AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer
- PMID: 24893891
- PMCID: PMC4315625
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0337
AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer
Abstract
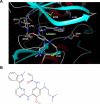
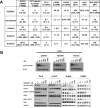
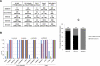
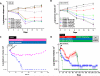
First-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKI) provide significant clinical benefit in patients with advanced EGFR-mutant (EGFRm(+)) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Patients ultimately develop disease progression, often driven by acquisition of a second T790M EGFR TKI resistance mutation. AZD9291 is a novel oral, potent, and selective third-generation irreversible inhibitor of both EGFRm(+) sensitizing and T790M resistance mutants that spares wild-type EGFR. This mono-anilino-pyrimidine compound is structurally distinct from other third-generation EGFR TKIs and offers a pharmacologically differentiated profile from earlier generation EGFR TKIs. Preclinically, the drug potently inhibits signaling pathways and cellular growth in both EGFRm(+) and EGFRm(+)/T790M(+) mutant cell lines in vitro, with lower activity against wild-type EGFR lines, translating into profound and sustained tumor regression in EGFR-mutant tumor xenograft and transgenic models. The treatment of 2 patients with advanced EGFRm(+) T790M(+) NSCLC is described as proof of principle.
Significance: We report the development of a novel structurally distinct third-generation EGFR TKI, AZD9291, that irreversibly and selectively targets both sensitizing and resistant T790M(+) mutant EGFR while harboring less activity toward wild-type EGFR. AZD9291 is showing promising responses in a phase I trial even at the first-dose level, with first published clinical proof-of-principle validation being presented.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
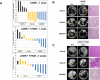
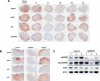
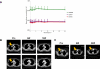
Similar articles
-
AZD9291 in EGFR-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients.Future Oncol. 2015 Nov;11(22):3069-81. doi: 10.2217/fon.15.250. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26450446 Review.
-
YH25448, an Irreversible EGFR-TKI with Potent Intracranial Activity in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 15;25(8):2575-2587. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2906. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30670498
-
Met gene amplification and protein hyperactivation is a mechanism of resistance to both first and third generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer treatment.Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 1;380(2):494-504. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.021. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27450722
-
Preclinical Comparison of Osimertinib with Other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastases Models, and Early Evidence of Clinical Brain Metastases Activity.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 15;22(20):5130-5140. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0399. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27435396
-
[3rd generation's TKI in lung cancer non-small cell EGFR-mutated having acquired a secondary T790M resistance].Bull Cancer. 2015 Sep;102(9):749-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Bull Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26235419 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Analysis of metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(3):206. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2925. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708833 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EGFR in lung cancer: Lessons learned and future perspectives.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Nov;45:67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 27. Mol Aspects Med. 2015. PMID: 26022942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in the Global Proteome and Phosphoproteome in Third Generation EGFR TKI Resistance Reveal Drug Targets to Circumvent Resistance.Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 1;81(11):3051-3066. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2435. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33727228 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of osimertinib in treating nonsmall cell lung cancer: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 21;99(34):e21826. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021826. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32846826 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma RNA profiling unveils transcriptional signatures associated with resistance to osimertinib in EGFR T790M positive non-small cell lung cancer patients.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):2064-2078. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-236. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36386450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker AJ, Gibson KH, Grundy W, Godfrey AA, Barlow JJ, Healy MP, et al. Studies leading to the identification of ZD1839 (IRESSA): an orally active, selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeted to the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001;11:1911–4. - PubMed
-
- Moyer JD, Barbacci EG, Iwata KK, Arnold L, Boman B, Cunningham A, et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Research. 1997;57:4838–48. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:13306–11. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

