Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of monotherapy with thiazide diuretics for primary hypertension
- PMID: 24869750
- PMCID: PMC10612990
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003824.pub2
Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of monotherapy with thiazide diuretics for primary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is a modifiable cardiovascular risk factor. Although it is established that low-dose thiazides reduce mortality as well as cardiovascular morbidity, the dose-related effect of thiazides in decreasing blood pressure has not been subject to a rigorous systematic review. It is not known whether individual drugs within the thiazide diuretic class differ in their blood pressure-lowering effects and adverse effects.
Objectives: To determine the dose-related decrease in systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure due to thiazide diuretics compared with placebo control in the treatment of patients with primary hypertension. Secondary outcomes included the dose-related adverse events leading to patient withdrawal and adverse biochemical effects on serum potassium, uric acid, creatinine, glucose and lipids.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2014, Issue 1), Ovid MEDLINE (1946 to February 2014), Ovid EMBASE (1974 to February 2014) and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: We included double-blind, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing fixed-dose thiazide diuretic monotherapy with placebo for a duration of 3 to 12 weeks in the treatment of adult patients with primary hypertension.
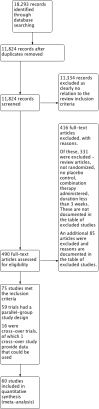
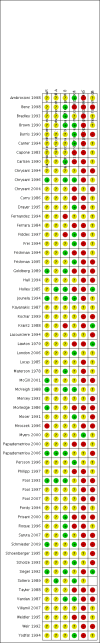
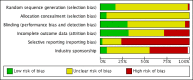
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently screened articles, assessed trial eligibility, extracted data and determined risk of bias. We combined data for continuous variables using a mean difference (MD) and for dichotomous outcomes we calculated the relative risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
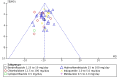
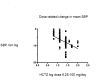
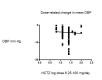
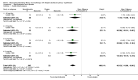
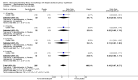
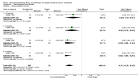
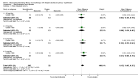
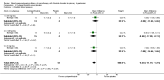
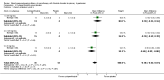
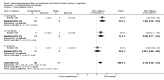
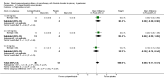
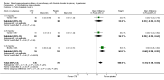
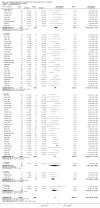
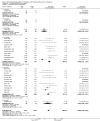
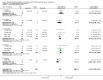
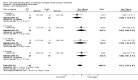
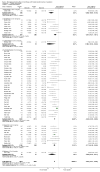
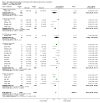
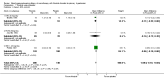
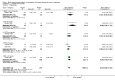
Main results: We included 60 randomized, double-blind trials that evaluated the dose-related trough blood pressure-lowering efficacy of six different thiazide diuretics in 11,282 participants treated for a mean duration of eight weeks. The mean age of the participants was 55 years and baseline blood pressure was 158/99 mmHg. Adequate blood pressure-lowering efficacy data were available for hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone and indapamide. We judged 54 (90%) included trials to have unclear or high risk of bias, which impacted on our confidence in the results for some of our outcomes.In 33 trials with a baseline blood pressure of 155/100 mmHg, hydrochlorothiazide lowered blood pressure based on dose, with doses of 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg, 25 mg and 50 mg/day lowering blood pressure compared to placebo by 4 mmHg (95% CI 2 to 6, moderate-quality evidence)/2 mmHg (95% CI 1 to 4, moderate-quality evidence), 6 mmHg (95% CI 5 to 7, high-quality evidence)/3 mmHg (95% CI 3 to 4, high-quality evidence), 8 mmHg (95% CI 7 to 9, high-quality evidence)/3 mmHg (95% CI 3 to 4, high-quality evidence) and 11 mmHg (95% CI 6 to 15, low-quality evidence)/5 mmHg (95% CI 3 to 7, low-quality evidence), respectively.Direct comparison of doses did not show evidence of dose dependence for blood pressure-lowering for any of the other thiazides for which RCT data were available: bendrofluazide, chlorthalidone, cyclopenthiazide, metolazone or indapamide.In seven trials with a baseline blood pressure of 163/88 mmHg, chlorthalidone at doses of 12.5 mg to 75 mg/day reduced average blood pressure compared to placebo by 12.0 mmHg (95% CI 10 to 14, low-quality evidence)/4 mmHg (95% CI 3 to 5, low-quality evidence).In 10 trials with a baseline blood pressure of 161/98 mmHg, indapamide at doses of 1.0 mg to 5.0 mg/day reduced blood pressure compared to placebo by 9 mmHg (95% CI 7 to 10, low-quality evidence)/4 (95% CI 3 to 5, low-quality evidence).We judged the maximal blood pressure-lowering effect of the different thiazides to be similar. Overall, thiazides reduced average blood pressure compared to placebo by 9 mmHg (95% CI 9 to 10, high-quality evidence)/4 mmHg (95% CI 3 to 4, high-quality evidence).Thiazides as a class have a greater effect on systolic than on diastolic blood pressure, therefore thiazides lower pulse pressure by 4 mmHg to 6 mmHg, an amount that is greater than the 3 mmHg seen with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and renin inhibitors, and the 2 mmHg seen with non-selective beta-blockers. This is based on an informal indirect comparison of results observed in other Cochrane reviews on ACE inhibitors, ARBs and renin inhibitors compared with placebo, which used similar inclusion/exclusion criteria to the present review.Thiazides reduced potassium, increased uric acid and increased total cholesterol and triglycerides. These effects were dose-related and were least for hydrochlorothiazide. Chlorthalidone increased serum glucose but the evidence was unclear for other thiazides. There is a high risk of bias in the metabolic data. This review does not provide a good assessment of the adverse effects of these drugs because there was a high risk of bias in the reporting of withdrawals due to adverse effects.
Authors' conclusions: This systematic review shows that hydrochlorothiazide has a dose-related blood pressure-lowering effect. The mean blood pressure-lowering effect over the dose range 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg, 25 mg and 50 mg/day is 4/2 mmHg, 6/3 mmHg, 8/3 mmHg and 11/5 mmHg, respectively. For other thiazide drugs, the lowest doses studied lowered blood pressure maximally and higher doses did not lower it more. Due to the greater effect on systolic than on diastolic blood pressure, thiazides lower pulse pressure by 4 mmHg to 6 mmHg. This exceeds the mean 3 mmHg pulse pressure reduction achieved by ACE inhibitors, ARBs and renin inhibitors, and the 2 mmHg pulse pressure reduction with non-selective beta-blockers as shown in other Cochrane reviews, which compared these antihypertensive drug classes with placebo and used similar inclusion/exclusion criteria.Thiazides did not increase withdrawals due to adverse effects in these short-term trials but there is a high risk of bias for that outcome. Thiazides reduced potassium, increased uric acid and increased total cholesterol and triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
Vijaya Musini: none known.
