A new lipid-based nano formulation of vinorelbine
- PMID: 24871553
- PMCID: PMC4179676
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-014-0146-3
A new lipid-based nano formulation of vinorelbine
Abstract
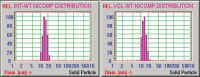
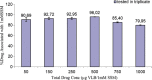
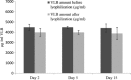
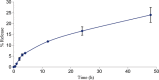
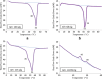
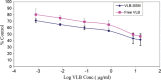
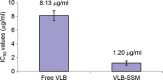
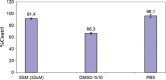
Vinorelbine (VLB) is a semi-synthetic Vinca alkaloid which is currently used in treatment of different cancer types mainly advanced breast cancer (ABC) and advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its marketed formulation has been reported to have serious side effects, such as granulocytopenia, which is the major dose-limiting toxicity. Other unwanted effects include venous discoloration and phlebitis proximal to the site of injection, as well as localized rashes and urticaria, blistering, and skin sloughing. Our long-term aim in synthesizing a novel nanomicellar vinorelbine formulation is to reduce or even eliminate these side effects and increase drug activity by formulating the drug in a lipid-based system as a nanomedicine targeted to the site of action. To this end, the purpose of this study was to prepare, characterize, and determine the in vitro efficacy of vinorelbine-loaded sterically stabilized, biocompatible, and biodegradable phospholipid nanomicelles (SSM; size, ∼15 nm). Our results indicated that vinorelbine incorporate at high quantities and within the interface between the core and palisade sections of the micelles. Incorporation ratio of drug within sterically stabilized micelles increased as the total amount of drug in the system increased, and no drug particles were formed at the highest drug concentrations tested. The nanomicellar formulation of vinorelbine was ∼6.7-fold more potent than vinorelbine dissolved in DMSO on MCF-7 cell line. Collectively, these data indicate that vinorelbine-loaded SSM can be developed as a new, safe, stable, and effective nanomedicine for the treatment of breast and lung cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Camptothecin in sterically stabilized phospholipid micelles: a novel nanomedicine.Nanomedicine. 2005 Mar;1(1):77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2004.11.002. Nanomedicine. 2005. PMID: 17292061
-
Vitamin E TPGS Emulsified Vinorelbine Bitartrate Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN): Formulation Development, Optimization and In vitro Characterization.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(8):1135-1145. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666180409105410. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29629662
-
Vinorelbine tartrate (Navelbine): drug profile and nursing implications of a new vinca alkaloid.Oncol Nurs Forum. 1995 May;22(4):635-46. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1995. PMID: 7675666 Review.
-
99mTc-vinorelbine tartrate loaded spherulites: Lung disposition study in Sprague-Dawley rats by gamma scintigraphy.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Apr;49:36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29337265
-
Vinorelbine. A review of its pharmacological properties and clinical use in cancer chemotherapy.Drugs Aging. 1994 Sep;5(3):200-34. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199405030-00006. Drugs Aging. 1994. PMID: 7803948 Review.
Cited by
-
A review of FDA approved drugs and their formulations for the treatment of breast cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 28;14:1184472. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1184472. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37576816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Drugs: Recent Strategies to Improve Stability Profile, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties.Molecules. 2022 Aug 25;27(17):5436. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175436. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Lipid-based Nanoparticles Hold Promise for Advancing the Clinical Translation of Anticancer Alkaloids?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 25;13(21):5346. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215346. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-responsive nutlin-loaded nanoparticles for combined chemotherapy and piezoelectric treatment of glioblastoma cells.Acta Biomater. 2022 Feb;139:218-236. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 33894347 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic, Apoptotic and Genotoxic Effects of Lipid-Based and Polymeric Nano Micelles, an In Vitro Evaluation.Toxics. 2017 Dec 30;6(1):7. doi: 10.3390/toxics6010007. Toxics. 2017. PMID: 29301191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou XJ, Placidi M, Rahmani R. Uptake and metabolism of Vinca alkaloids by freshly isolated human hepatocytes in suspension. Anticancer Res. 1994;14(3A):1017–22. - PubMed
-
- Etievant C, Barret JM, Kruczynski A, Perrin D, Hill BT. Vinflunine (20′,20′-difluoro-3′,4′-dihydrovinorelbine), a novel Vinca alkaloid, which participates in P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-mediated multidrug resistance in vivo and in vitro. Investig New Drugs. 1998;16(1):3–17. doi: 10.1023/A:1006022811895. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duflos A, Jacquesy JC, Kruczynski A, Etievant C, Barret JM, Hill BT, et al. Extending the scope of Vinca alkaloids with superacid chemistry. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:3794S-S.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

