Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults
- PMID: 24876561
- PMCID: PMC4110664
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-564997
Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults
Abstract
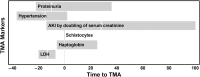
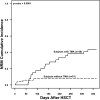
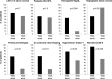
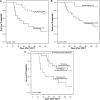
Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) leads to generalized endothelial dysfunction that can progress to multiorgan injury, and severe cases are associated with poor outcomes after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Identifying patients at highest risk for severe disease is challenging. We prospectively evaluated 100 consecutive HSCT recipients to determine the incidence of moderate and severe TMA and factors associated with poor overall outcomes. Thirty-nine subjects (39%) met previously published criteria for TMA. Subjects with TMA had a significantly higher nonrelapse mortality (43.6% vs 7.8%, P < .0001) at 1 year post-HSCT compared with those without TMA. Elevated lactate dehydrogenase, proteinuria on routine urinalysis, and hypertension were the earliest markers of TMA. Proteinuria (>30 mg/dL) and evidence of terminal complement activation (elevated sC5b-9) in the blood at the time of TMA diagnosis were associated with very poor survival (<20% at 1 year), whereas all TMA subjects without proteinuria and a normal sC5b-9 serum concentration survived (P < .01). Based on these prospective observations, we conclude that severe TMA occurred in 18% of HSCT recipients in our cohort and propose an algorithm to identify the highest-risk patients who might benefit from prompt clinical interventions.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Increase in Complement Terminal Pathway Activation Marker sC5b-9 Is Predictive for the Development of Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Stem Cell Transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 May;24(5):989-996. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29339271
-
Use of Eculizumab in Patients With Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Study From the SFGM-TC.Transplantation. 2015 Sep;99(9):1953-9. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000601. Transplantation. 2015. PMID: 25651309
-
Transplantation-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy Risk Stratification: Is There a Window of Opportunity to Improve Outcomes?Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Jul;28(7):392.e1-392.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.04.019. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 35490975 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Concepts in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation-Associated Renal Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Prospects for New Treatments.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Dec;72(6):857-865. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 30146419 Review.
-
Renal Complications after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Role of Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Renal Thrombotic Microangiopathy.J Nippon Med Sch. 2020 Mar 11;87(1):7-12. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2020_87-102. Epub 2019 Nov 28. J Nippon Med Sch. 2020. PMID: 31776318 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating CAR T-Cell Therapy and Transplantation: Comparisons of Safety and Long-Term Efficacy of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation After CAR T-Cell or Chemotherapy-Based Complete Remission in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:605766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.605766. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025637 Free PMC article.
-
Eculizumab therapy in adults with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016 Sep;51(9):1241-4. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2016.87. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27064689 No abstract available.
-
Allogeneic reactivity-mediated endothelial cell complications after HSCT: a plea for consensual definitions.Blood Adv. 2019 Aug 13;3(15):2424-2435. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000143. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31409584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical emergencies in pediatric blood & marrow transplant and cellular therapies.Front Pediatr. 2023 Feb 7;11:1075644. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1075644. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36824648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement Mediated Endothelial Damage in Thrombotic Microangiopathies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 25;9:811504. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.811504. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35547236 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Jodele S. Small vessels, big trouble in the kidneys and beyond: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood. 2011;118(6):1452–1462. - PubMed
-
- Cooke KR, Jannin A, Ho V. The contribution of endothelial activation and injury to end-organ toxicity following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(1 Suppl 1):23–32. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani S. Chronic kidney disease after pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(1 Suppl 1):84–87. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz A, Haller H, Schmitt R, et al. Biopsy-diagnosed renal disease in patients after transplantation of other organs and tissues. Am J Transplant. 2010;10(9):2017–2025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