Mark nazer: none known.
Ken Bassett: none known.
James Wright: none known.
Figures






















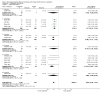
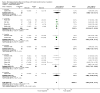
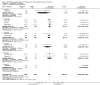







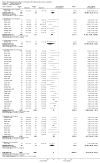




Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003824
Similar articles
-
First-line drugs for hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 18;4(4):CD001841. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001841.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29667175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First-line diuretics versus other classes of antihypertensive drugs for hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 13;7(7):CD008161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008161.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37439548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of loop diuretics for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 22;2015(5):CD003825. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003825.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26000442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of chlorthalidone and hydrochlorothiazide in combination with amiloride in multiple doses on blood pressure in patients with primary hypertension: a protocol for a factorial randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Dec 16;20(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3909-z. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31843024 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 5;4(4):CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28379619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of dapagliflozin according to baseline systolic blood pressure in the Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse Outcomes in Heart Failure trial (DAPA-HF).Eur Heart J. 2020 Sep 21;41(36):3402-3418. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa496. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32820334 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of indapamide vs. bendroflumethiazide for primary hypertension: a systematic review.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;85(2):285-303. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13787. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30312512 Free PMC article.
-
Thiazide diuretics and the risk of hip fracture after stroke: a population-based propensity-matched cohort study using Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database.BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 27;7(9):e016992. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016992. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28963293 Free PMC article.
-
[Diuretics as a problem-Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, use in edema or hypertension].Internist (Berl). 2021 Feb;62(2):215-220. doi: 10.1007/s00108-021-00945-x. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Internist (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33492424 Review. German.
-
Diuretics in primary hypertension - Reloaded.Indian Heart J. 2016 Sep-Oct;68(5):720-723. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2016.08.013. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Indian Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27773415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ambrosioni 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ambrosioni E, Safar M, Degaute JP, Malin PL, MacMahon M, Pujol DR, et al. Low‐dose antihypertensive therapy with 1.5 mg sustained‐release indapamide: results of randomised double‐blind controlled studies. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16:1677‐84. - PubMed
-
- Asmar R, Guez D, Malbezin M, Brault Y, Cordoue A, Barrandon S, et al. Therapeutic benefit of a low dosage of indapamide: result of a double‐blind, placebo controlled European study [Benefice therapeutique d'une faible dose d'indapamide: resultats d'une etude europeenne controlee en double aveugle contre placebo]. Archives des Maladies du Coeur et des Vaisseaux 1995;88:1083‐7. - PubMed
-
- Guez D, Mallion J‐M, Degaute J‐P, Malini P‐L, Baldwin R, Rodriguez‐Pujol D, et al. Treatment of hypertension with indapamide 1.5 mg sustained‐release form: synthesis of results [Traitement de l'hypetension arterielle par l'indapamide 1,5 mg comprime enrobe a liberation prolongee: synthese des resultats]. Archives des Maladies du Coeur et des Vaisseaux 1996;89(IV):17‐25. - PubMed
-
- Leonetti G. Clinical positioning of indapamide sustained release 1.5mg in management protocols for hypertension. Drugs 2000;59(Suppl 2):27‐38. - PubMed
-
- Mallion J‐M, Asmar R, Boutelant S, Guez D. Twenty‐four hour antihypertensive efficacy of indapamide, 1.5‐mg sustained release: results of two randomized double‐blind controlled studies. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1998;32(4):673‐8. - PubMed
Benz 1998 {published data only}
-
- Benz JR, Black HR, Graff A, Reed A, Fitzsimmons S, Shi Y. Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. A multiple dose, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial comparing combination therapy with monotherapy. Journal of Human Hypertension 1998;12:861‐6. - PubMed
Bradley 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bradley K, Flack JM, Belcher J, Elmer P, Miller P, Grimm R Jr. Chlorthalidone attenuates the reduction in total cholesterol and small, dense LDL cholesterol subclass associated with weight loss. American Journal of Hypertension 1993;6(7 Pt 1):636‐9. - PubMed
Brown 1990 {published data only}
-
- Brown CL, Backhouse CI, Grippat JC, Santoni JP. The effect of perindopril and hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination on blood pressure and on the renin‐angiotensin system in hypertensive subjects. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1990;39(4):327‐32. - PubMed
Burris 1990 {published data only}
-
- Burris JF, Weir MR, Oparil S, Wever M, Cady WJ, Stewart WH. An assessment of diltiazem and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension. Application of factorial trial design to a multicenter clinical trial of combination therapy. JAMA 1990;263(11):1507‐12. - PubMed
Canter 1994 {published data only}
-
- Canter D, Frank GJ, Knapp LE, Phelps M, Quade M, Texter M. Quinapril and hydrochlorothiazide combination for control of hypertension:assessment by factorial design. Quinapril Investigator Group [see comments]. Journal of Human Hypertension 1994;8(3):155‐62. - PubMed
Capone 1983 {published data only}
-
- Capone P, Vukovich RA, Neiss ES, Bolton S, Reeves RL. Multicenter dose‐response study of the effect of indapamide in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1983;5(3):305‐16. - PubMed
Carlsen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Carlsen JE, Kober L, Torp‐Pedersen CT, Johansen P. The optimal dose of bendroflumathiazide in hypertension. A randomized double‐blind dose‐response study [Optimal dosis af bendroflumetiazid ved hypertension. En randomiseret dobbeltblind dosis‐responsunderogelse]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1990;152(42):3072‐5. - PubMed
Chrysant 1994 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, The Lisinopril‐Hydrochlorothiazide Group. Antihypertensive effectiveness of low‐dose lisinopril‐hydrochlorothiazide combination. A large multicenter study. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(7):737‐43. - PubMed
Chrysant 1996 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Fagan T, Glazer R, Kriegman A. Effects of benazepril and hydrochlorothiazide, given alone and in low‐ and high‐dose combinations, on blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Archives of Family Medicine 1996;5(1):17‐24. - PubMed
