MicroRNAs in lupus
- PMID: 24826805
- PMCID: PMC4239026
- DOI: 10.3109/08916934.2014.915955
MicroRNAs in lupus
Abstract
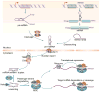
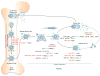
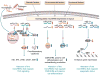
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a prototypic autoimmune disease characterized by the production of an array of pathogenic autoantibodies, including high-affinity anti-dsDNA IgG antibodies, which play an important role in disease development and progression. Lupus preferentially affects women during their reproductive years. The pathogenesis of lupus is contributed by both genetic factors and epigenetic modifications that arise from exposure to the environment. Epigenetic marks, including DNA methylation, histone post-translational modifications and microRNAs (miRNAs), interact with genetic programs to regulate immune responses. Epigenetic modifications influence gene expression and modulate B cell functions, such as class-switch DNA recombination, somatic hypermutation and plasma cell differentiation, thereby informing the antibody response. Epigenetic dysregulation can result in aberrant antibody responses to exogenous antigens or self-antigens, such as chromatin, histones and dsDNA in lupus. miRNAs play key roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of most gene-regulatory pathways and regulate both the innate and adaptive immune responses. In mice, dysregulation of miRNAs leads to aberrant immune responses and development of systemic autoimmunity. Altered miRNA expression has been reported in human autoimmune diseases, including lupus. The dysregulation of miRNAs in lupus could be the result of multiple environmental factors, such as sex hormones and viral or bacterial infection. Modulation of miRNA is a potential therapeutic strategy for lupus.
Keywords: Activation-induced cytidine deaminase; autoantibody; autoimmunity; class-switch DNA recombination; epigenetics; microRNA; somatic hypermutation; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AID dysregulation in lupus-prone MRL/Fas(lpr/lpr) mice increases class switch DNA recombination and promotes interchromosomal c-Myc/IgH loci translocations: modulation by HoxC4.Autoimmunity. 2011 Dec;44(8):585-98. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2011.577128. Epub 2011 May 18. Autoimmunity. 2011. PMID: 21585311 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in lupus.Autoimmunity. 2014 Jun;47(4):213-4. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.915393. Autoimmunity. 2014. PMID: 24826881
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases.Trends Mol Med. 2011 Dec;17(12):714-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.07.005. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Trends Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21885342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The critical role of epigenetics in systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmunity.J Autoimmun. 2016 Nov;74:118-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.06.020. Epub 2016 Jul 6. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27396525 Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate B cell microRNAs that silence AID and Blimp-1 expression for epigenetic modulation of antibody and autoantibody responses.J Immunol. 2014 Dec 15;193(12):5933-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401702. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25392531 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IL-16/miR-125a axis controls neutrophil recruitment in pristane-induced lung inflammation.JCI Insight. 2018 Aug 9;3(15):e120798. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.120798. eCollection 2018 Aug 9. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30089723 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of microRNA-183-96-182 Cluster in Lymphocytes Suppresses Anti-DsDNA Autoantibody Production and IgG Deposition in the Kidneys in C57BL/6-Faslpr/lpr Mice.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 7;13:840060. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.840060. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35873462 Free PMC article.
-
Cross Talk between Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Innate Immunocytes Concerning Lupus Disease.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Dec;18(8):2781-2796. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10397-x. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35876958 Review.
-
Epigenetics of the antibody and autoantibody response.Curr Opin Immunol. 2020 Dec;67:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.09.004. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Curr Opin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33176228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle- and particle-mediated communication shapes innate and adaptive immune responses.J Exp Med. 2021 Aug 2;218(8):e20202579. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202579. Epub 2021 Jun 28. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34180950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2110–2121. - PubMed
-
- Zan H, Zhang J, Ardeshna S, Xu Z, Park S-R, Casali P. Lupus-prone MRL/Faslpr/lpr mice display increased AID expression and extensive DNA lesions, comprising deletions and insertions, in the immunoglobulin locus: Concurrent upregulation of somatic hypermutation and class switch DNA recombination. Autoimmunity. 2009;42:89–103. - PMC - PubMed
-
- White CA, Seth Hawkins J, Pone EJ, Yu ES, Al-Qahtani A, Mai T, Zan H, Casali P. AID dysregulation in lupus-prone MRL/Faslpr/lpr mice increases class switch DNA recombination and promotes interchromosomal c-Myc/IgH loci translocations: modulation by HoxC4. Autoimmunity. 2011;44:585–598. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
