Transport proteins of parasitic protists and their role in nutrient salvage
- PMID: 24808897
- PMCID: PMC4010794
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00153
Transport proteins of parasitic protists and their role in nutrient salvage
Abstract
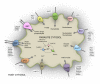
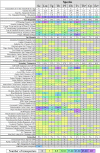
The loss of key biosynthetic pathways is a common feature of important parasitic protists, making them heavily dependent on scavenging nutrients from their hosts. This is often mediated by specialized transporter proteins that ensure the nutritional requirements of the parasite are met. Over the past decade, the completion of several parasite genome projects has facilitated the identification of parasite transporter proteins. This has been complemented by functional characterization of individual transporters along with investigations into their importance for parasite survival. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on transporters from parasitic protists and highlight commonalities and differences in the transporter repertoires of different parasitic species, with particular focus on characterized transporters that act at the host-pathogen interface.
Keywords: amino acid; hexose; parasite; protist; protozoa; purine; transport; transporter.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrient transport and pathogenesis in selected parasitic protozoa.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Apr;10(4):483-93. doi: 10.1128/EC.00287-10. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21216940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiparasitic chemotherapy: tinkering with the purine salvage pathway.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;625:116-32. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77570-8_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18365663 Review.
-
Pathogenic Protist Transmembranome database (PPTdb): a web-based platform for searching and analysis of protist transmembrane proteins.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Jul 24;20(Suppl 13):382. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2857-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31337335 Free PMC article.
-
Hide-and-Seek: A Game Played between Parasitic Protists and Their Hosts.Microorganisms. 2021 Nov 25;9(12):2434. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122434. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34946036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleoside transporters of parasitic protozoa.Trends Parasitol. 2001 Mar;17(3):142-5. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(00)01806-7. Trends Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11286799 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic Diversity of NTT Nucleotide Transport Proteins in Free-Living and Parasitic Bacteria and Eukaryotes.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Feb 1;9(2):480-487. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx015. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28164241 Free PMC article.
-
The purine nucleoside phosphorylase pnp-1 regulates epithelial cell resistance to infection in C. elegans.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Apr 20;17(4):e1009350. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009350. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33878133 Free PMC article.
-
Protean permeases: Diverse roles for membrane transport proteins in kinetoplastid protozoa.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2019 Jan;227:39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 24. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 30590069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Queuine Salvaging in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica.Cells. 2022 Aug 12;11(16):2509. doi: 10.3390/cells11162509. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010587 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Re-sequencing Reveals Natural Variation and Adaptive Evolution of Phytophthora sojae.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2792. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02792. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31849921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali V., Shigeta Y., Tokumoto U., Takahashi Y., Nozaki T. (2004). An intestinal parasitic protist, Entamoeba histolytica, possesses a non-redundant nitrogen fixation-like system for iron-sulfur cluster assembly under anaerobic conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 16863–16874 10.1074/jbc.M313314200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

