Drosophila melanogaster Hox transcription factors access the RNA polymerase II machinery through direct homeodomain binding to a conserved motif of mediator subunit Med19
- PMID: 24786462
- PMCID: PMC4006704
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004303
Drosophila melanogaster Hox transcription factors access the RNA polymerase II machinery through direct homeodomain binding to a conserved motif of mediator subunit Med19
Abstract
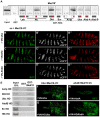
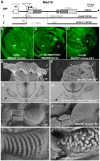
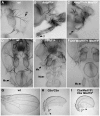
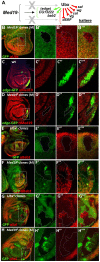
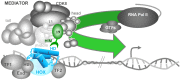
Hox genes in species across the metazoa encode transcription factors (TFs) containing highly-conserved homeodomains that bind target DNA sequences to regulate batteries of developmental target genes. DNA-bound Hox proteins, together with other TF partners, induce an appropriate transcriptional response by RNA Polymerase II (PolII) and its associated general transcription factors. How the evolutionarily conserved Hox TFs interface with this general machinery to generate finely regulated transcriptional responses remains obscure. One major component of the PolII machinery, the Mediator (MED) transcription complex, is composed of roughly 30 protein subunits organized in modules that bridge the PolII enzyme to DNA-bound TFs. Here, we investigate the physical and functional interplay between Drosophila melanogaster Hox developmental TFs and MED complex proteins. We find that the Med19 subunit directly binds Hox homeodomains, in vitro and in vivo. Loss-of-function Med19 mutations act as dose-sensitive genetic modifiers that synergistically modulate Hox-directed developmental outcomes. Using clonal analysis, we identify a role for Med19 in Hox-dependent target gene activation. We identify a conserved, animal-specific motif that is required for Med19 homeodomain binding, and for activation of a specific Ultrabithorax target. These results provide the first direct molecular link between Hox homeodomain proteins and the general PolII machinery. They support a role for Med19 as a PolII holoenzyme-embedded "co-factor" that acts together with Hox proteins through their homeodomains in regulated developmental transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mediator complex subunit Med19 binds directly GATA transcription factors and is required with Med1 for GATA-driven gene regulation in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 25;295(39):13617-13629. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013728. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32737196 Free PMC article.
-
The Hox transcription factor Ultrabithorax binds RNA and regulates co-transcriptional splicing through an interplay with RNA polymerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 25;50(2):763-783. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1250. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34931250 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the binding of the Hox protein Ultrabithorax and the Hox cofactor Homothorax in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 5;6(4):e14778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014778. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483667 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for intrinsic disorder and fuzziness in generating context-specific function in Ultrabithorax, a Hox transcription factor.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;725:86-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0659-4_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22399320 Review.
-
Cellular analysis of newly identified Hox downstream genes in Drosophila.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Feb-Mar;89(2-3):273-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.11.012. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20018403 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Enhancer-Core-Promoter Communication via Transcription Factors and Cofactors.Trends Genet. 2016 Dec;32(12):801-814. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Trends Genet. 2016. PMID: 27816209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor TFIIEβ interacts with two exposed positions in helix 2 of the Antennapedia homeodomain to control homeotic function in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 15;13(10):e0205905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205905. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30321227 Free PMC article.
-
Homeodomain proteins: an update.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(3):497-521. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0543-8. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26464018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediator Complex Subunit 19 Promotes the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 3;11:792285. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.792285. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35047403 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput method to identify trans-activation domains within transcription factor sequences.EMBO J. 2018 Aug 15;37(16):e98896. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798896. Epub 2018 Jul 13. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 30006452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis EB (1978) A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature 276: 565–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

