Induction of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 activation-mediated C6 glioma cell invasion after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy
- PMID: 24884636
- PMCID: PMC4049398
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-148
Induction of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 activation-mediated C6 glioma cell invasion after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy
Abstract
Background: Anti-angiogenic therapy inhibits tumor growth and is considered as a potential clinical therapy for malignant glioma. However, inevitable recurrences and unexpected tumor resistance, particularly increased invasion ability of glioma cell, were observed after anti-angiogenic treatment. The underlying mechanism remains undetermined. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) are closely associated with cell migration; therefore, we investigated the possible role of these kinases in rat C6 glioma cell invasion induced by bevacizumab, a recombinant monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
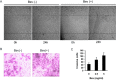
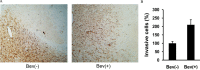
Methods: The effects of bevacizumab on migration and invasion of C6 glioma cells were investigated in vitro and in vivo. The cells proliferation, migration, and invasion were determined by MTT assay, wound healing, and transwell assay, respectively. Invasive potential of glioma cells in vivo was assessed by counting vimentin-positive cells crossing the solid tumor rim by immunohistochemical staining. The total and phosphorylated protein levels of FAK and Pyk2 were detected by Western blotting.
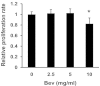
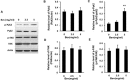
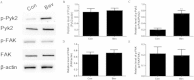
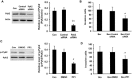
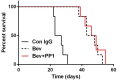
Results: Bevacizumab exposure increased migration and invasion of cultured C6 cells in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, the continuous bevacizumab treatment also promoted tumor invasion in rat C6 intracranial glioma models. Bevacizumab treatment enhanced Pyk2 phosphorylation at Tyr402, but no effect on FAK phosphorylation at Tyr397 both in vitro and in vivo. Knockdown of Pyk2 by siRNA or inhibition of Pyk2 phosphorylation by Src kinase specific inhibitor PP1 partially inhibited bevacizumab-induced cell invasion in cultured C6 glioma cells. Furthermore, the combined administration of bevacizumab and PP1 significantly suppressed glioma cell invasion into surrounding brain tissues compared to bevacizumab treatment alone in experimental rats.
Conclusions: These results suggest that anti-VEGF treatment promotes glioma cell invasion via activation of Pyk2. Inhibition of Pyk2 phosphorylation might be a potential target to ameliorate the therapeutic efficiency of anti-VEGF treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suppression of store-operated Ca2+ entry regulated by silencing Orai1 inhibits C6 glioma cell motility via decreasing Pyk2 activity and promoting focal adhesion.Cell Cycle. 2020 Dec;19(24):3468-3479. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1843814. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 33269647 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Pyk2 in Human Cancers.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 14;24:8172-8182. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913479. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30425234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of ROS-alpha v beta 3 integrin-FAK/Pyk2 in the inhibitory effect of melatonin on U251 glioma cell migration and invasion under hypoxia.J Transl Med. 2015 Mar 20;13:95. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0454-8. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889845 Free PMC article.
-
Store-operated Ca(2+) entry regulates glioma cell migration and invasion via modulation of Pyk2 phosphorylation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 30;33(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0098-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25433371 Free PMC article.
-
Activated PyK2 and Its Associated Molecules Transduce Cellular Signaling from the Cancerous Milieu for Cancer Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 7;23(24):15475. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415475. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of store-operated Ca2+ entry regulated by silencing Orai1 inhibits C6 glioma cell motility via decreasing Pyk2 activity and promoting focal adhesion.Cell Cycle. 2020 Dec;19(24):3468-3479. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1843814. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 33269647 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Pyk2 in Human Cancers.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 14;24:8172-8182. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913479. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30425234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct antitumor activity of bevacizumab: an overlooked mechanism?Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 23;15:1394878. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394878. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38716237 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting SRC Family Kinases in Mesothelioma: Time to Upgrade.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 11;12(7):1866. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071866. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32664483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF regulates the blood‑brain barrier through MMP‑9 in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Oct 24;24(6):728. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11664. eCollection 2022 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36382093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT. Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:610–622. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Wang J, Gong L, Wen Z, Xu C, Huang X. Correlation of Delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4) with VEGF and HIF-1alpha expression in human glioma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:215–218. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4733–4740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.8721. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