Chrysant 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chrysant SG, Weber MA, Wang AC, Hinman DJ. Evaluation of antihypertensive therapy with the combination of olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide. American Journal of Hypertension 2004;17(3):252‐9. - PubMed
Curry 1986 {published data only}
-
- Curry CL, Janda SM, Harris R, MacKay JH, Nugent CA, Ryan J, et al. Clinical studies of a new, low‐dose formulation of metolazone for the treatment of hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1986;9(1):47‐62. - PubMed
Drayer 1995 {published data only}
-
- Drayer JI, Stimpel M, Fox A, Weber M. The antihypertensive properties of the angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor moexipril given alone or in combination with a low dose of a diuretic. American Journal of Therapeutics 1995;2(8):525‐31. - PubMed
Fernandez 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez M, Madero R, Gonzalez D, Camacho P, Villalpando J, Arriaga J. Combined versus single effect of fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1994;23(Suppl 1):I207‐10. - PubMed
Ferrara 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ferrara LA, Simone G, Mancini M, Fasano ML, Pasanisi F, Vallone G. Changes in left ventricular mass during a double‐blind study with chlorthalidone and slow‐release nifedipine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1984;27(5):525‐8. - PubMed
Fiddes 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fiddes R, Blumenthal J, Dawson JE, Dyckman E, John Hammond PG, Harris S, et al. Evaluation of indapamide 1.25 mg once daily in elderly patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1997;11(4):239‐44. - PubMed
Frei 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frei M, Küster L, Gardosch von Krosigk PP, Koch HF, Küppers H. Moxonidine and hydrochlorothiazide in combination: a synergistic antihypertensive effect. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1994;24(Suppl 1):S25‐8. - PubMed
Frishman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frishman WH, Bryzinski BS, Coulson LR, DeQuattro VL, Vlachakis ND, Mroczek WJ, et al. A multifactorial trial design to assess combination therapy in hypertension. Treatment with bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide. Archives of Internal Medicine 1994;154(13):1461‐8. - PubMed
Frishman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Frishman WH, Burris JF, Mroczek WJ, Weir MR, Alemayehu D, Simon JS, et al. First‐line therapy option with low‐dose bisoprolol fumarate and low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide in patients with stage I and stage II systemic hypertension. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1995;35(2):182‐8. - PubMed
Goldberg 1989 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg MR, Rockhold FW, Offen WW, Dornseif BE. Dose‐effect and concentration‐effect relationships of pinacidil and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1989;46(2):208‐18. - PubMed
Hall 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hall WD, Weber MA, Ferdinand K, Flamenbaum W, Marbury T, Jain AK, et al. Lower dose diuretic therapy in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1994;8(8):571‐5. - PubMed
Hulley 1985 {published data only}
-
- Black DM, Brand RJ, Greenlick M, Hughes G, Smith J. Compliance to treatment for hypertension in elderly patients: The SHEP trial. Journal of Gerontology 1987;42(5):552‐7. - PubMed
-
- Hulley SB, Feigal D, Ireland C, Kuller LH, Smith WM. Systolic hypertension in the elderly program (SHEP). The first three months. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1986;34(2):101‐5. - PubMed
-
- Hulley SB, Furberg CD, Gurland B, McDonald R, Perry HM, Schnaper HW, et al. Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP): Antihypertensive efficacy of chlorthalidone. American Journal of Cardiology 1985;56(15):913‐1038. - PubMed
-
- Kostis JB, Davis BR, Cutler J, Grimm RH, Berge KG, Cohen JD, et al. Prevention of heart failure by antihypertensive drug treatment in older persons with isolated systolic hypertension. SHEP Cooperative Research Group. JAMA 1997;278(3):212‐6. - PubMed
-
- Moye LA, Davis BR, Hawkins CM, Probstfield JL. Conclusions and implications of the systolic hypertension in the elderly program. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension 1993;15(6):911‐24. - PubMed
Jounela 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jounela AJ, Lilja M, Lumme J, Morlin C, Hoyem A, Wessel‐Aas T, et al. Relation between low dose of hydrochlorothiazide, antihypertensive effect and adverse effects. Blood Pressure 1994;3(4):231‐5. - PubMed
Kayanakis 1987 {published data only}
Kochar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kochar M, Guthrie R, Triscari J, Kassler‐Taub K, Reeves RA. Matrix study of irbesartan with hydrochlorothiazide in mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12(8 Pt 1):797‐805. - PubMed
Krantz 1988 {published data only}
-
- Krantz DS, Contrada R, Durel LA, Hill DR, Friedler E. Comparative effects of two beta‐blockers on cardiovascular reactivity and type A behaviour in hypertensives. Psychosomatic Medicine 1988;50:615‐26. - PubMed
Lacourciere 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lacourciere Y, Arnott W. Placebo‐controlled comparison of the effects of nebivolol and low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide as monotherapies and in combination on blood pressure and lipid profile in hypertensive patients. Journal of Human Hypertension 1994;8(4):283‐8. - PubMed
-
- Lacourciere Y, Lefebvre J, Poirier L, Archambault F, Arnott W. Treatment of ambulatory hypertensives with nebivolol or hydrochlorothiazide alone and in combination. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled factorial‐design trial. American Journal of Hypertension 1994;7(2):137‐45. - PubMed
Lawton 1979 {published data only}
-
- Lawton WJ, Fitz A, Grant C, Witte DL. Dopamine beta‐hydroxylase and plasma renin activity in patients with low‐, normal‐, and high‐renin essential hypertension. Circulation 1979;59(5):1063‐9. - PubMed
London 2006 {published data only}
-
- London G, Schmieder R, Calvo C, Asmar R. Indapamide SR versus candesartan and amlodipine in hypertension: the X‐CELLENT study. American Journal of Hypertension 2006;19:113‐21. - PubMed
Lucas 1985 {published data only}
-
- Lucas CP, Morledge JH, Tessman DK. Comparison of hydrochlorothiazide and hydrochlorothiazide plus bevantolol in hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1985;8(1):49‐60. - PubMed
Materson 1978 {published data only}
-
- Materson BJ, Oster JR, Ulrich FM, Bolton SM, et al. Dose response to chlorthalidone in patients with mild hypertension. Efficacy of a lower dose. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1978;24(2):192‐8. - PubMed
McGill 2001 {published data only}
-
- Littlejohn III TW. Clinical considerations in hypertensive black patients: the role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in combination with a diuretic. Blood Pressure Monitoring 2001;6(Suppl 1):S15‐21.
-
- McGill JB. Angiotensin II receptor antagonist plus a thiazide diuretic is more efficacious for treating hypertension than either drug alone. Blood Pressure Monitoring 2001;6 (supplement 1):S3‐13.
-
- McGill JB, Reilly PA. Telmisartan plus hydrochlorothiazide versus telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide monotherapy in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(6):833‐50. - PubMed
McVeigh 1988 {published data only}
Mersey 1993 {published data only}
-
- Mersey J, D'Hemecourt P, Blaze K. Once‐daily fixed combination of captopril and hydrochlorothiazide as first line therapy for mild to moderate hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research and Clinical Experiment 1993;53(5):502‐12.
