of the Association between Urbanicity and Incident Hypertension among Chinese Adults.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 1;17(1):304. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010304. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31906366 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Educational inequalities, urbanicity and levels of non-communicable diseases risk factors: evaluating trends in Argentina (2005-2013).BMC Public Health. 2021 Aug 20;21(1):1572. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11617-8. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34416876 Free PMC article.
-
Urbanization and health: The effects of the built environment on chronic disease risk factors among women in Tanzania.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 3;15(11):e0241810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241810. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33141863 Free PMC article.
-
Multilevel socioeconomic differentials in allostatic load among Chinese adults.Health Place. 2018 Sep;53:182-192. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Health Place. 2018. PMID: 30172822 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the reasons for women to engage in sex work in Tehran, Iran: A qualitative study.Heliyon. 2021 Nov 29;7(12):e08512. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08512. eCollection 2021 Dec. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34926855 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition Transition with Accelerating Urbanization? Empirical Evidence from Rural China.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 12;13(3):921. doi: 10.3390/nu13030921. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33809126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, O'Brien WL, Bassett DR, Jr., Schmitz KH, Emplaincourt PO, Jacobs DR, Jr., Leon AS. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Medicine and science in sports and exercise. 2000;32:S498–504. - PubMed
-
- Alberti K, Zimmet P, Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome, A new worldwide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabetic Medicine. 2006;23:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Browning CR, Cagney KA, Iveniuk J. Neighborhood stressors and cardiovascular health: Crime and C-reactive protein in Dallas, USA. Social Science & Medicine. 2012;75:1271–1279. - PubMed
-
- Cagney KA, Cornwell EY. Neighborhoods and Health in Later Life: The Intersection of Biology and Community. Annual Review of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2010;30:323–348.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HD38700/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD038700/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R24HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD030880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K01HD071948-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5R24HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD30880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL108427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HD071948/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HD007168/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007168/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

