miR-125b controls apoptosis and temozolomide resistance by targeting TNFAIP3 and NKIRAS2 in glioblastomas
- PMID: 24901050
- PMCID: PMC4611719
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.245
miR-125b controls apoptosis and temozolomide resistance by targeting TNFAIP3 and NKIRAS2 in glioblastomas
Abstract
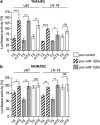
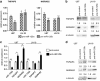
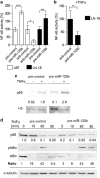
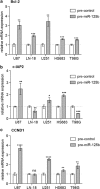
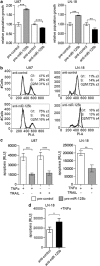
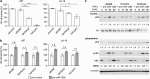
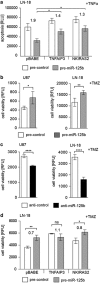
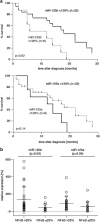
Diffusely infiltrating gliomas are among the most prognostically discouraging neoplasia in human. Temozolomide (TMZ) in combination with radiotherapy is currently used for the treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) patients, but less than half of the patients respond to therapy and chemoresistance develops rapidly. Epigenetic silencing of the O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) has been associated with longer survival in GBM patients treated with TMZ, but nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-mediated survival signaling and TP53 mutations contribute significantly to TMZ resistance. Enhanced NF-κB is in part owing to downregulation of negative regulators of NF-κB activity, including Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) and NF-κB inhibitor interacting RAS-like 2 (NKIRAS2). Here we provide a novel mechanism independent of TP53 and MGMT by which oncogenic miR-125b confers TMZ resistance by targeting TNFAIP3 and NKIRAS2. GBM cells overexpressing miR-125b showed increased NF-κB activity and upregulation of anti-apoptotic and cell cycle genes. This was significantly associated with resistance of GBM cells to TNFα- and TNF-related inducing ligand-induced apoptosis as well as resistance to TMZ. Conversely, overexpression of anti-miR-125b resulted in cell cycle arrest, increased apoptosis and increased sensitivity to TMZ, indicating that endogenous miR-125b is sufficient to control these processes. GBM cells overexpressing TNFAIP3 and NKIRAS2 were refractory to miR-125b-induced apoptosis resistance as well as TMZ resistance, indicating that both genes are relevant targets of miR-125b. In GBM tissues, high miR-125b expression was significantly correlated with nuclear NF-κB confirming that miR-125b is implicated in NF-κB signaling. Most remarkably, miR-125b overexpression was clearly associated with shorter overall survival of patients treated with TMZ, suggesting that this microRNA is an important predictor of response to therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-125b-2 confers human glioblastoma stem cells resistance to temozolomide through the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 2012 Jan;40(1):119-29. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1179. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21879257
-
Sulforaphane enhances temozolomide-induced apoptosis because of down-regulation of miR-21 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in glioblastoma.J Neurochem. 2015 Sep;134(5):811-8. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13174. Epub 2015 Jun 11. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25991372
-
Resveratrol reverses temozolomide resistance by downregulation of MGMT in T98G glioblastoma cells by the NF-κB-dependent pathway.Oncol Rep. 2012 Jun;27(6):2050-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1715. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22426504
-
MicroRNAs as the pivotal regulators of Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma.Mol Brain. 2024 Jul 2;17(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01113-6. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 38956588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Recent Research Progress of NF-κB Signaling on the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Immune Escape and Drug Resistance of Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10337. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210337. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Functions of non-coding RNAs in the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament-derived cells].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Jun 1;38(3):330-337. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2020.03.018. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32573144 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
MiR-21, miR-34a, miR-125b, miR-181d and miR-648 levels inversely correlate with MGMT and TP53 expression in primary glioblastoma patients.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Mar;15(2):504-512. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2017.69374. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30899304 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of the p53-Related miR-34c, -125b, and -203 in the Osteoblastic Differentiation and the Malignant Transformation of Bone Sarcomas.Cells. 2020 Mar 27;9(4):810. doi: 10.3390/cells9040810. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32230926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory feedback control of NF-κB signalling in health and disease.Biochem J. 2021 Jul 16;478(13):2619-2664. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210139. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 34269817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum miR-125b is a non-invasive predictive biomarker of the pre-operative chemoradiotherapy responsiveness in patients with rectal adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28647-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8725. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27081702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2Mitchell PP, Ellison DWD. Mendelow ADA. Surgery for malignant gliomas: mechanistic reasoning and slippery statistics. Lancet Neurol 2005; 4: 10–10. - PubMed
-
- 3Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 459–466. - PubMed
-
- 4Esteller M, Garcia-Foncillas J, Andion E, Goodman SN, Hidalgo OF, Vanaclocha V et al. Inactivation of the DNA-repair gene MGMT and the clinical response of gliomas to alkylating agents. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- 5Hegi ME, Diserens A-C, Gorlia T, Hamou M-F, de Tribolet N, Weller M et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 997–1003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