Morledge 1986 {published data only}
-
- Morledge JH, Ettinger B, Aranda J, McBarron F, Barra P, Gorwit J, et al. Isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly. A placebo‐controlled, dose‐response evaluation of chlorthalidone. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1986;34(3):199‐206. - PubMed
Moser 1991 {published data only}
-
- Moser M, Abraham PA, Bennett WM, Brachfeld N, Goodman RP, McKenney JM, et al. The effects of benazepril, a new angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor, in mild to moderate essential hypertension: a multicenter study. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;49(3):322‐9. - PubMed
Mroczek 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mroczek WJ, Stimpel M. A double‐blind evaluation of moexipril versus hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension. Advances in Therapy 1996;13(2):79‐87.
Myers 2000 {published data only}
-
- Myers MG, Asmar R, Leenen FHH, Safar M. Fixed low‐dose combination therapy in hypertension ‐ a dose response study of perindopril and indapamide. Journal of Hypertension 2000;18(3):317‐25. - PubMed
Papademetriou 2000 {published data only}
-
- Papademetriou V, Reif M, Henry D, et al. Combination therapy with candesartan cilexetil and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with systemic hypertension. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 2000;2:372‐8.
Papademetriou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Papademetriou V, Hainer JW, Sugg J, Munzer D, ATTACH Study Group. Factorial antihypertensive study of an extended‐release metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide combination. American Journal of Hypertension 2006;19(12):1217‐25. - PubMed
Persson 1996 {published data only}
-
- Persson B, Stimpel M. Evaluation of the antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of moexipril, a new ACE inhibitor, compared to hydrochlorothiazide in elderly patients. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1996;50:259‐64. - PubMed
Philipp 1997 {published data only}
-
- Philipp T, Letzel H, Arens HJ. Dose‐finding study of candesartan cilexetil plus hydrochlorothiazide in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1997;11(Suppl 2):S67‐8. - PubMed
Pool 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pool PE, Applegate WB, Woehler T, Sandall P, Cady WJ. A randomized, controlled trial comparing diltiazem, hydrochlorothiazide, and their combination in the therapy of essential hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 1993;13(5):487‐93. - PubMed
Pool 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Cushman WC, Saini RK, Nwachuku CE, Battikha JP. Use of the factorial design and quadratic response surface models to evaluate the fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1997;10(1):117‐23. - PubMed
Pool 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pool JL, Glazer R, Weinberger M, Alvarado R, Huang J, Graff A. Comparison of valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy at doses up to 320/25 mg versus monotherapy: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study followed by long‐term combination therapy in hypertensive adults. Clinical Therapeutics 2007;29(1):61‐73. - PubMed
Pordy 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pordy RC and the Cilazapril/Hydrochlorothiazide 4x3 Factorial Design Study Group. Cilazapril plus hydrochlorothiazide: improved efficacy without reduced safety in mild to moderate hypertension. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled multicenter study of factorial design. Cardiology 1994;85:311‐22. - PubMed
Prisant 2000 {published data only}
-
- Prisant LM. Ambulatory blood pressure profiles in patients treated with once‐daily diltiazem extended‐release or indapamide alone or in combination. American Journal of Therapeutics 2000;7:177‐84. - PubMed
Roque 1996 {published data only}
-
- Roque F, Mon G, Cravero C, Courreges J, et al. Antihypertensive efficacy of hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Advances in Therapy 1996;13(5):284‐91.
Saruta 2007 {published data only}
-
- Saruta T, Ogihara T, Matsuoka H, Suzuki H, Toki M, Hirayama Y, et al. Antihypertensive efficacy and safety of fixed‐dose combination therapy with losartan plus hydrochlorothiazide in Japanese patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension Research 2007;30(8):729‐39. - PubMed
Schmieder 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schmieder RE, Philipp T, Guerediaga J, Gorostidi M, Smith B, Weissbach N, et al. Long‐term antihypertensive efficacy and safety of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren. A 12‐month randomized, double‐blind comparator trial with hydrochlorothiazide. Circulation 2009;119:417‐25. - PubMed
Schoenberger 1995 {published data only}
-
- MacKay JH, Arcuri KE, Goldberg AI, Snapinn SM, Sweet CS. Losartan and low‐dose hydrochlolorthiazide in patients with essential hypertension. Archives of Internal Medicine 1996;156:278‐85. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberger JA, Bauer J, Barden LP, Brown R, Byyny R, Cohen J, et al. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide in the treatment of hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1995;13(Suppl 1):S43‐7. - PubMed
Scholze 1993 {published data only}
-
- Scholze J, Breitstadt A, Cairns V, Bauer B, Bender N, Priestley C, et al. Short report: ramipril and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in hypertension: a clinical trial of factorial design. The East Germany Collaborative Trial Group. Journal of Hypertension 1993;11(2):217‐21. - PubMed
Siegel 1992 {published data only}
-
- Siegel D, Hulley SB, Black DM, Cheitlin MD, Sebastian A, Seeley DG, et al. Diuretics, serum, and intracellular electrolyte levels, and ventricular arrhythmias in hypertensive men. JAMA 1992;267(8):1083‐9. - PubMed
-
- Siegel D, Saliba P, Haffner S. Glucose and insulin levels during diuretic therapy in hypertensive men. Hypertension 1994;23(6 Pt 1):688‐94. - PubMed
Soltero 1989 {published data only}
-
- Soltero I, Fuenmayor I, Colmenares A, et al. Action of indapamide on lipid profiles: a double blind cross over study. Current Therapeutic Research 1989;46(1):163‐72.
Taylor 1988 {published data only}
-
- Taylor DR, Constable J, Sonnekus M, Milne FJ. Effect of indapamide on serum and red cell cations, with and without magnesium supplementation, in subjects with mild hypertension. South African Medical Journal 1988;74(6):273‐6. - PubMed
Vardan 1987 {published data only}
-
- Vardan S, Mehrotra KG, Mookherjee S, Willsey GA, Gens JD, Green DE. Efficacy and reduced metabolic side effects of a 15‐mg chlorthalidone formulation in the treatment of mild hypertension. A multicenter study. JAMA 1987;258(4):484‐8. - PubMed
Villamil 2007 {published data only}
-
- Villamil A, Chrysant SG, Calhoun D, Schober B, Hsu H, Matrisciano‐Dimichino L, et al. Renin inhibition with aliskiren provides additive antihypertensive efficacy when used in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. Journal of Hypertension 2007;25:217‐26. - PubMed
Weidler 1995 {published data only}
-
- Weidler D, Jallad NS, Curry C, Ferdinand K, Jain AK, Schnaper HW, et al. Efficacious response with lower dose indapamide therapy in the treatment of elderly patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1995;35:45‐51. - PubMed
Weir 1992 {published data only}
-
- Weir MR, Weber MA, Punzi HA, Serfer HM, Rosenblatt S, Cady WJ. A dose escalation trial comparing the combination of diltiazem SR and hydrochlorothiazide with the monotherapies in patients with essential hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 1992;6(2):133‐8. - PubMed
Yodfat 1994 {published data only}
-
- Yodfat Y, Zimilchman R and the Israeli‐Italian Cilazapril/Hydrochlorothiazide Research Study Group. Dose‐finding and dose justification of once‐daily cilazapril in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in non‐obese patients with mild‐to‐moderate essential hypertension. Journal of Drug Development 1994;6(3):117‐21.
