BU08073 a buprenorphine analogue with partial agonist activity at μ-receptors in vitro but long-lasting opioid antagonist activity in vivo in mice
- PMID: 24903063
- PMCID: PMC4292977
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12796
BU08073 a buprenorphine analogue with partial agonist activity at μ-receptors in vitro but long-lasting opioid antagonist activity in vivo in mice
Abstract
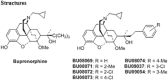
Background and purpose: Buprenorphine is a potent analgesic with high affinity at μ, δ and κ and moderate affinity at nociceptin opioid (NOP) receptors. Nevertheless, NOP receptor activation modulates the in vivo activity of buprenorphine. Structure activity studies were conducted to design buprenorphine analogues with high affinity at each of these receptors and to characterize them in in vitro and in vivo assays.
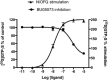
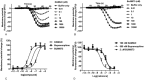
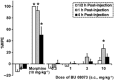
Experimental approach: Compounds were tested for binding affinity and functional activity using [(35) S]GTPγS binding at each receptor and a whole-cell fluorescent assay at μ receptors. BU08073 was evaluated for antinociceptive agonist and antagonist activity and for its effects on anxiety in mice.
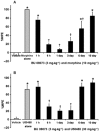
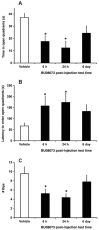
Key results: BU08073 bound with high affinity to all opioid receptors. It had virtually no efficacy at δ, κ and NOP receptors, whereas at μ receptors, BU08073 has similar efficacy as buprenorphine in both functional assays. Alone, BU08073 has anxiogenic activity and produces very little antinociception. However, BU08073 blocks morphine and U50,488-mediated antinociception. This blockade was not evident at 1 h post-treatment, but is present at 6 h and remains for up to 3-6 days.
Conclusions and implications: These studies provide structural requirements for synthesis of 'universal' opioid ligands. BU08073 had high affinity for all the opioid receptors, with moderate efficacy at μ receptors and reduced efficacy at NOP receptors, a profile suggesting potential analgesic activity. However, in vivo, BU08073 had long-lasting antagonist activity, indicating that its pharmacokinetics determined both the time course of its effects and what receptor-mediated effects were observed.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Opioids: New Pathways to Functional Selectivity. To view the other articles in this section visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.2015.172.issue-2.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor activation attenuates antinociception induced by mixed nociceptin/orphanin FQ/mu-opioid receptor agonists.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Dec;331(3):946-53. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.156711. Epub 2009 Aug 27. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19713488 Free PMC article.
-
The first universal opioid ligand, (2S)-2-[(5R,6R,7R,14S)-N-cyclopropylmethyl-4,5-epoxy-6,14-ethano-3-hydroxy-6-methoxymorphinan-7-yl]-3,3-dimethylpentan-2-ol (BU08028): characterization of the in vitro profile and in vivo behavioral effects in mouse models of acute pain and cocaine-induced reward.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Mar;336(3):952-61. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.175620. Epub 2010 Dec 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21177476 Free PMC article.
-
Activities of mixed NOP and mu-opioid receptor ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Feb;153(3):609-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707598. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18059322 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid ligands having delayed long-term antagonist activity: potential pharmacotherapies for opioid abuse.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003 Mar;3(2):137-44. doi: 10.2174/1389557033405395. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12570846 Review.
-
Buprenorphine: an analgesic with an expanding role in the treatment of opioid addiction.CNS Drug Rev. 2002 Winter;8(4):377-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00235.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2002. PMID: 12481193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treating Chronic Pain: An Overview of Clinical Studies Centered on the Buprenorphine Option.Drugs. 2018 Aug;78(12):1211-1228. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0953-z. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30051169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperactivity in Mice Induced by Opioid Agonists with Partial Intrinsic Efficacy and Biased Agonism Administered Alone and in Combination with Morphine.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 2;13(6):935. doi: 10.3390/biom13060935. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371516 Free PMC article.
-
The NOP Receptor System in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders: Discrepancies, Peculiarities and Clinical Progress in Developing Targeted Therapies.CNS Drugs. 2021 Jun;35(6):591-607. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00821-0. Epub 2021 May 31. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34057709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opioid Overdose Deaths with Buprenorphine Detected in Postmortem Toxicology: a Retrospective Analysis.J Med Toxicol. 2021 Jan;17(1):10-15. doi: 10.1007/s13181-020-00795-3. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Med Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32648229 Free PMC article.
-
Buprenorphine: Far Beyond the "Ceiling".Biomolecules. 2021 May 31;11(6):816. doi: 10.3390/biom11060816. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34072706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anseloni VC, Coimbra NC, Morato S, Brandao ML. A comparative study of the effects of morphine in the dorsal periaqueductal gray and nucleus accumbens of rats submitted to the elevated plus-maze test. Exp Brain Res. 1999;129:260–268. - PubMed
-
- Bloms-Funke P, Gillen C, Schuettler AJ, Wnendt S. Agonistic effects of the opioid buprenorphine on the nociceptin/OFQ receptor. Peptides. 2000;21:1141–1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

