Functional toxicology: tools to advance the future of toxicity testing
- PMID: 24847352
- PMCID: PMC4017141
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00110
Functional toxicology: tools to advance the future of toxicity testing
Abstract
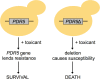
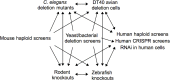
The increased presence of chemical contaminants in the environment is an undeniable concern to human health and ecosystems. Historically, by relying heavily upon costly and laborious animal-based toxicity assays, the field of toxicology has often neglected examinations of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity for the majority of compounds-information that, if available, would strengthen risk assessment analyses. Functional toxicology, where cells or organisms with gene deletions or depleted proteins are used to assess genetic requirements for chemical tolerance, can advance the field of toxicity testing by contributing data regarding chemical mechanisms of toxicity. Functional toxicology can be accomplished using available genetic tools in yeasts, other fungi and bacteria, and eukaryotes of increased complexity, including zebrafish, fruit flies, rodents, and human cell lines. Underscored is the value of using less complex systems such as yeasts to direct further studies in more complex systems such as human cell lines. Functional techniques can yield (1) novel insights into chemical toxicity; (2) pathways and mechanisms deserving of further study; and (3) candidate human toxicant susceptibility or resistance genes.
Keywords: functional genomics; functional profiling; functional toxicology; toxicity testing; toxicology; yeast.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Functional genomic screening approaches in mechanistic toxicology and potential future applications of CRISPR-Cas9.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015 Apr-Jun;764:31-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 25. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 26041264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative animal models in predictive toxicology.Toxicology. 2022 Jan 15;465:153053. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.153053. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Toxicology. 2022. PMID: 34838596 Review.
-
Toxicogenomic approach for assessing toxicant-related disease.Mutat Res. 2003 Nov;544(2-3):415-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2003.06.014. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 14644344 Review.
-
Toxicology and genetic toxicology in the new era of "toxicogenomics": impact of "-omics" technologies.Mutat Res. 2002 Jan 29;499(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00292-5. Mutat Res. 2002. PMID: 11804602 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Genes That Modulate Susceptibility to Formaldehyde and Imatinib by Functional Genomic Screening in Human Haploid KBM7 Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2016 May;151(1):10-22. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw032. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27008852 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecific diversity is critical to population-level risk assessments.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 29;14(1):25883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76734-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468236 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Inhibition and DNA Damage Induced by X-Phenols in Yeast: A Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Study.ACS Omega. 2017 Dec 31;2(12):8568-8579. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01200. Epub 2017 Dec 1. ACS Omega. 2017. PMID: 29302629 Free PMC article.
-
The continuing evolution of barcode applications: Functional toxicology to cell lineage.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Dec;247(23):2119-2127. doi: 10.1177/15353702221121600. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 36113119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Toxicogenomic Profiling Expands Insight into Modulators of Formaldehyde Toxicity in Yeast.Front Genet. 2016 Nov 17;7:200. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00200. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27909446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayadi A., Birling M.-C., Bottomley J., Bussell J., Fuchs H., Fray M., et al. (2012). Mouse large-scale phenotyping initiatives: overview of the European Mouse Disease Clinic (EUMODIC) and of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Mouse Genetics Project. Mamm. Genome. 23, 600–610 10.1007/s00335-012-9418-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