References to studies excluded from this review
Amery 1978 {published data only}
-
- Amery A, Bulpitt, Schaepdryver A, Fagard R, Hellemans J, Mutsers A, et al. Glucose intolerance during diuretic therapy. Results of trial by the European Working Party on Hypertension in the Elderly. Lancet 1978;311(8066):681‐3. - PubMed
Anavekar 1979 {published data only}
-
- Anavekar SN, Ludbrooke A, Louis WJ, Doyle AE. Evaluation of indapamide in the treatment of hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1979;1(4):389‐94. - PubMed
Bateman 1979 {published data only}
Batterman 1966 {published data only}
-
- Batterman RC. Hypertensive treatment with veratrum alkaloids and thiazides alone and in combination. The Angiology Research Foundation Inc. 1966;3(1):1‐11. - PubMed
Blaufox 1992 {published data only}
-
- Blaufox MD, Lee HB, Davis B, Oberman A, Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Langford H. Renin predicts diastolic blood pressure response to nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapy. JAMA 1992;267:1221‐5. - PubMed
Boike 1982 {published data only}
-
- Boike SC, Durley Y, Cubberley RB. Atenolol and chlorthalidone administered alone and in combination for essential hypertension. Clinical Pharmacy 1982;1:449‐53. - PubMed
Borghi 1993 {published data only}
-
- Borghi L, Meschi T, Guerra A, Novarini A. Randomized prospective study of a non thiazide diuretic, indapamide, in preventing calcium stone recurrences. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1993;22(Suppl 6):S78‐86. - PubMed
Carretta 1988a {published data only}
-
- Carretta R, Fabris B, Bardelli M, Muiesan S, Fischetti F, Vran F, et al. Arterial compliance and baroreceptor sensitivity after chronic treatment with indapamide. Journal of Human Hypertension 1988;2:171‐5. - PubMed
Carretta 1988b {published data only}
-
- Carretta R, Fabris B, Fischetti F, Muiesan S, Bardelli M, Melchior C, et al. Platelet alpha2‐adrenoceptor modifications induced by long‐term treatment with indapamide in essential hypertension. American Journal of Medicine 1988;84(Suppl 1B):31‐5. - PubMed
Chalmers 1976 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers J, Tiller D, Horvath J, Bune A. Effects of timolol and hydrochlorothiazide on blood‐pressure and plasma renin activity. Double‐blind factorial trial. Lancet 1976;2(7981):328‐31. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers JP, Horvath JS, Korner PI, Tiller DJ, Bune AJ, England JD, et al. Quantitative effects of timolol and hydrochlorothiazide on blood pressure, heart rate and plasma renin activity: results of a double‐blind factorial trial in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Sciences and Molecular Medicine 1976;51:517S‐19S. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers JP, Korner PI, Tiller DJ, Bune AJ, Steiner JD, West MJ, et al. Double‐blind factorial trial of prindolol and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension. The Medical Journal of Australia 1976;1:650‐3. - PubMed
Chalmers 1982 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers JP, Wing LMH, Grygiel MJ, Graham JR, Bune AJ. Effects of once daily indapamide and pindolol on blood pressure, plasma aldosterone concentration and plasma renin activity in a general practice setting. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1982;22:191‐6. - PubMed
Chalmers 1986 {published data only}
-
- Chalmers JP, Morris JM, Wing LMH, West MJ, Bune AJC, Elliott JM. Effects of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide on blood pressure, renin‐angiotensin system, and atrial natriuretic factor in essential hypertension: a double‐blind factorial cross‐over study. Australian New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1986;16:475‐80. - PubMed
Christiansen 1981 {published data only}
-
- Christiansen C, Christensen MS, Hagen C, Stocklund K‐E, Transbol I. Effects of natural estrogen/gestagen and thiazide on coronary risk factors in normal postmenopausal women. A 2‐year double‐blind placebo study. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1981;60:407‐12. - PubMed
Consoli 1985 {published data only}
-
- Consoli G, Martino G. Evaluation of the hypotensive efficacy in a double‐blind study of xipamide versus chlorthalidone [Valutazione dellefficacia ipotensiva in uno studio a doppio cieco della xipamide verso il clortalidone]. La Clinica Terapeutica 1985;113(5):379‐83. - PubMed
Cranston 1962 {published data only}
-
- Cranston WI, Juel‐Jensen BE. The effects of spironolactone and chlorthalidone on arterial pressure. The Lancet 1962;June 2:1161‐4. - PubMed
Crowe 1987 {published data only}
-
- Crowe PF, Finnegan OC, Rusell CJMcL, Varma MPS. A double‐blind study of inderex in the treatment of essential hypertension. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1987;41(10):967‐70. - PubMed
Datta 1989 {published data only}
-
- Datta SR. A double‐blind comparison of indapamide with placebo in the treatment of elderly hypertensives. Clinical Trials Journal 1989;26(5):356‐62.
