Tumor-associated neutrophils as a new prognostic factor in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24906014
- PMCID: PMC4048155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098259
Tumor-associated neutrophils as a new prognostic factor in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN) have been reported in a variety of malignancies. We conducted an up-to-date meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic role of TAN in cancer.
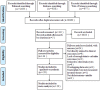
Method: Pubmed, Embase and web of science databases were searched for studies published up to April 2013. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. The impact of neutrophils localization and primary antibody were also assessed.
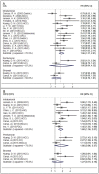
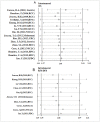
Results: A total of 3946 patients with various solid tumors from 20 studies were included. High density of intratumoral neutrophils were independently associated with unfavorable survival; the pooled HRs were 1.68 (95%CI: 1.36-2.07, I2 = 55.8%, p<0.001) for recurrence-free survival (RFS)/disease-free survival (DFS), 3.36 (95%CI: 2.08-5.42, I2 = 0%, p<0.001) for cancer-specific survival (CSS) and 1.66 (95%CI: 1.37-2.01, I2 = 70.5%, p<0.001) for overall survival (OS). Peritumoral and stromal neutrophils were not statistically significantly associated with survival. When grouped by primary antibody, the pooled HRs were 1.80 (95%CI: 1.47-2.22, I2 = 67.7%, p<0.001) for CD66b, and 1.44 (95%CI: 0.90-2.30, I2 = 45.9%, p = 0.125) for CD15, suggesting that CD66b positive TAN might have a better prognostic value than CD15.
Conclusion: High levels of intratumoral neutrophils are associated with unfavorable recurrence-free, cancer-specific and overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumour-associated CD66b+ neutrophil count is an independent prognostic factor for recurrence in localised cervical cancer.Br J Cancer. 2013 May 28;108(10):2116-22. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.167. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23591202 Free PMC article.
-
High myeloperoxidase positive cell infiltration in colorectal cancer is an independent favorable prognostic factor.PLoS One. 2013 May 29;8(5):e64814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064814. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23734221 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral neutrophils: a poor prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma following resection.J Hepatol. 2011 Mar;54(3):497-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.044. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21112656
-
Prognostic role of Twist or Snail in various carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2014 Nov;44(11):1072-94. doi: 10.1111/eci.12343. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 25257753 Review.
-
Prognostic role of elevated preoperative systemic inflammatory markers in localized soft tissue sarcoma.Cancer Biomark. 2016;16(3):333-42. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160571. Cancer Biomark. 2016. PMID: 26835589 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating secretory organelles and endosomes in neutrophils and their implications for inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2016 Sep;273(1):249-65. doi: 10.1111/imr.12452. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27558339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of TGFβ1 Activity in Cancer and Its Influence on the Quality of Anti-Tumor Immunity.J Clin Med. 2016 Aug 31;5(9):76. doi: 10.3390/jcm5090076. J Clin Med. 2016. PMID: 27589814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Drive Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Tumors to Augment Growth.Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 1;79(21):5626-5639. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0800. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31519688 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 and Endometrial Cancer Development: Insights from a Mouse Model.Cells. 2022 Mar 7;11(5):909. doi: 10.3390/cells11050909. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269532 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic Transformation of Immune Cell Metabolism Within the Microenvironment of Oral Cancers.Front Oral Health. 2020 Dec 16;1:585710. doi: 10.3389/froh.2020.585710. eCollection 2020. Front Oral Health. 2020. PMID: 35047983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144: 646–674. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454: 436–444. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21: 309–322. - PubMed
-
- Galdiero MR, Bonavita E, Barajon I, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, et al. (2013) Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology 218: 1402–1410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

