CXCL12-CXCR4 axis promotes the natural selection of breast cancer cell metastasis
- PMID: 24810923
- PMCID: PMC4158177
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-1816-1
CXCL12-CXCR4 axis promotes the natural selection of breast cancer cell metastasis
Abstract
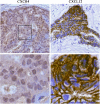
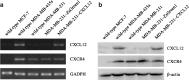
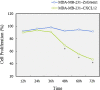
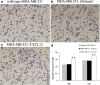
CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 can promote the proliferation, survival, and invasion of cancer cells. They have been shown to play an important role in regulating metastasis of breast cancer to specific organs. High CXCR4 expression was also correlated to poor clinical outcome. Previous study also showed that tumor cells express a high level of CXCR4 and that tumor metastasis target tissues (lung, liver, and bone) express high levels of the ligand CXCL12, allowing tumor cells to directionally migrate to target organs via a CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic gradient. However, the exact mechanisms of how CXCR4 and CXCL12 enhance metastasis and/or tumor growth and their full implications on breast cancer progression are unknown. Yet it is likely that chemokine receptor signaling may provide more than just a migrational advantage by also helping the metastasized cells establish and survive in secondary environments. In this study, we investigated CXCR4 and CXCL12 expression in breast cancer and analyzed its association with clinicopathological factors by immunohistochemistry first. Then, we detected the mRNA and protein expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in breast cancer cell lines by Western blot and RT-PCR. The MDA-MB-231 has CXCR4 expression and very weak CXCL12 expression. So, we constructed the functional CXCL12 expression in MDA-MB-231 using a gene transfection technique. Further experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of CXCL12 transfection on the biological behaviors of MDA-MB-231. The cell proliferation of MDA-MB-231-CXCL12 was accessed by MTT assay; the apoptosis was analyzed by an AnnexinV-FITC/propidium iodide double staining of flow cytometry method; and the cell invasive ability was examined by Matrigel invasion assay. Immunohistochemical analysis showed the co-expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 correlated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage (p < 0.01). It suggested that the chemokine CXCL12 and its sole ligand CXCR4 play important role in the malignance of breast cancer. To gain a deeper insight into it, we picked CXCR4-expressing cells MDA-MB-231 to be transfected with CXCL12 stably. The decreased cellular proliferation, increased apoptosis, and invasive ability were found in MDA-MB-231 with successful CXCL12 transfection (p < 0.05). Our findings underlined the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis correlated tightly with breast cancer metastasis. CXCL12-CXCR4 axis can increase the invasion and apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 simultaneously. These data strongly support the hypothesis that CXCL12-CXCR4 axis promotes the natural selection of breast cancer cell metastasis. Our findings could have significant implications in terms of breast cancer aggressiveness and the effectiveness of targeting the receptors and downstream signaling pathways for the treatment of breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic manipulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 attests the pivotal role of the autocrine SDF-1-CXCR4 pathway in the aggressiveness of breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2005 May;26(5):1429-34. Int J Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15809737
-
Stromal cell derived factor-1: its influence on invasiveness and migration of breast cancer cells in vitro, and its association with prognosis and survival in human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(4):R402-10. doi: 10.1186/bcr1022. Epub 2005 Apr 4. Breast Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15987445 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer metastasis to liver and lung is facilitated by Pit-1-CXCL12-CXCR4 axis.Oncogene. 2018 Mar;37(11):1430-1444. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0036-8. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29321662
-
[The role of SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in tumor metastasis].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Oct;24(5):1180-3. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18027722 Review. Chinese.
-
[Correlations of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor to tumor metastasis].Ai Zheng. 2007 Feb;26(2):220-4. Ai Zheng. 2007. PMID: 17298758 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Endosteal Niche in Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 13;10:335. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00335. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32232008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different Modes of Mechanism of Gamma-Mangostin and Alpha-Mangostin to Inhibit Cell Migration of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Concerning CXCR4 Downregulation and ROS Generation.Iran J Pharm Res. 2023 Nov 10;22(1):e138856. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-138856. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 38655233 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4 or CXCR7 antagonists treat endometriosis by reducing bone marrow cell trafficking.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Feb;24(4):2464-2474. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14933. Epub 2020 Jan 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31904910 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial CXCR7 regulates breast cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2016 Mar 31;35(13):1716-24. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.236. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26119946 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased methylation in the SNAI2 and ADAM23 genes associated with de-differentiation and haematogenous dissemination in breast cancers.BMC Cancer. 2018 Sep 6;18(1):875. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4783-x. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30189837 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