Davis 1993 {published data only}
-
- Davis BR, Blaufox MD, Oberman A, Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Zimbaldi N, Cutler JA, et al. Reduction in long‐term antihypertensive medication requirements. Effects of weight reduction by dietary intervention in overweight persons with mild hypertension. Archives of Internal Medicine 1993;153(15):1773‐82. - PubMed
Dean 1971 {published data only}
-
- Dean G, Louw S, Hersch C, Kirsten HO, Brereton DN, Finnemore L, et al. A double‐blind trial in hypertension comparing Baycaron (FBA 1500), hydrochlorothiazide and placebo. South African Medical Journal 1971;45(12):323. - PubMed
Durel 1992 {published data only}
-
- Durel LA, Hayashi PJ, Weidler DJ, Schneiderman N. Effectiveness of antihypertensive medications in office and ambulatory settings: a placebo‐controlled comparison of atenolol, metoprolol, chlorthalidone, verapamil, and an atenolol‐chlorathalidone combination. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1992;32:564‐70. - PubMed
Eames 2005 {published data only}
-
- Eames PJ, Robinson TG, Panerai RB, Potter JF. Bendrofluazide fails to reduce elevated blood pressure levels in the immediate post‐stroke period. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;19:253‐9. - PubMed
Elliot 1991 {published data only}
-
- Elliot WJ, Weber RP, Murphy MB. A double‐blind randomised, placebo‐controlled comparison of the metabolic effects of low‐dose hydrochlorothiazide and indapamide. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1991;31:751‐7. - PubMed
Erwteman 1984 {published data only}
Fagard 1976 {published data only}
-
- Fagard R, Amery A, Plaen J‐F, Lijnen P, Missotten A. Relative value of beta blockers and thiazides for initiating antihypertensive therapy. Acta Cardiologica 1976;31(5):411‐26. - PubMed
Fernandez 1980 {published data only}
Flack 2001 {published data only}
-
- Flack JM, Saunders E, Gradman A, Kraus WE, Lester M, Pratt JH, et al. Antihypertensive efficacy and safety of losartan alone and in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in adult African Americans with mild to moderate hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 2001;23(8):1193‐208. - PubMed
Gall 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gall MA, Rossing P, Skott P, Hommel E, Mathiesen ER, Geradel LU, et al. Placebo‐controlled comparison of captopril, metoprolol, and hydrochlorothiazide therapy in non‐insulin dependent diabetic patients with primary hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 1992;5(5 Pt 1):257‐65. - PubMed
Galloway 1974 {published data only}
Gerber 1985 {published data only}
-
- Gerber A, Weidmann P, Bianchetti MG, Ferrier C, Laederach K, Mordasini R, et al. Serum lipoproteins during treatment with the antihypertensive agent indapamide. Hypertension 1985;7(6 Suppl II):II164‐9. - PubMed
Gleerup 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gleerup G, Petersen JR, Mehelsen J, Winther K. Effect of spirapril and hydrochlorothiazide on platelet function and euglobulin clot lysis time in patients with mild hypertension. Angiology 1996;47(10):951‐6. - PubMed
Goldman 1980 {published data only}
-
- Goldman AI, Steele BW, Schnaper HW, Fitz AE, Frohlich ED, Perry HM Jr. Serum lipoprotein levels during chlorthalidone therapy. A Veterans Administration‐National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Cooperative Study on Antihypertensive Therapy: mild hypertension. JAMA 1980;244(15):1691‐5. - PubMed
Grimm 1981 {published data only}
-
- Grimm RH, Leon AS, Hunninghake DB, Lenz K, Hannan P, Blackburn H. Effect of thiazide diuretics on plasma lipids and lipoproteins in mildly hypertensive patients. Annals of Internal Medicine 1981;1(94):7‐11. - PubMed
Grimm 2002 {published data only}
-
- Grimm Jr. RH, Black H, Rowen R, Lewin A, Shi H, Ghadanfar M and the Amlodipine study group. Amlodipine versus chlorthalidone versus placebo in the treatment of stage I isolated systolic hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2002;15(1 Part 1):31‐6. - PubMed
Hobbs 1964 {published data only}
-
- Hobbs LF. Essential hypertension. Management with reserpine‐thiazide combination and the separate components (report of a double‐blind study). Western Medicine ‐ the Medical Journal of the West 1964;5:316‐9. - PubMed
Horvath 1979 {published data only}
-
- Horvath JS, Caterson RJ, Collett P, Duggin GG, Kelly DH, Tiller DJ. Labetolol and bendrofluazide: comparison of their antihypertensive effects. Medical Journal of Australia 1979;1:626‐62. - PubMed
Jackson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Jackson G, Rowland M, Adam G, MacFarlane E, Jackson PG. Placebo controlled double‐blind randomised cross‐over trial of atenolol, hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride, and the combination (Kalten) in patients over 60 years of age. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1986;40(6):230‐4. - PubMed
Jain 1985 {published data only}
-
- Jain AK, Hiremath A, Michael R, Ryan JR, McMahon FG. Clonidine and guanfacine in hypertension. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1985;37(3):271‐6. - PubMed
Johnson 1986 {published data only}
-
- Johnson BF, Saunders R, Hickler R, Marwaha R, Johnson J. The effect of thiazide diuretics upon plasma lipoproteins. Journal of Hypertension 1986;4:235‐9. - PubMed
Jueng 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jueng C, Halperin AK, Hashimoto F, Callender K. Nifedipine GITS and hydrochlorothiazide in essential hypertension. Journal of Clinical Hypertension 1987;3:695‐703. - PubMed
Koskelainen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Koskelainen J, Turpeinen T, Lehto H, et al. Metabolic effects of hydrochlorothiazide and hydrochlorothiazide‐amiloride and trichlormethiazide‐triamterene combinations. Current Therapeutic Research 1985;37(3):554‐65.
Kuramoto 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kuramoto K, Matsushita S, Kuwajima I, Murakami M. Prospective study on the treatment of mild hypertension in the aged. Japanese Heart Journal 1981;22(1):75‐85. - PubMed
Kuramoto 1985 {published data only}
-
- Kuramoto K, Masuyama Y. Comparison of the clinical usefulness of diuretics in elderly and younger essential hypertension‐double blind trial using tripamide. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi (Japanese Journal of Geriatrics) 1985;22(4):346‐53. - PubMed
Lechi 1982 {published data only}
-
- Lechi A, Pomari S, Berto R, Buniotto P, Parrinello A, Marini F, et al. Clinical evaluation of labetalol alone and combined with chlorthalidone in essential hypertension: a double‐blind multicentre controlled study. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1982;22:289‐93. - PubMed
Lutterodt 1980 {published data only}
-
- Lutterodt A, Nattel S, Mclead PJ. Duration of antihypertensive effect of a single daily dose of hydrochlorothiazide. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1980;27(3):324‐7. - PubMed
Materson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Henderson WG. Results of the combination antihypertensive therapy after failure of each of the components. Journal of Human Hypertension 1995;9:791‐6. - PubMed
-
- Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, Massie BM, Freis ED, Kochar MS, et al. Single‐drug therapy for hypertension in men. A comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;328(13):914‐21. - PubMed
Maus 1978 {published data only}
-
- Maus Y, Rorive G. Comparison using the double‐blind method of the hypotensive action of indapamide and that of another salidiuretic agent, chlorthalidone [Comparison selon la method du double insu de laction hypotensive de lindapamide avec celle dun autre salidiuretique la chlorthalidone]. Revue Medicale de Liege 1978;33(10):365‐8. - PubMed
Maximilian 1970 {published data only}
-
- Maximilian V, Gavrila F, Zeana C, Barbulescu I, Dimitriu CG. Effectiveness of a compound preparation (DCR 515) in the treatment of arterial hypertension (double‐blind test) [Eficacitatea unui preparat compus (DCR 515) in tratamentul hipertensiunii arteriale (test dublu orb)]. Medicina Interna 1970;22(3):297‐305. - PubMed
McCorvey 1993 {published data only}
-
- McCorvey E Jr, Wright JT Jr, Culbert JP, McKenny M, Proctor JD, Annet MP. Effect of hydrochlorothiazide, enalapril, and propranolol on quality of life and cognitive and motor function in hypertensive patients. Clinical Pharmacy 1993;12:300‐5. - PubMed
Merrill 1987 {published data only}
-
- Merrill BA, Byyny RL, Carr A, Dauer AD, Kazilionis JE, Lester FM, et al. Lisinopril/HCTZ in essential hypertension. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1987;41(2):227 [Abstract].
Milliez 1975 {published data only}
-
- Milliez P, Tehaedakoff P. Antihypertensive activity of a new agent, indapamide: a double‐blind study. Current Medical Research Opinion 1975;3:9‐15. - PubMed
Morgan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Morgan TO, Anderson AIE, MacInnis RJ. ACE inhibitors, beta‐blockers, calcium blockers, and diuretics for the control of systolic hypertension. American Journal of Hypertension 2001;14(3):241‐7. - PubMed
Moser 1986 {published data only}
-
- Moser M. Low dose diuretic therapy for hypertension. Clinical Therapeutics 1986;8(5):554‐62. - PubMed
MRC Working Party 1983 {published data only}
Muiesan 1987 {published data only}
-
- Muiesan G, Agabiti‐Rosei E, Buoninconti R, Cagli V, Carotti A, Corea L, et al. Antihypertensive efficacy and tolerability of captopril in the elderly: comparison with hydrochlorothiazide and placebo in a multicentre, double‐blind study. Journal of Hypertension 1987;5(Suppl 5):S599‐602. - PubMed
Myers 1982 {published data only}
-
- Myers MG, Wein ME, Fisher RH, Gryfe CI, Shulman HS. Unnecessary diuretic therapy in the elderly. Age and Aging 1982;11:213‐21. - PubMed
Myers 1983 {published data only}
-
- Myers MG. Effects of atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide on blood pressure and plasma catecholamines in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1983;5:591‐6. - PubMed
Okun 1978 {published data only}
-
- Okun R, Beg M. Tricynafen and hydrochlorothiazide in hypertension. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1978;23(6):703‐11. - PubMed
Okun 1979 {published data only}
-
- Okun R, Beg MA. A double‐blind study of tienilic acid with two year follow‐up of patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1979;55(Suppl 3):103‐9. - PubMed
PATS Col. Group 1995 {published data only}
-
- PATS Collaborating Group. Epidemiology Survey. Post‐stroke antihypertensive treatment study: a preliminary result. Chinese Medical Journal 1995;108(9):710‐7. - PubMed
Petersen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Petersen JR, Drabaek H, Gleerup G, Mehlsen J, Petersen LJ, Winther K. ACE inhibitor with spirapril improves diastolic function at rest independent of vasodilation during treatment with spirapril in mild to moderate hypertension. Angiology 1996;47(3):233‐40. - PubMed
Reisin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Reisin E, Weir MR, Falkner B, Hutchinson HG, Anzalone DA, Tuck ML. Lisinopril versus hydrochlorothiazide in obese hypertensive patients: a multicenter placebo‐controlled trial. Treatment in obese patients with hypertension (TROPHY) study group. Hypertension 1997;30(1 Pt 1):140‐5. - PubMed
-
- Weir MR, Reisin E, Falkner B, Hutchinson HG, Sha L, Tuck ML. Nocturnal reduction of blood pressure and the antihypertensive response to a diuretic or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor in obese hypertensive patients. TROPHY study group. American Journal of Hypertension 1998;11(8 Pt 1):914‐20. - PubMed
Russel 1968 {published data only}
-
- Russel RP, Lindeman RD, Prescott LF. Metabolic and hypotensive effect of ethacrynic acid. Comparative study with hydrochlorothiazide. JAMA 1968;205(1):81‐5. - PubMed
Safar 1994 {published data only}
-
- Safar M, Zanchetti A, Sever PS, et al. Perindopril and indapamide as a combination in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension ‐ a double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled European multicenter study [POSTER]. American Journal of Hypertension 1994;7(4):43A.
Salvetti 1969 {published data only}
-
- Salvetti A, Magagna A, Innocenti P, Ponzanelli F, Caiganelli A, et al. Chlorthalidone does not increase the hypotensive effect of nifedipine in essential hypertensives: a crossover multicenter study. Journal of Hypertension 1969;7(Suppl 6):S250‐1. - PubMed
Salvetti 1989 {published data only}
-
- Salvetti A, Magagna A, Innocenti P, Cagianelli A, Cipriani M, Gandolfi E, et al. Chlorthalidone does not increase the hypotensive effect of nifedipine in essential hypertensives: a cross over multicentre study. Journal of Hypertension 1989;7(Suppl 6):S250‐1. - PubMed
-
- Salvetti A, Magagna A, Innocenti P, Ponzanelli F, Caiganelli A, et al. The combination of chlorthalidone with nifedipine dose does not exert an additive antihypertensive effect in essential hypertensives: A crossover multicenter study. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1991;17:332‐5. - PubMed
Samson 1965 {published data only}
-
- Samson WE. Clinical evaluation of polythiazide in hypertension and congestive heart failure: a comparative double‐blind study. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 1965;249:571‐5. - PubMed
Schaller 1985 {published data only}
-
- Schaller M‐D, Waeber B, Brunner HR. Double‐blind comparison of indapamide with a placebo in hypertensive patients treated by practicing physicians. Clinical and Experimental Theory and Practice 1985;A7(7):985‐94. - PubMed
Shahinfar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Shahinfar S, Simpson RL, Carides AD, Thiyagarajan B, Nakagawa Y, Umans JG, et al. Safety of losartan in hypertensive patients with thiazide‐induced hyperuricemia. Kidney International 1999;56:1879‐85. - PubMed
Shimizu 1977 {published data only}
-
- Shimizu N, Miyashita H, Koide K, Inoue N, Ogasawara M. Comparative study of anti‐aldosterone agents and hypotensive diuretics in essential hypertension by a double bind test. Horumon To Rinsho 1977;25(2):167‐74. - PubMed
Siegel 1990 {published data only}
-
- Siegel D, Cheitlin MD, Black DM, Seeley D, Hearst N, Hulley SB. Risk of ventricular arrhythmias in hypertensive men with left ventricular hypertrophy. American Journal of Cardiology 1990;65(11):742‐7. - PubMed
Stein 1992 {published data only}
-
- Stein CM, Neill P, Kusemarnuriwo T. Antihypertensive effects of low doses of hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive black Zimbabweans. International Journal of Cardiology 1992;37:231‐5. - PubMed
Stornello 1990 {published data only}
-
- Stornello M, Valvo EV, Scapellato L. Effect of sustained‐release nicardipine, chlorthalidone, and the two drugs combined in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 1990;47(2):405‐11.
TOMHS 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lewis CE, Grandits GA, Flack J, McDonald, Elmer PJ. Efficacy and tolerance of antihypertensive treatment in men and women with stage 1 diastolic hypertension. Archives of Internal Medicine 1996;156(4):377‐85. - PubMed
-
- Liebson PR, Grandits GA, Dianzumba S, Prineas RJ, Grimm Jr. RH, Neaton JD, et al. Comparison of five antihypertensive mono therapies and placebo for change in left ventricular mass in patients receiving nutritional‐hygienic therapy in the treatment of mild hypertension study (TOMHS). Circulation 1995;91(3):698‐706. - PubMed
-
- The Treatment of Mild Hypertension Research Group (TOMHS). The treatment of mild hypertension study. A randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of a nutritional‐hygienic regiment along with various drug monotherapies. Archives of Internal Medicine 1991;151:1413‐23. - PubMed
Valmin 1975 {published data only}
-
- Valmin K, Hansen T. Treatment of benign essential hypertension. Comparison of furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1975;8:393‐401. - PubMed
Wassertheil‐Smoller 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wassertheil‐Smoller S, Oberman A, Blaufox M, et al. The trial of antihypertensive medications (TAIM) study. Final results with regards to blood pressure, cardiovascular risk and quality of life. American Journal of Hypertension 1992;5:37‐44. - PubMed
Weber 1977 {published data only}
Webster 1980 {published data only}
-
- Webster J, Dollery CT, Hensby CN. Circulating prostacyclin concentrations may be increased by bendrofluazide in patients with essential hypertension. Clinical Science 1980;59:125‐8S. - PubMed
-
- Webster J, Dollery CT, Hensby CN, Friedman LA. Antihypertensive action of bendroflumethiazide: increased prostacyclin production?. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1980;28(6):751‐8. - PubMed
Weinberger 1983 {published data only}
-
- Weinberger MH. Influence of an angiotensin converting‐enzyme inhibitor on diuretic‐induced metabolic effects in hypertension. Hypertension 1983;5(5 Suppl III):III132‐III138. - PubMed
Wiggam 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wiggam MI, Bell PM, Sheridan B, Walmsley A, Atkinson AB. Low dose bendrofluazide (1.25 mg) effectively lowers blood pressure over 24 hours. Results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled cross over study. American Journal of Hypertension 1999;12:528‐31. - PubMed
Wilcox 1978 {published data only}
Wing 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wing LMH, West MJ, Graham JR, Chalmers JP. Long‐acting and short‐acting diuretics in mild essential hypertension. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension ‐ Theory and Practice 1982;A4(8):1429‐41. - PubMed
Wing 1997 {published data only}
-
- Wing LMH, Arnolda LF, Harvey PJ, Upton J, et al. Lacidipine, hydrochlorothiazide and their combination in systolic hypertension in the elderly. Journal of Hypertension 1997;15:1503‐10. - PubMed
Wing 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wing LMH, Arnolda LF, Harvey PJ, Upton J, Molloy D, Gabb GM, et al. Low‐dose diuretic and/or dietary sodium restriction when blood pressure is resistant to ACE inhibitor. Blood Pressure 1998;7:299‐307. - PubMed
Zachariah 1993 Study #1 {published data only}
-
- Zachariah PK, Messerli FH, Mroczek W. Low‐dose bisoprolol/hydrochlorothiazide: an option in first‐line, antihypertensive treatment. Clinical Therapeutics 1993;15(5):779‐87. - PubMed
Zachariah 1993 Study #2 {published data only}
-
- Zachariah PK, Messerli FH, Mroczek W. Low‐dose bisoprolol/hydrochlorothiazide: an option in first‐line, antihypertensive treatment. Clinical Therapeutics 1993;15(5):779‐87. - PubMed
Additional references
Allen 1982
-
- Allen JH, McKenney JM, Stratton MA, Link K. Antihypertensive effect of hydrochlorothiazide administered once or twice daily. Clinical Pharmacology 1982;1:239–43. - PubMed
Campbell 2004
-
- Campbell B, Brackman F. Cardiovascular protective properties of indapamide. American Journal of Cardiology 2004;65(17):H11‐27. - PubMed
Carter 2004
-
- Carter BL, Ernst ME, Cohen JD. Hydrochlorothiazide versus chlorthalidone evidence supporting their interchangeability. Hypertension 2004;43:4‐9. - PubMed
Chen 2009
Edwin 2006
-
- Edwin JK. Diuretics. In: Brunton Lawrence L, et al. editor(s). Goodman & Gillman's The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics. 11th Edition. New York: McGraw Hill, 2006.
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Heran 2009a
Heran 2009b
Hughes 2004
-
- Hughes AD. How do thiazide and thiazide like diuretics lower blood pressure?. Journal of the Renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone System 2004;5(4):155‐60. - PubMed
Kurtz 2010
-
- Kurtz TW. Chlorthalidone: don't call it "thiazide‐like" anymore. Hypertension 2010;56:335‐7. - PubMed
Law 2009
Messerli 2011
-
- Messerli FH, Makani H, Benjo A, Romero J, Alviar C, Bangalore S. Antihypertensive efficacy of hydrochlorothiazide as evaluated by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: a meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Journal of American College of Cardiology 2011;57:590‐600. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.07.053] - DOI - PubMed
Musini 2008
Musini 2009a
Musini 2009b
Musini 2009c
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Riess 1977
-
- Riess W, Dubach UC, Burckhardt D, Theobald W, Vuillard P, ZimmerliM. Pharmacokinetic studies with chlorthalidone (Hygroton) in man. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1977;12:375–82. - PubMed
Russell 1981
-
- Russell JG, Mayhew SR, Humphries IS. Chlorthalidone in mild hypertension:dose response relationship. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1981;20:407–11. - PubMed
Wells 2009 [Computer program]
-
- Wells GA, Sultan SA, Chen L, Khan M, Coyle D. Indirect treatment comparison. Version 1. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technology in Health, 2009.
Wong 2014
Wright 2009
References to other published versions of this review
Musini 2000
-
- Musini V. A systematic review of the blood pressure lowering efficacy of thiazide and loop diuretics in the treatment of primary hypertension (Masters Thesis). Available at http://hdl.handle.net/2429/10427. University of British Columbia, 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

